Streamline Your Project Management with Our Kanban Boards
Optimise your team's productivity with our intuitive Kanban boards. Visualise tasks, track progress, and manage projects with ease. Transform your workflow today!
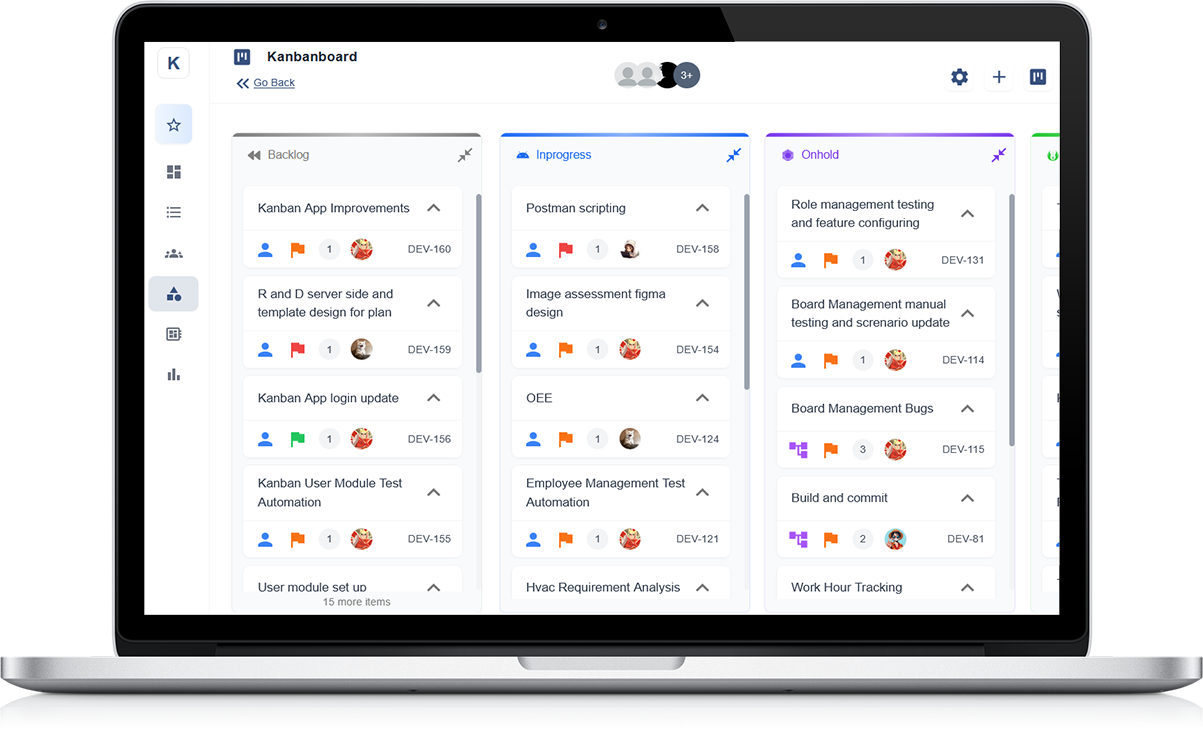






Task Management
Kanban project management software allows users to create, assign, and track tasks associated with a project. Users can set deadlines, prioritise tasks, and monitor progress, ensuring that everyone stays on schedule and accountable for their responsibilities.
This feature streamlines workflow, enhances accountability, and facilitates seamless coordination among team members for project success.
Book Free Demo
Planning Schedule Software
Kanban Project Management Software plays a pivotal role in schedule planning, offering robust features to streamline the process. These tools facilitate the creation of detailed project schedules, enabling managers to allocate resources, set milestones, and define task dependencies efficiently. With built-in Gantt charts, managers can visualise project timelines, identify critical paths, and adjust schedules as needed.
Additionally, collaborative features allow team members to update progress in real-time, ensuring everyone stays aligned with the project timeline. Overall, project management software enhances schedule planning by providing a centralised platform for coordination, tracking, and optimising project schedules for successful delivery.
