A Scrum board is a visual representation of a project's workflow, commonly used in Agile project management methodologies like Scrum. It serves as a focal point for the Scrum team to track and manage tasks throughout the project lifecycle. This board typically consists of columns representing different stages of the project, and tasks or user stories are visualised as cards that move across the board as work progresses.
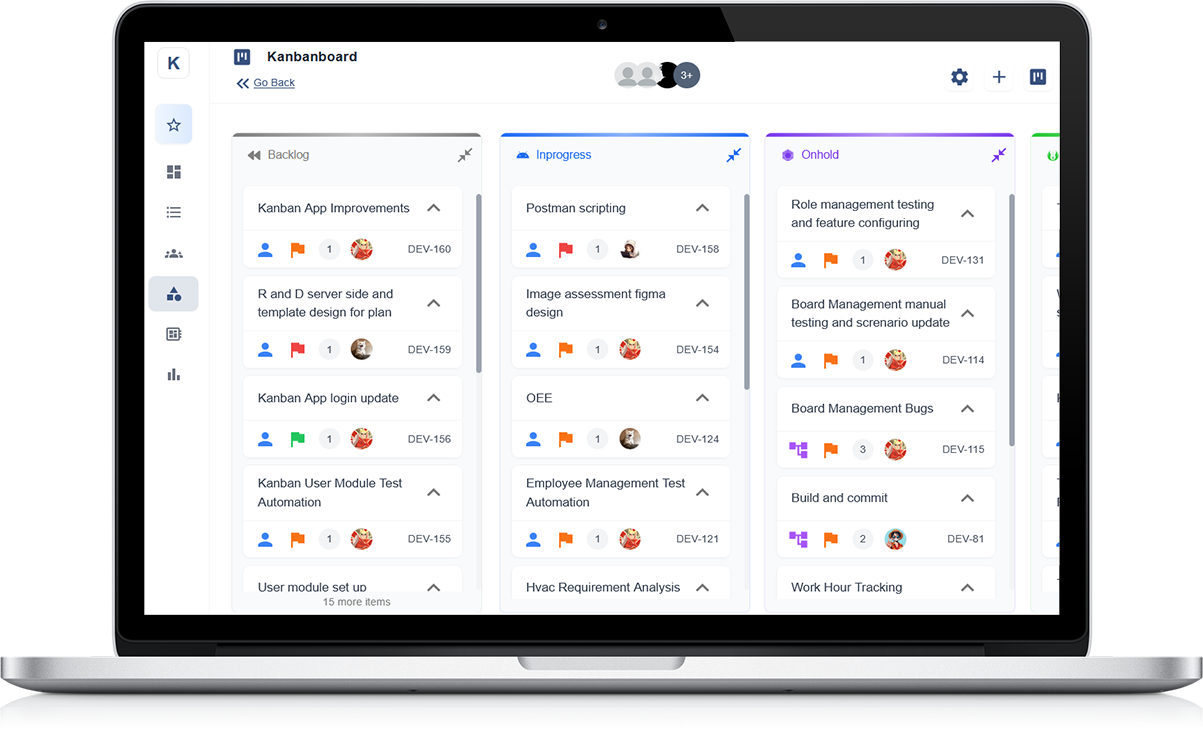
Let's delve deeper into the key aspects of a Scrum board:
Visual Representation: A Scrum board provides a visual representation of the project's workflow, making it easy for team members to understand the status of tasks at a glance. The board is usually divided into columns representing various stages of the project, such as backlog, to-do, in progress, testing, and done. Each column represents a different phase of work, and tasks move from left to right as they progress through these stages.
Task Cards: Tasks or user stories are represented as cards on the Scrum Board. These cards contain information about the task, including its title, description, priority, and assignee. Each task card represents a specific piece of work that needs to be completed as part of the project. Team members can easily identify tasks and their associated details by viewing the task cards on the board.
Workflow Visualisation: The Scrum board provides a clear visualisation of the project's workflow. As tasks move from one stage to another, team members can see the progress of work and identify any bottlenecks or delays in the process. This visual representation helps teams to stay focused, prioritise tasks effectively, and identify areas where improvements can be made to streamline the workflow.
Collaboration and Transparency: The Scrum Board promotes collaboration and transparency within the Scrum team. By providing a shared visual representation of the project, team members can easily communicate about the status of tasks, identify dependencies between tasks, and coordinate their efforts to ensure smooth progress. Everyone has visibility into what tasks are being worked on, who is responsible for them, and what stage they are at in the process.
Daily Stand-up Meetings: The Scrum board is often used as a focal point during daily stand-up meetings, where team members gather to discuss progress, identify any obstacles, and plan their work for the day. During the stand-up, team members can use the Scrum Board to update the status of tasks, discuss any blockers or challenges they are facing, and re-prioritise work as needed to ensure that the project stays on track.
Adaptability and Flexibility: One of the key advantages of using a Scrum board is its adaptability and flexibility. Teams can customise the board to suit their specific needs and preferences, adding or removing columns, adjusting the workflow stages, and defining their own criteria for task progression. This flexibility allows teams to tailor the board to the unique requirements of their project and adapt it as the project evolves over time.
Scrum Board is a valuable tool for Agile teams to manage tasks, track progress, and collaborate effectively during a project. By providing a visual representation of the workflow, promoting transparency and collaboration, and supporting adaptability and flexibility, the Scrum board helps teams to stay organised, focused, and productive throughout the project lifecycle.
Scrum Board Usage Guide
A Scrum Board is a visual tool used by Scrum teams to manage and track the progress of tasks within a sprint. It helps the team stay organised, increases transparency, and facilitates collaboration. Here's a guide on how to effectively use a Scrum board:
1. Setting Up the Scrum Board
A Scrum Board typically consists of several columns that represent the stages of work in a sprint. The basic columns on a Scrum board include:
- Backlog: Tasks or user stories that are planned for the sprint but not yet started.
- To Do: Tasks that are ready to be worked on and are part of the current sprint.
- In Progress: Tasks that are actively being worked on.
- Testing: Tasks that are completed and are being tested or reviewed.
- Done: Tasks that are finished and meet the team’s definition of done.
The columns may be customised depending on the team’s workflow or specific needs.
2. Creating Tasks (Cards)
Each task or user story is represented by a card on the Scrum board. When creating a task card, it should include:
- Title: A brief description of the task or user story.
- Description: A detailed explanation of the task, including requirements or user needs.
- Priority: The level of importance or urgency (e.g., High, Medium, Low).
- Assignee: The team member responsible for completing the task.
- Estimation: The estimated effort required to complete the task (commonly in story points or hours).
Colour-coding cards can help differentiate between various types of tasks, such as development tasks, testing, or bug fixes.
3. Moving Tasks Through the Columns
As tasks progress through the sprint, they are moved across the board. Here’s how the flow typically works:
- Tasks begin in the Backlog (if they are part of the sprint but haven’t started yet).
- Once a task is selected for work, it moves to the To Do column.
- As team members start working on a task, it is moved to In Progress.
- When the task is ready for testing or review, it moves to Testing.
- Once the task has passed testing and is complete, it moves to the Done column.
This visual flow allows the team to easily see the status of tasks and track progress.
4. Managing Bottlenecks
A key benefit of using a Scrum board is identifying bottlenecks early. If there are too many tasks stuck in a particular column (such as In Progress), this signals a potential issue. It could mean that team members are overloaded or that certain tasks are encountering roadblocks. Regularly review the board and adjust resources or priorities to keep things moving smoothly.
5. Daily Standups and Board Updates
Scrum teams typically hold daily standups to discuss the progress of tasks and address any issues. During the standup:
- The team reviews the Scrum Board and updates the status of each task.
- Team members move tasks to the appropriate columns as work progresses.
- Any blockers or challenges are highlighted so that the team can quickly address them.
Keeping the Scrum board updated during these daily meetings ensures that everyone is aligned on progress and can make adjustments as needed.
6. Collaboration and Communication
Scrum Boards promote collaboration by making the workflow transparent. Team members can see which tasks are being worked on and who is working on what. They can also leave comments on task cards to provide updates or request clarification. This promotes open communication and ensures that everyone is working toward the same goals.
7. Sprint Reviews and Retrospectives
At the end of the sprint, the team will review the Scrum board to assess what was completed and what still needs attention. During the sprint review:
- Tasks in the Done column are reviewed to ensure they meet the team's definition of done.