Book Free Demo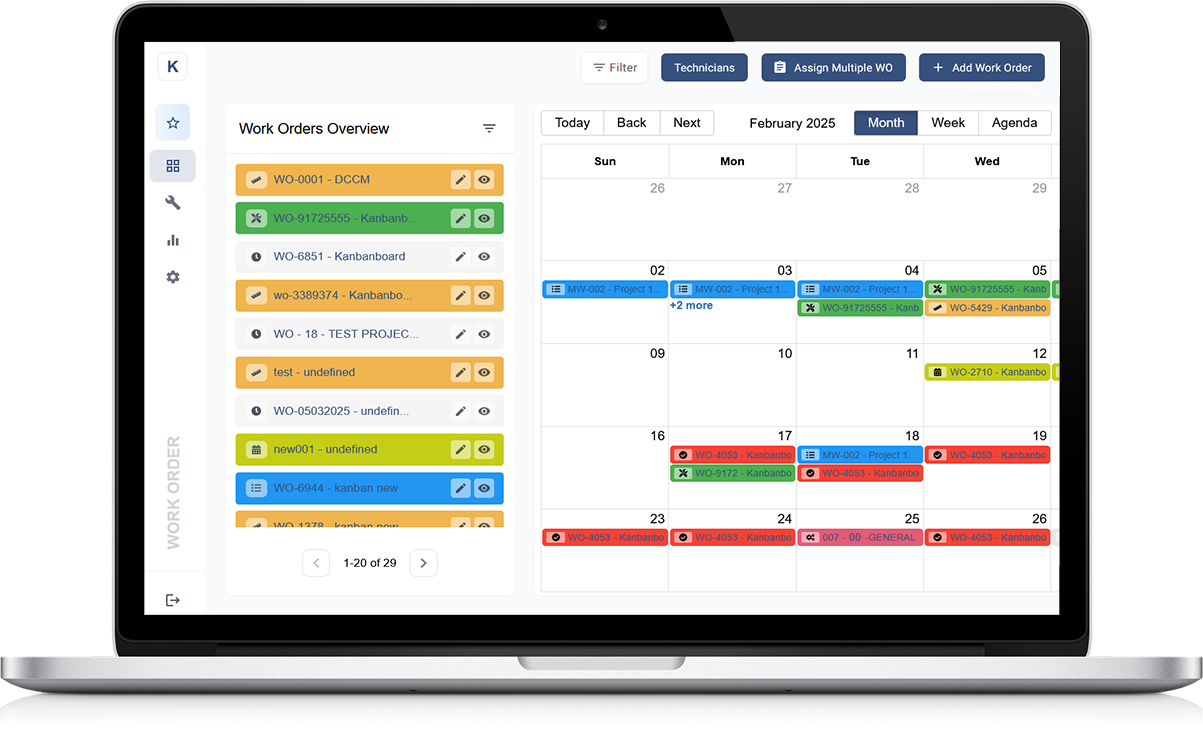
Gantt chart
A Gantt chart is a bar chart that shows a project's schedule, including the start and end dates, duration, and task descriptions. It can also show the relationships between activities and the current schedule status.
They illustrate the start and end dates of projects, key milestones, and dependencies. By integrating Gantt charts with Kanban board, organisations can better track progress toward strategic goals and ensure timely execution.
Book Free Demo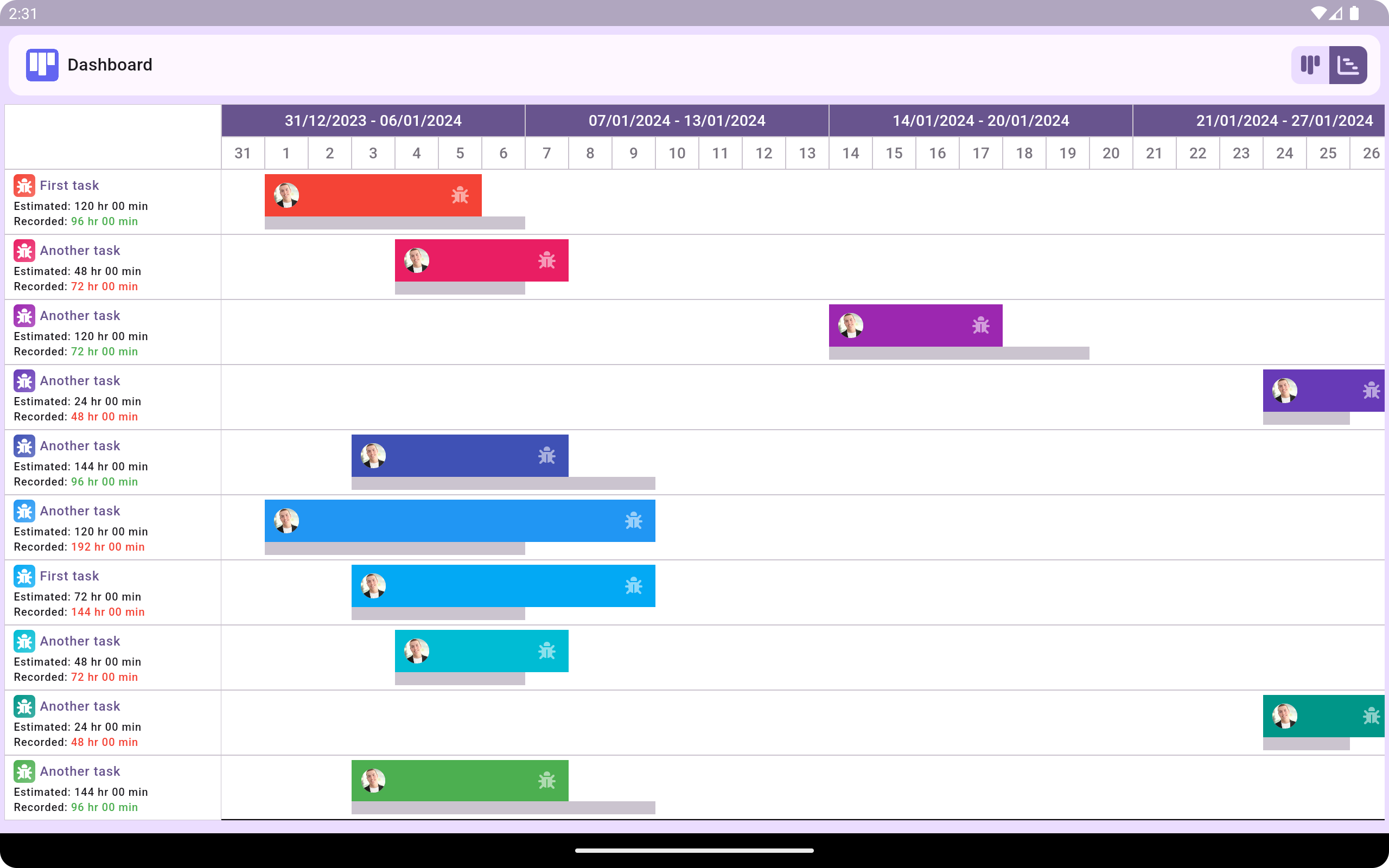
Resource allocation
Kanban Project Management Software greatly simplifies resource allocation by offering comprehensive tools for managing team members, equipment, and other resources effectively. These platforms provide visibility into resource availability, enabling project managers to assign tasks based on individual skills, workload, and availability. Advanced features such as resource leveling and capacity planning help optimise resource utilisation, preventing overallocation or bottlenecks.
Additionally, integration with calendars and scheduling tools ensures seamless coordination and avoids conflicts. By centralising resource management, project management software enhances efficiency, productivity, and ultimately, project success.
Book Free Demo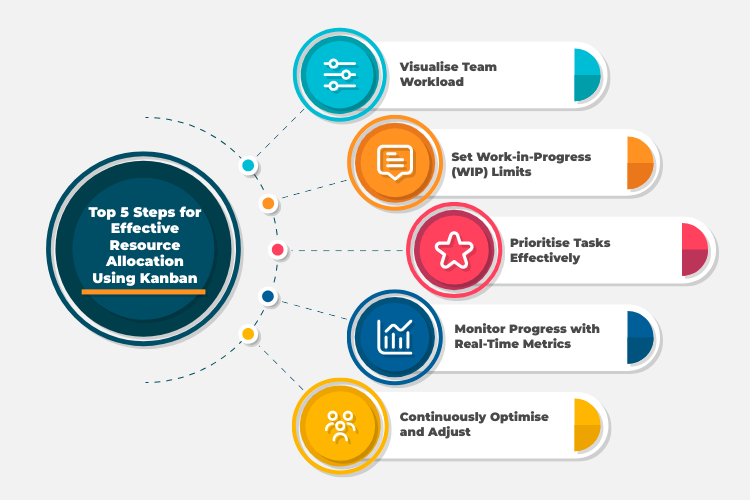
Team collaboration
Kanban Project Management Software fosters collaboration by providing a centralised platform where team members can communicate, share files, and collaborate on tasks in real-time. These tools offer features such as discussion boards, chat functionalities, and document sharing, facilitating seamless communication and information exchange among team members. Additionally, collaborative editing features enable simultaneous work on documents, fostering teamwork and speeding up the decision-making process.
By promoting transparency and accessibility, project management software enhances collaboration, ensures everyone is on the same page, and ultimately contributes to project success by harnessing the collective expertise and efforts of the team.
Book Free Demo
Reporting and Analytics
Reporting and analytics in project management software provide insights into project progress, resource utilisation, and performance metrics. Users can track key indicators, identify trends, and make data-driven decisions to optimise project outcomes.
This feature enables informed decision-making, facilitates continuous improvement, and enhances project efficiency and effectiveness.
Book Free Demo
How to Create a Kanban Board in 5 Easy Steps
A Kanban board is a visual project management tool that helps teams visualise their workflow, limit work-in-progress (WIP), and optimise efficiency by using cards to represent tasks and columns to represent stages of a process.
- Visualise Workflow: Define process stages and create corresponding columns.
- Identify Work Types: Categorise tasks and assign color codes.
- Add Tasks to the Board:Use cards to represent tasks and prioritise them.
- Manage Workflow: Move tasks across stages based on progress.
- Optimise and Improve: Monitor performance and implement WIP limits.
features
Kanban Project management software offers a range of services designed to streamline project planning, execution, and monitoring. These services typically include:
Task Management
Kanban project management software allows users to create, assign, and track tasks associated with a project. Users can set deadlines, prioritise tasks, and monitor progress, ensuring that everyone stays on schedule and accountable for their responsibilities.
Scheduling
These tools provide features like Gantt charts, which visualise project timelines, task dependencies, and critical paths. Users can adjust schedules as needed, allocate resources efficiently, and identify potential bottlenecks to keep projects on track.
Resource Allocation
Kanban project management software helps in managing resources such as team members, equipment, and materials. Users can allocate resources based on availability, skills, and workload, preventing overallocation and ensuring optimal resource utilisation.
Collaboration
These platforms facilitate collaboration among team members by offering communication tools such as chat, discussion boards, and document sharing. Collaborative editing features allow multiple users to work on documents simultaneously, promoting teamwork and accelerating decision-making processes.
Reporting and Analytics
Kanban project management software generates reports and analytics to provide insights into project progress, resource utilisation, and performance metrics. Users can track key indicators, identify trends, and make data-driven decisions to improve project outcomes.
Integration
Many project management tools offer integration with other software and platforms such as calendars, email clients, and productivity apps. This ensures seamless data exchange and workflow automation, enhancing efficiency and productivity.
Notifications and Alerts
Notifications and alerts keep teams informed with real-time updates on task status, due dates, comments, and project changes. They can be delivered via email, in-app notifications, or push notifications on mobile.
Customisation and Scalability
Kanban project management software often allows users to customise workflows, templates, and dashboards to suit their specific needs. Additionally, these tools are scalable, accommodating projects of varying sizes and complexities.
Transform Your Workflow with a Kanban Board!
"Visualise your workflow and manage tasks efficiently with a dynamic Kanban Board. Organised into clear stages, it helps teams track progress, prioritise work, and boost productivity in real time."
Kanban Board/Cards
"A Kanban board is a visual tool used in project management to visualise workflow, track progress, and manage tasks. It originated from the manufacturing industry but is now widely used in various sectors, especially in agile software development."