- Any incomplete tasks may be carried over to the next sprint.
In the sprint retrospective, the team discusses any issues with the process, including how the Scrum Board was used, and looks for opportunities to improve the workflow for the next sprint.

Benefits of Using a Scrum Board
- Clear Visualisation: The Scrum Board provides a clear view of the status of all tasks, making it easier to track progress.
- Increased Collaboration: Team members can easily communicate and collaborate by seeing what others are working on.
- Improved Focus: The board helps the team focus on the most important tasks and ensures that work is prioritised correctly.
- Enhanced Transparency: Everyone can see the current state of the sprint, which encourages accountability and proactive problem-solving.
An Introduction to Scrum Boards and Their Role in Agile Projects
Scrum boards are a vital tool in agile project management, helping teams visualise their workflow and collaborate effectively. They are an essential part of the Scrum framework, which is one of the most widely used agile methodologies. Here's a brief overview of their role in agile projects:

1. Visualisation of Work
A Scrum Board provides a visual representation of a project’s tasks, breaking them down into manageable chunks. Typically divided into columns such as “To Do,” “In Progress,” and “Done,” the board allows team members to easily track the progress of each task. This visual system enhances transparency and ensures everyone understands the current state of the project.
2. Sprint Planning and Tracking
In Scrum, work is organised into time-boxed iterations known as sprints, usually lasting two to four weeks. The Scrum Board helps teams plan and track the progress of tasks during each sprint. As tasks are completed, they are moved across the board, providing an at-a-glance understanding of how much work remains to be done.
3. Enhancing Collaboration
Scrum boards foster team collaboration by making all work visible to everyone involved in the project. This helps team members discuss issues, share updates, and adjust priorities as needed. The board serves as a central hub for communication, making it easier for everyone to stay aligned and focused on the same goals.
Scrum Boards are a simple yet powerful tool that enhances organisation, improves communication, and drives efficiency in agile projects, ensuring teams stay on track and meet their sprint goals.
Scrum Process
Scrum is a popular agile framework used for managing team-based projects, particularly in software development, by breaking down work into short time-boxed iterations called sprints. It's a collaborative approach that encourages self-organisation, continuous improvement, and adaptation to changing requirements.
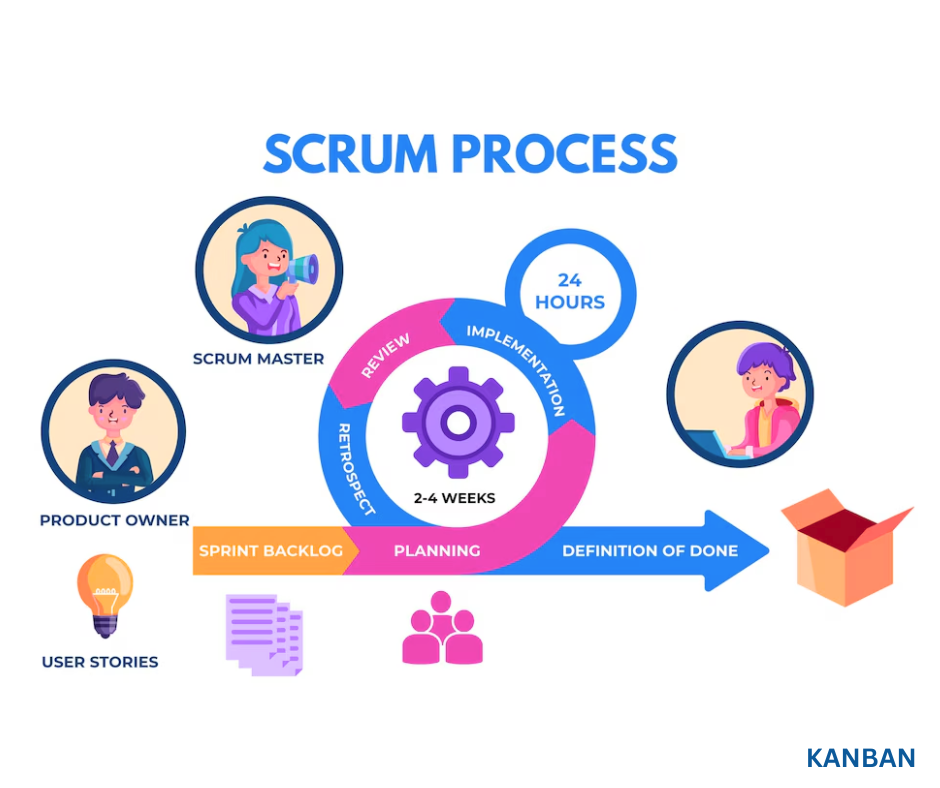
The Key Differences Between Scrum Boards and Kanban Boards
Both Scrum Boards and Kanban boards are widely used tools for managing workflows in agile environments. While they share similarities, they also have distinct features that cater to different types of project management. Here’s a breakdown of the key differences between Scrum boards and Kanban boards:
1. Structure and Framework
Scrum boards are typically used within the Scrum framework, which divides work into fixed-length sprints, usually lasting 2–4 weeks. Tasks are moved across the board during each sprint, with columns such as “To Do,” “In Progress,” and “Done.” Kanban boards, on the other hand, are not limited to sprints and offer a continuous flow of tasks. The focus in Kanban is on visualising work and improving process efficiency, with columns tailored to the specific workflow.