Kanban Board
A Kanban board is a visual tool used in project management to track tasks through stages like "To Do," "In Progress," and "Done." It enhances workflow transparency, limits work-in-progress, and boosts team collaboration.

Tcard Board
Tcard Software/Board is a digital tool used for managing tasks and projects via a visual interface similar to Kanban boards. It helps teams organise, prioritise, and track tasks through customisable columns, enhancing workflow efficiency and collaboration.

Scrum Board
A Scrum Board is a visual tool used in agile project management to track tasks during a Scrum sprint. It features columns like "To Do," "In Progress," and "Done," helping teams monitor progress, collaborate effectively, and achieve sprint goals.

Kamishibai Boards
Kamishibai Boards are visual management tools used in lean manufacturing to display routine tasks and audits. Featuring cards that indicate daily, weekly, or monthly tasks, they help ensure consistency, track performance, and highlight areas needing attention, promoting continuous improvement.
1. What are Kanban Boards?
Kanban boards are visual workflow management tools used to optimise task management and process efficiency. They consist of columns representing different workflow stages and cards representing tasks.
2. Kanban System
The Kanban system is a production management system that uses visualisation to regulate workflow and reduce waste. It can be used in both professional and personal settings.
3. History of Kanban Systems
The Kanban system originated in the 1940s as part of the Toyota Production System (TPS). It was developed by Taiichi Ohno, an industrial engineer at Toyota, to improve manufacturing efficiency by reducing waste and optimising inventory management.
4. Core Principles of Kanban
The Kanban system is built on four core principles that make it a flexible and practical approach to managing work. It starts with "Begin with What You Do Now," meaning you don’t have to overhaul your entire process to adopt Kanban—you can integrate it into your existing workflow and improve over time. The second principle, "Encourage Incremental, Evolutionary Change," emphasises small, continuous improvements rather than drastic shifts, making change easier to manage. Kanban also stresses the importance of "Respecting Current Roles and Responsibilities," allowing teams to refine their processes without disrupting established roles. Lastly, "Fostering Leadership at All Levels" ensures that improvement is not just a top-down effort but something that everyone can contribute to. By following these principles, organisations can create a more transparent, efficient, and adaptable work environment where productivity and collaboration thrive.
5. Kanban Practices
Kanban practices focus on visualising workflow, limiting work in progress (WIP), managing flow, making policies explicit, implementing feedback loops, and improving collaboratively through experimentation.
6. Key Components of a Kanban Board
A Kanban board's key components are columns (representing workflow stages), cards (representing tasks), Work-in-Progress (WIP) limits, and swimlanes (for categorisation), all working together to visualise and manage workflows effectively.
7. Kanban Board Features and Components
A Kanban board is a visual tool for managing workflows, featuring columns representing stages, cards for tasks, and Work-in-Progress (WIP) limits to optimise flow and transparency.
8. Types of Kanban Boards
Kanban boards can be physical (whiteboards and sticky notes) or digital (software-based) and are used in various industries like manufacturing, IT, healthcare, and logistics.
9. Top 5 Benefits of Using a Kanban Board
1. Increased transparency
2. Better workflow visualisation
3. Improved efficiency
4. Reduced bottlenecks
5. Enhanced collaboration
10. How to Create a Kanban Board?
Define Your Workflow
Start by identifying the key stages of your process. Common stages include To-Do, In Progress, and Done, but you can customise them based on your team's workflow.
Set Up Columns
Each column on the Kanban board represents a stage in the workflow. Add columns that reflect your process, such as Backlog, Development, Review, Testing, and Deployment for software teams.
Add Work Items (Kanban Cards)
Create Kanban cards for each task or work item. Include key details such as task descriptions, deadlines, priorities, and assignees.
Implement Work-in-Progress (WIP) Limits
To prevent overload, set a limit on how many tasks can be in progress at the same time. This helps maintain focus and ensures smooth task completion.
Track and Move Tasks
As work progresses, move the Kanban cards across the columns to reflect their current status. This real-time tracking keeps the team informed and improves visibility.
Continuously Improve the Process
Regularly review the board to identify bottlenecks, inefficiencies, or delays. Use feedback loops and team discussions to make incremental improvements.
11. Kanban in Lean Manufacturing
Kanban is a key component of Lean Manufacturing, designed to optimise workflow efficiency and minimise waste. Originating from Toyota's production system, Kanban enables just-in-time (JIT) manufacturing, ensuring that materials and tasks move smoothly through the production process.
How Kanban Supports Lean Manufacturing
1. Visualising Workflow
Kanban boards provide a clear visual representation of work-in-progress (WIP), allowing teams to identify bottlenecks and inefficiencies in real time.
2. Reducing Waste
By limiting WIP and ensuring tasks are completed before new ones are started, Kanban eliminates overproduction, excess inventory, and unnecessary movement—all forms of waste in Lean.
3. Enhancing Just-in-Time (JIT) Production
Kanban ensures that materials and products are only produced when needed, preventing overstocking and reducing storage costs.
4. Improving Process Efficiency
By tracking work items from raw material to finished product, Kanban helps maintain continuous flow and minimises delays.
5. Encouraging Continuous Improvement
Teams can analyse Kanban metrics, such as lead time and cycle time, to refine processes and implement Kaizen (continuous improvement) strategies for better efficiency.
12. How to Choose the Right Kanban Board Software?
Consider factors such as usability, customisation, integration options, reporting capabilities, and scalability when selecting Kanban software.
13. How Can the Kanban Board Affect Your ROI?
Implementing a Kanban board can significantly impact your Return on Investment (ROI) by enhancing efficiency, reducing waste, and improving overall workflow management. Businesses that adopt Kanban often experience increased productivity, cost savings, and better resource utilisation.
Key Ways Kanban Boards Improve ROI
1. Enhancing Workflow Efficiency
By providing a visual representation of work in progress, Kanban helps teams identify bottlenecks and optimise task management, leading to faster project completion and better resource allocation.
2. Reducing Waste and Costs
Kanban supports Lean principles, minimising unnecessary work, reducing overproduction, and optimising inventory levels. This results in significant cost savings and higher profit margins.
3. Improving Team Productivity
By limiting work-in-progress (WIP) and enabling smooth task transitions, Kanban reduces context-switching and enhances focus, leading to higher efficiency and more output in less time.
4. Increasing Customer Satisfaction
With streamlined workflows and faster delivery times, businesses can meet customer demands more efficiently, leading to improved satisfaction and higher customer retention rates.
5. Data-Driven Decision Making
Kanban provides valuable performance metrics such as cycle time and lead time, enabling businesses to make informed decisions that optimise processes and drive long-term growth.
14. How Does an Online Kanban Board Help Remote or Distributed Teams?
Online Kanban boards significantly benefit remote and distributed teams by providing a shared, visual representation of workflow, promoting transparency, and facilitating better collaboration and communication, even across different locations and time zones.
15. How Does a Kanban Board Work?
A Kanban board is a visual tool used to manage workflow and improve efficiency. It helps teams track work items as they move through different stages of a process. The board is divided into columns, each representing a stage in the workflow.
Key Components of a Kanban Board
- Columns: Represent different stages of the workflow (e.g., To-Do, In Progress, Done).
- Kanban Cards: Each card represents a task, containing details like task description, priority, and deadlines.
- Work-in-Progress (WIP) Limits: Restrict the number of tasks allowed in a column to prevent overload.
- Swimlanes: Horisontal sections to categorise tasks by priority, team, or project type.
16. Kanban List View
A Kanban List View or Kanban view is a card-based way to visualise data, typically used in project management or sales, where records are grouped into columns representing different stages or statuses, allowing for easy tracking and movement of items through a process.
Key Features of Kanban List View
- Task Organisation: Tasks are arranged in categorised lists, often grouped by status, priority, or assigned team members.
- Progress Tracking: Each task includes labels, due dates, assignees, and progress indicators to maintain workflow transparency.
- Compact Visualisation: Unlike traditional Kanban boards with drag-and-drop cards, the list view offers a streamlined, scrollable interface for quick task reviews.
- Filtering & Sorting: Users can filter tasks by status, deadline, or priority, making it easier to manage complex workflows.
- Collaboration & Updates: Comments, attachments, and status updates are available within each task for team collaboration.
When to Use Kanban List View?
- When managing tasks with high volume that require a structured layout.
- When users prefer a linear view over a visual board.
- When dealing with workflows that rely on detailed task attributes rather than a visual drag-and-drop system.
17. Kanban Metrics and Performance Indicators
Kanban metrics are key performance indicators (KPIs) used to measure and analyse the flow of work in a Kanban system, providing insights into team performance, identifying bottlenecks, and enabling process improvements.
18. Workflow Management with Kanban
Kanban is a visual project management methodology that helps teams manage workflow, prioritise tasks, and optimise productivity. It’s based on principles such as continuous improvement, limiting work in progress (WIP), and delivering tasks at the right time. Below is an overview of how Kanban can be utilised for effective workflow management.
Key Principles of Kanban for Workflow Management
- Visualise the Workflow: Using a Kanban board, teams visualise every step of their workflow. Tasks are represented by cards, and the workflow stages are depicted as columns. This visual representation helps team members understand the current status of tasks and where bottlenecks may exist.
- Limit Work In Progress (WIP): One of the core principles of Kanban is limiting the amount of work in progress at any given time. This helps prevent overloading team members and ensures that tasks move smoothly through the workflow. Setting WIP limits at each stage ensures that the team focuses on completing tasks before starting new ones.
- Focus on Flow: Kanban emphasizes improving the flow of tasks from one stage to the next. By continuously measuring cycle time (the time it takes to complete a task) and identifying bottlenecks, teams can make adjustments to improve efficiency.
- Continuous Improvement: Teams using Kanban are encouraged to continuously evaluate their workflow and make incremental improvements. This is typically done through regular meetings, such as retrospectives, where the team reviews the process, identifies inefficiencies, and implements improvements.
Benefits of Kanban for Workflow Management
- Increased Efficiency: Kanban helps identify and eliminate bottlenecks by visualising the entire process. This allows teams to focus on the most critical tasks and resolve issues quickly, leading to improved efficiency.
- Improved Collaboration: Kanban boards promote transparency and communication within teams. Everyone can see the status of tasks, which leads to better collaboration and quicker decision-making.
- Flexibility and Adaptability: Unlike more rigid project management methodologies, Kanban is highly flexible. Teams can adjust their processes, workflows, and priorities as needed without disrupting the entire system.
- Enhanced Focus: By limiting work in progress, Kanban ensures that team members remain focused on completing tasks rather than juggling multiple projects. This leads to higher quality and faster delivery of work.
- Faster Delivery: With tasks flowing through the system efficiently, teams can deliver results faster. The visual nature of Kanban helps teams prioritise urgent tasks and ensure timely delivery.
Using Kanban for Different Workflow Types
- Software Development: In software development, Kanban helps manage feature development, bug fixes, and code reviews. Developers focus on completing a limited set of tasks, ensuring a smooth and continuous flow of work.