2. Work Flow
Scrum boards are designed to manage a predefined set of tasks that need to be completed during each sprint. The goal is to achieve a specific set of deliverables by the end of the sprint. Kanban boards, however, are more flexible, with tasks being continuously added or adjusted based on priority, ensuring work moves at a steady pace without specific time frames.
3. Flexibility and Change
Scrum Boards encourage a more structured approach, with work committed to before the sprint starts. Kanban boards are highly adaptable, allowing teams to reprioritise tasks at any time and move them between columns as needed, offering greater flexibility.
Understanding these differences can help teams choose the right board for their specific project management needs, whether they prefer the structured sprint approach of Scrum or the flexible, continuous flow of Kanban.
How Scrum Boards Help Organise and Prioritise Tasks
Scrum boards are an essential tool for teams working in the Scrum framework, helping to visualise, organise, and prioritise tasks efficiently. They are designed to support the agile methodology, where tasks are completed in short, iterative cycles known as sprints. Here’s how Scrum boards help teams manage their work:
1. Visualising Task Flow
A Scrum Board provides a clear visual representation of tasks, typically organised into columns such as “To Do,” “In Progress,” and “Done.” This allows the team to see the status of each task at a glance, helping to streamline communication and avoid bottlenecks. It’s a simple yet powerful way to keep everyone on the same page.
2. Fostering Team Collaboration
With tasks laid out on a Scrum board, all team members can easily see which tasks are being worked on and who is responsible for them. This transparency fosters collaboration, as it’s easy to spot areas where team members may need help or where resources may need to be adjusted.
3. Prioritising Tasks
Scrum boards also play a key role in task prioritisation. At the beginning of each sprint, the team decides which tasks are the most important and places them at the top of the board. This ensures that high-priority tasks are tackled first, helping teams meet deadlines and achieve sprint goals more effectively.
Overall, Scrum boards help teams stay organised, focused, and aligned, making it easier to manage workflows and ensure successful delivery of tasks within each sprint.
The Essential Elements of a Scrum Board
A Scrum Board is a central tool in the agile methodology, helping teams visualise and manage their tasks throughout each sprint. It is designed to streamline workflows, enhance collaboration, and ensure that tasks are prioritised and completed on time. Here are the essential elements that make up a Scrum board:
1. Columns
The Scrum Board is typically divided into several columns that represent different stages of the workflow. The most common columns include “To Do,” “In Progress,” and “Done.” These columns allow team members to track the status of tasks at a glance, ensuring clarity and visibility across the board.
2. Cards
Each task or user story is represented by a card on the Scrum board. These cards contain key information about the task, such as the task name, description, and assigned team member. Cards can be moved across columns as the task progresses, providing a clear overview of the team’s workflow.
3. Swimlanes
Swimlanes are horizontal rows on the board that can be used to group tasks by specific criteria, such as team member, priority, or project type. Swimlanes provide a way to visually distinguish different types of work and help prevent confusion in busy workflows.
4. Backlog
The backlog is a list of tasks that need to be completed in future sprints. It is typically kept separate from the Scrum Board but is linked to it, ensuring that tasks are pulled into the sprint as needed. The backlog helps teams plan and prioritise tasks for upcoming work cycles.
By incorporating these key elements, a Scrum board helps teams stay organised, collaborate effectively, and maintain a clear view of their sprint goals and progress.
Understanding the Three Key Columns on a Scrum Board
A Scrum board is an essential tool for teams using the Scrum framework in agile project management. It provides a visual representation of work tasks during a sprint, helping teams stay organised and focused. The board is typically divided into three main columns: “To Do,” “In Progress,” and “Done.” Each column plays a crucial role in tracking the progress of tasks. Here’s a closer look at each of these columns:
1. To Do
The “To Do” column holds all tasks or user stories that are planned for the current sprint but have not yet been started. This column represents the work that is waiting to be tackled. By visualising tasks in this column, the team can easily see what work needs to be done and plan accordingly. Tasks in the “To Do” column are typically moved to “In Progress” once work begins.
2. In Progress
Once a task is being worked on, it is moved to the “In Progress” column. This column indicates that the task is actively being worked on by one or more team members. The “In Progress” column provides visibility into what is happening at any given time during the sprint and helps prevent overloading team members with too many tasks at once.
3. Done
The “Done” column represents tasks that have been completed and are finished. Once a task meets the agreed-upon definition of done (e.g., fully tested and reviewed), it is moved to this column. The “Done” column provides a clear visual of the team’s progress and achievements throughout the sprint, fostering a sense of accomplishment and motivating the team to continue delivering.
By organising work into these three simple columns, Scrum boards help teams stay focused, manage their workflow efficiently, and ensure tasks are completed on time.

How to Set Up Your First Scrum Board for a Successful Sprint
Setting up your first Scrum board can be a key step toward successfully managing your team’s sprint. A Scrum Board helps visualise tasks, track progress, and ensure that the team stays on track during the sprint. Here's how to set up a Scrum board effectively:
1. Define Your Columns
The first step is to divide the board into three main columns: “To Do,” “In Progress,” and “Done.” These columns represent the workflow stages of each task. The “To Do” column will contain tasks planned for the sprint, “In Progress” is where tasks currently being worked on will go, and “Done” is where completed tasks will reside.
2. Add Tasks
Once your columns are set up, add tasks to the “To Do” column. These tasks should be user stories or work items from the sprint backlog. Ensure each task is clear and actionable, with a defined goal. You can write these tasks on sticky notes or digital cards if using a digital board.
3. Assign Tasks
Assign team members to each task according to their strengths and capacity. This step ensures that everyone knows what they’re responsible for during the sprint. By visualising who is working on which task, the team can avoid confusion and better manage workload.
4. Track Progress
As work begins, move tasks from the “To Do” column to the “In Progress” column. This provides a visual cue for the entire team on the status of tasks. Once a task is completed, it is moved to the “Done” column. Tracking progress this way ensures tasks are being completed and gives a clear overview of the sprint’s status.
By setting up your Scrum Board with clear columns and tasks, your team can stay organised and focused throughout the sprint, helping ensure a successful outcome.
The Benefits of Using Scrum Boards for Agile Teams
Scrum boards are an essential tool for Agile teams, providing a clear and visual way to manage tasks, improve collaboration, and increase productivity. Here are some of the key benefits of using Scrum boards in Agile environments:
1. Enhanced Visualisation
Scrum boards offer a visual representation of tasks, allowing teams to see the entire project workflow at a glance. By dividing tasks into columns like “To Do,” “In Progress,” and “Done,” everyone can easily track the status of work. This clarity helps team members understand priorities and ensures that no task is overlooked.
2. Improved Collaboration
With Scrum boards, team members can see who is working on what, which fosters collaboration and communication. The board serves as a central point for discussions, making it easier for the team to collaborate and solve problems quickly. It also highlights bottlenecks in the workflow, enabling the team to address them promptly.
3. Increased Accountability
As tasks are assigned to individual team members, Scrum boards increase accountability. Each team member can track their progress, and there’s a clear visual representation of who is responsible for each task. This encourages ownership of tasks and ensures that work is completed on time.