- Marketing Teams: Marketing teams can use Kanban to manage campaigns, content creation, and social media posts. With clear visualisation, tasks are prioritised based on deadlines, and the team can quickly adapt to new requirements.
- Manufacturing and Operations: In manufacturing, Kanban is used to manage inventory and production schedules. It ensures that the right amount of materials is available at the right time without overstocking.
19. How Do I Create a Workflow in Kanban Board?
A Kanban workflow helps visualise the stages of a process, enabling teams to track progress and improve efficiency. Follow these steps to create an effective workflow in a Kanban board.
Step-by-Step Guide to Creating a Kanban Workflow
1. Define Your Workflow Stages
Identify the key phases of your process. Common stages include:
- Backlog: Tasks that are planned but not yet started.
- To-Do: Tasks ready to be worked on.
- In Progress: Tasks currently being worked on.
- Review: Tasks awaiting approval or testing.
- Done: Completed tasks.
2. Set Up Columns for Each Stage
Each workflow stage is represented by a column on the Kanban board. Customise columns based on your team's needs.
3. Create Kanban Cards
Each task is represented as a Kanban card. Include details such as:
- Task description
- Assignee
- Priority level
- Due date
4. Implement Work-in-Progress (WIP) Limits
To prevent bottlenecks, set a limit on the number of tasks allowed in each column at any given time.
5. Track and Move Tasks Across the Workflow
As tasks progress, move them across columns to reflect their current status.
20. Personal Kanban
Personal Kanban is a simple, flexible, and visual framework for managing your tasks and projects. It applies the principles of the Kanban methodology to personal workflow management, helping individuals stay organised, prioritise tasks, and focus on what's important. It's especially useful for people juggling multiple responsibilities or seeking more effective ways to manage their time.
Key Principles of Personal Kanban
- Visualise Your Work: Similar to traditional Kanban, Personal Kanban uses a visual board to organise tasks. Typically, tasks are represented by cards that move through columns, such as "To Do," "In Progress," and "Done." This gives you a clear view of your current workload and task priorities.
- Limit Work In Progress (WIP): One of the main goals of Personal Kanban is to reduce overwhelm by limiting the number of tasks you're working on at any given time. This helps you focus on completing tasks before starting new ones, leading to greater efficiency and less stress.
- Prioritise Tasks: With Personal Kanban, you can prioritise your tasks by importance or deadline. By organising tasks in a visual way, you can easily see which tasks need your immediate attention and which can be deferred. This ensures you focus on high-priority tasks first.
- Continuous Improvement: Personal Kanban encourages regular reflection on your work process. After each task is completed, it’s important to assess what worked, what didn’t, and make improvements to how you organise and manage your tasks. This approach leads to more streamlined workflows over time.
Benefits of Personal Kanban
- Increased Productivity: By visualising your tasks and limiting work in progress, you can stay focused on completing tasks without being overwhelmed by a large to-do list. It helps prevent multitasking, which often leads to inefficiency.
- Reduced Stress and Overwhelm: The clarity that comes with visualising your tasks and limiting WIP reduces feelings of stress and mental clutter. You know exactly what you need to focus on, and you can see your progress in real-time.
- Improved Focus: Personal Kanban enables you to concentrate on one task at a time, reducing distractions. Since you’ve limited your WIP, you can avoid switching between different projects and maintain a steady focus on completing the task at hand.
- Better Time Management: With Personal Kanban, you can clearly see how much time tasks take to complete and adjust your schedule accordingly. This helps you plan your day better, making time for important tasks while keeping deadlines in mind.
- Flexibility: One of the strengths of Personal Kanban is its flexibility. You can adjust the system to fit your specific needs—whether you’re working on personal projects, work tasks, or a combination of both. You can use a simple board, a physical board with sticky notes, or a digital tool to track tasks.
How to Use Personal Kanban
- Set Up Your Kanban Board: Start by creating a simple board with three columns: “To Do,” “In Progress,” and “Done.” If you're using a digital tool, you can customise these columns and add features like due dates, tags, or priorities.
- Break Down Tasks: Write each task you need to accomplish on a separate card or sticky note. Be specific and break larger tasks into smaller, more manageable steps.
- Limit WIP: Set a limit for how many tasks can be in the “In Progress” column at one time. This ensures you're focused on completing tasks and prevents spreading yourself too thin.
- Move Tasks Through the Columns: As you work on tasks, move them from "To Do" to "In Progress" and then to "Done" once completed. This provides a sense of accomplishment and keeps you motivated.
- Review and Reflect: Regularly review your board to assess progress and reflect on how your system is working. Adjust the number of tasks in progress or the way you prioritise tasks as needed.
21. What Metrics Can Be Tracked and Measured Using Kanban Tool?
Using a Kanban tool, you can track and measure key metrics like lead time, cycle time, throughput, work-in-progress (WIP), and flow efficiency to improve workflow efficiency and predictability.
22. How Do You Track Progress in Kanban?
Tracking progress in Kanban is essential for managing workflows and ensuring tasks are completed efficiently. Kanban uses visual tools and metrics to provide insight into how work is progressing through the system. Below are the main methods used to track progress in a Kanban system:
1. Kanban Board
- The most basic way to track progress is by using a Kanban board. A Kanban board consists of columns that represent different stages of work, typically including "To Do," "In Progress," and "Done." Each task is represented by a card that moves from one column to the next as it progresses through stages.
- To Do: Tasks that are yet to be started.