4. Better Sprint Management
Scrum boards provide a structured way to manage sprints. By breaking down tasks and setting clear priorities, teams can easily focus on completing the most important work. They also allow for quick adjustments, ensuring that the team stays on track even if unexpected issues arise during the sprint.
By using Scrum boards, Agile teams can improve efficiency, enhance communication, and deliver projects with greater speed and accuracy.
How Scrum Boards Promote Transparency and Accountability
Scrum boards play a crucial role in enhancing both transparency and accountability within Agile teams. By offering a clear visual representation of tasks, they ensure everyone is aligned and aware of progress throughout the project.
1. Clear Visibility of Work
Scrum boards break down tasks into manageable columns, such as “To Do,” “In Progress,” and “Done,” making it easy for all team members to see what needs to be done, who is working on what, and the current status of each task. This transparency helps the team stay focused and aligned, preventing misunderstandings and reducing the risk of overlooked tasks.
2. Transparent Progress Tracking
With tasks moving across the board as they progress, team members and stakeholders can quickly track the flow of work. This visual representation helps identify bottlenecks, delays, or areas where additional support is needed. Transparency in progress encourages quicker problem-solving and keeps the team moving forward without unnecessary setbacks.
3. Accountability for Task Ownership
Scrum boards clearly assign tasks to individual team members, which increases accountability. Each team member is responsible for their tasks, and it’s easy to see who is working on what. This level of visibility ensures that everyone knows their responsibilities and encourages ownership of tasks. If tasks are delayed, it’s easy to pinpoint the issue and address it promptly.
Overall, Scrum boards foster a collaborative environment where transparency and accountability are central, leading to more efficient workflows and better project outcomes.
The Role of Scrum Boards in Daily Stand-Up Meetings
Scrum boards are an essential tool during daily stand-up meetings, offering a clear visual representation of the team's progress. These boards help facilitate effective communication and ensure that everyone is aligned with the project's current status. By referencing the Scrum board, teams can stay focused and make the most of their daily stand-up sessions.
1. Visualising Progress
During daily stand-ups, team members can refer to the Scrum board to quickly visualise the status of tasks. The board typically displays tasks in columns such as "To Do," "In Progress," and "Done," which allows everyone to instantly see what work is being done and where each task stands. This visual clarity reduces confusion and enhances team collaboration.
2. Identifying Obstacles
The Scrum board is key to identifying any obstacles or bottlenecks early in the process. If a task is stuck in the "In Progress" column for too long, it signals that the team needs to discuss and resolve the issue. Daily stand-up meetings provide the perfect platform for addressing these challenges, ensuring that issues are dealt with swiftly and preventing delays.
3. Ensuring Accountability
By displaying tasks and their owners, the Scrum board ensures that each team member is accountable for their work. During stand-ups, team members can quickly discuss their progress, any difficulties they are facing, and what they plan to do next. This daily check-in helps keep everyone on track and aligned with the team's goals.
In short, Scrum boards are an indispensable tool in daily stand-up meetings, offering visual clarity, promoting accountability, and enabling teams to tackle obstacles early on.
How to Manage a Product Backlog Using Scrum Boards
Managing a product backlog efficiently is key to the success of any Scrum-based project. Scrum boards play a vital role in keeping the backlog organised, helping teams visualise tasks and prioritise them effectively. Here’s how to manage your product backlog using Scrum boards.
1. Organising the Product Backlog
The first step in using Scrum boards for backlog management is to organise the product backlog in a clear and structured way. The backlog should be broken down into smaller tasks or user stories that are easy to track. Each item in the backlog can be represented as a card on the Scrum board. These cards should be placed in the "To Do" column until they are ready to be worked on.
2. Prioritising Backlog Items
Once the tasks are listed, it’s important to prioritise them based on business value, urgency, and dependencies. The most critical tasks should be placed at the top of the backlog. During each sprint planning session, the Scrum team can pull the highest-priority items from the backlog and move them into the "To Do" column on the Scrum board for active work.
3. Reviewing and Refining the Backlog
Scrum boards help with ongoing refinement of the product backlog. As new requirements emerge or priorities shift, the Scrum board provides a visual representation of the backlog, making it easier to add, modify, or remove tasks. Regularly reviewing the backlog ensures that the team remains focused on delivering the most valuable features first.