- In Progress: Tasks that are being worked on.
- Done: Completed tasks.
- The movement of cards across the board gives a clear visual representation of where work is in the process, allowing you to track the status of each task at any given time.
2. Work In Progress (WIP) Limits
- Kanban uses WIP limits to prevent overloading the system with too many tasks at once. These limits are set for each stage of the workflow (e.g., no more than three tasks in the "In Progress" column). Tracking WIP limits ensures that team members focus on completing tasks before starting new ones, and helps identify bottlenecks in the system.
- When WIP limits are exceeded, it's a signal that the flow is being disrupted, allowing teams to take action and improve workflow efficiency.
3. Cycle Time
- Cycle time refers to the amount of time it takes for a task to move from the start of the workflow (e.g., from "To Do") to completion (e.g., "Done"). Tracking cycle time helps teams understand how long it takes to complete tasks and provides insights into the efficiency of the workflow.
- Shorter cycle times typically indicate an efficient workflow, while longer cycle times may signal delays or bottlenecks in the process.
4. Cumulative Flow Diagram (CFD)
- A Cumulative Flow Diagram (CFD) is a visual tool used to track the progress of tasks over time. It shows the number of tasks in each workflow stage (e.g., To Do, In Progress, Done) over a period of time. The graph provides insights into how the workflow is performing and helps identify potential problems.
- A steady increase in the number of tasks in the "Done" column is a positive indicator.
- A buildup of tasks in the "In Progress" column may indicate a bottleneck.
5. Throughput
- Throughput measures the number of tasks or work items completed over a specific time period. By tracking throughput, teams can gauge their overall productivity and how quickly they are completing work. It helps teams identify trends, set realistic expectations, and plan for future work.
- Throughput is typically measured over a day, week, or month, depending on the context of the work being done.
6. Lead Time
- Lead time measures the total time taken from when a task is requested to when it is completed. This includes both the time a task spends waiting to be worked on (e.g., in the "To Do" column) and the time spent in progress.
- Tracking lead time helps teams assess how long it takes to deliver value to customers and identify areas where delays are occurring in the process.
7. Task Burndown
- A task burndown chart is a graphical representation of how many tasks are completed versus remaining over time. It helps track the rate at which work is being completed and provides a clear picture of progress toward completing a set of tasks or a project.
- The ideal burndown should show a steady decline in remaining tasks, indicating consistent progress.
8. Regular Stand-up Meetings
- Regular stand-up meetings, or daily Kanban meetings, are often used to discuss the current state of tasks and ensure progress is on track. During these meetings, team members review the status of the tasks, discuss any obstacles, and ensure that the board is up to date.
- These meetings allow for real-time adjustments and problem-solving, helping to keep the workflow moving efficiently.
23. Kanban Board Use Cases Across Industries
Kanban boards, with their visual workflow management, are used across industries for task management, project tracking, and process improvement, offering transparency and efficiency.
Industries such as IT, healthcare, logistics, and marketing use Kanban to improve workflow and efficiency.
24. What is the Difference Between Cycle Time and Lead Time in Kanban?
In Kanban, Cycle Time and Lead Time are two key performance indicators used to measure efficiency and workflow progress. Although they are often confused, they have distinct meanings and applications.
What is Lead Time?
Lead Time is the total time from when a task is requested (added to the backlog) until it is completed and delivered. It includes both waiting time and active work time.
- Formula: Lead Time = Completion Date - Request Date
- Example: If a task is requested on March 1st and completed on March 10th, the Lead Time is 10 days.
What is Cycle Time?
Cycle Time is the actual working time spent on a task, starting from when it moves into "In Progress" until it is completed. It does not include waiting time.
- Formula: Cycle Time = Completion Date - Start Date
- Example: If a task was started on March 5th and completed on March 10th, the Cycle Time is 6 days.
25. Benefits of Using a Kanban Board
Kanban boards offer numerous benefits for teams, including enhanced visualisation of workflow, improved collaboration, increased efficiency, and better focus, ultimately leading to faster project delivery and continuous improvement.
26. Kanban Reports
Kanban reports provide essential insights into the performance of your workflow, helping to identify bottlenecks, track progress, and make data-driven decisions. These reports typically focus on key metrics that allow teams to evaluate their productivity, efficiency, and workflow health. Below are common types of Kanban reports:
1. Cumulative Flow Diagram (CFD)
- A Cumulative Flow Diagram (CFD) is one of the most commonly used Kanban reports. It provides a visual representation of how tasks move through the workflow over time.
- Purpose: The CFD shows the number of tasks in each workflow stage (e.g., To Do, In Progress, Done) across a timeline.
- Benefits:
- Identifies bottlenecks in the workflow (e.g., when too many tasks accumulate in the "In Progress" column).
- Shows the overall stability and flow of tasks.
- Helps to forecast project completion based on past performance.
2. Lead Time and Cycle Time Reports
- Lead time and cycle time are critical metrics that measure the time it takes to complete a task, from when it enters the workflow to when it is finished.
- Lead Time Report: Measures the total time it takes for a task to move from the "To Do" column to the "Done" column.
- Cycle Time Report: Measures the time taken for a task to move through the "In Progress" phase, excluding the time spent waiting in the "To Do" column.
- Benefits:
- Helps to assess how long tasks take to complete, providing insights into the efficiency of the process.
- Allows teams to identify areas where delays are occurring and make improvements.
3. Throughput Report
- The Throughput Report tracks the number of tasks or work items completed within a specific time frame.
- Purpose: It measures the team's productivity by counting the number of completed tasks over a set period (e.g., daily, weekly, monthly).
- Benefits:
- Helps to gauge the team's performance and capacity.
- Identifies trends in productivity, allowing for better workload forecasting.
- A steady throughput indicates a stable workflow.
4. Work In Progress (WIP) Report
- The WIP Report tracks the number of tasks in progress at any given time.
- Purpose: It shows the number of tasks in each stage of the process (e.g., To Do, In Progress, Done).
- Benefits:
- Ensures that WIP limits are being respected.
- Helps identify bottlenecks where tasks are piling up.
- Provides insights into workload distribution across team members.
5. Task Burndown Chart
- The Task Burndown Chart is a graphical representation of the number of tasks remaining versus the tasks completed over time.
- Purpose: It helps to track progress toward completing a set of tasks or a project.
- Benefits:
- Provides a clear visual of progress and the rate of task completion.
- Helps identify if the team is on track to meet deadlines.
- A steady decline in remaining tasks is a positive indicator of progress.
6. Blocked Task Report
- The Blocked Task Report focuses on tasks that are currently blocked or delayed in the workflow.
- Purpose: It identifies tasks that are stuck due to external dependencies or internal obstacles.
- Benefits:
- Helps to quickly resolve issues that prevent progress.
- Keeps track of tasks that are waiting on input or approvals.
- Provides insight into common roadblocks, allowing teams to make process improvements.
7. Flow Efficiency Report
- The Flow Efficiency Report measures the percentage of time that tasks spend in active work versus waiting time.
- Purpose: It calculates how much of the time spent on a task is spent in the "In Progress" stage versus the time it spends waiting in the "To Do" or "Done" columns.
- Benefits:
- Identifies inefficiencies where tasks are waiting for extended periods.
- Helps to optimise the flow of tasks, reducing delays and improving throughput.
8. WIP Limit Violations Report
- The WIP Limit Violations Report tracks any instances where the number of tasks in progress exceeds the set WIP limits.
- Purpose: It helps ensure that the team is not overloaded and maintains a balanced workflow.
- Benefits:
- Ensures that WIP limits are being followed, preventing inefficiency and bottlenecks.
- Identifies when the team might need to adjust WIP limits to better manage capacity.
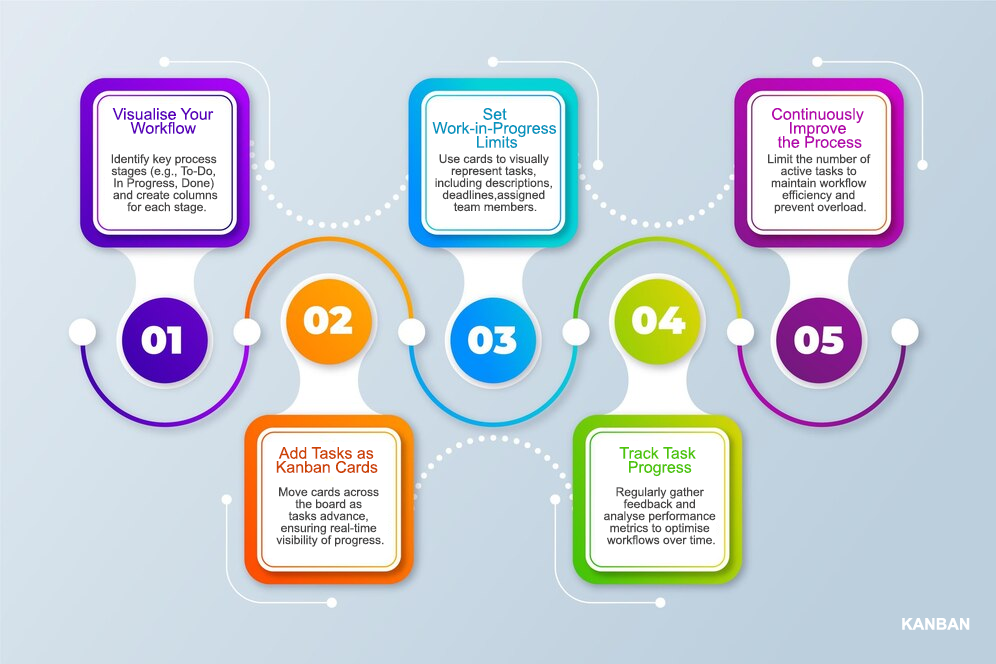
27. How to Use Kanban Boards?
A Kanban board is a powerful visual tool that helps teams manage workflows effectively by tracking tasks and limiting work in progress. Follow these steps to use a Kanban board efficiently:
1. Define Workflow Stages
Start by breaking your workflow into different stages. Common stages include:
- To-Do: Tasks that need to be started.
- In Progress: Tasks currently being worked on.
- Done: Completed tasks.
You can customise these stages based on your project needs.
2. Add Tasks as Kanban Cards
Each work item is represented as a Kanban card. Add task details such as:
- Task Title
- Description
- Priority Level
- Assigned Team Member
- Due Date
3. Implement Work-in-Progress (WIP) Limits
Set a limit on the number of tasks allowed in the "In Progress" column to prevent overloading the team and maintain workflow efficiency.
4. Move Cards Across Columns
As work progresses, move tasks through the workflow stages. This provides a clear visual representation of task status and bottlenecks.
5. Track Performance and Optimise
Regularly review the Kanban board to analyse workflow patterns, identify inefficiencies, and make improvements using metrics like:
- Cycle Time (Time spent actively working on a task)
- Lead Time (Total time from request to completion)