In summary, Scrum boards offer a simple and visual way to manage and prioritise the product backlog, keeping teams aligned and ensuring the timely delivery of features and improvements.
Real-World Examples of Scrum Boards in Action
Scrum boards are widely used in various industries to streamline workflows, improve collaboration, and boost productivity. Here are a few real-world examples of how Scrum boards are applied in different settings.
1. Software Development Teams
In software development, Scrum boards are essential tools for managing complex projects. Developers use the board to break down tasks into smaller, manageable pieces. The board typically includes columns such as "To Do," "In Progress," and "Done," allowing the team to track their progress during each sprint. This visual organisation helps identify bottlenecks early, ensuring that the team stays on track to meet deadlines.
2. Marketing Teams
Marketing teams also benefit from Scrum boards to manage campaigns and projects. Tasks like content creation, social media management, and email campaigns are visualised on the board, making it easier to allocate resources and track progress. Scrum boards help ensure that marketing activities are completed in a timely manner, and they foster better communication between team members and departments.
3. Product Management
In product management, Scrum boards help track the progress of new features and improvements. The product backlog is organised, and the team can easily prioritise tasks based on customer needs or business goals. Scrum boards allow product managers to maintain a clear overview of the project's progress, ensuring that the most valuable features are delivered first.
These examples illustrate the versatility of Scrum boards in different industries, highlighting their ability to enhance workflow and productivity through visual organisation and prioritisation.
Why Scrum Boards Are Crucial for Sprint Planning
Scrum boards are essential tools for effective sprint planning, helping teams organise tasks and track progress in an agile workflow. These boards provide a visual representation of all the tasks required to achieve the goals of a sprint, ensuring clarity and focus throughout the process.
1. Clear Task Visualisation
One of the main benefits of using a Scrum board is the clear visualisation of tasks. During sprint planning, teams break down work into manageable chunks and allocate them to the "To Do" column. This makes it easier for all team members to see what needs to be done, reducing confusion and ensuring everyone is aligned with the sprint goals.
2. Improved Prioritisation
Scrum boards allow teams to prioritise tasks effectively. With a visual layout, it becomes easy to see which tasks are critical and which ones can be worked on later. This ensures that the team focuses on the most important items first, delivering value early in the sprint.
3. Progress Tracking
Scrum boards provide real-time tracking of progress. As tasks move from the "To Do" to "In Progress" and then to "Done," the board helps everyone monitor how much work has been completed and what is still pending. This promotes transparency and accountability within the team.
Overall, Scrum boards are crucial for sprint planning because they improve organisation, prioritisation, and tracking, enabling teams to manage their work efficiently and meet sprint objectives successfully.
The Evolution of Scrum Boards: From Physical to Digital
Scrum boards have evolved significantly over the years, transitioning from physical boards to digital platforms. This shift has greatly improved the way teams manage projects in agile environments, making it easier to collaborate, track progress, and adapt to changes quickly.
1. The Physical Scrum Board
In the early days of Scrum, teams relied on physical boards to manage their tasks. These boards were typically simple whiteboards or corkboards with sticky notes or cards representing tasks. Each task would move through different columns, such as "To Do," "In Progress," and "Done," providing a clear visual representation of the team’s workflow. While effective, physical boards had limitations, particularly when it came to remote teams and real-time updates.
2. The Shift to Digital Scrum Boards
With the rise of remote work and distributed teams, digital Scrum boards became the next step in the evolution. Digital tools allow for real-time updates and easier collaboration across different locations. They offer features like task assignment, comments, and document attachments, making it simpler to manage tasks and communicate with team members, no matter where they are located.
3. Benefits of Digital Scrum Boards
Digital Scrum boards offer several advantages over their physical counterparts. They streamline the management of tasks, reduce the risk of errors, and ensure that all team members have access to the most up-to-date information. Furthermore, they integrate seamlessly with other project management tools, improving overall efficiency and transparency within the team.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using a Scrum Board
Scrum boards are essential tools for managing tasks in agile projects, but using them effectively requires attention to detail. Here are some common mistakes teams should avoid when using a Scrum board:
1. Overloading the Board
One common mistake is overcrowding the Scrum board with too many tasks at once. While it's tempting to list every single task, this can overwhelm the team and make it harder to focus on priorities. Keep the board clear and concise, only displaying tasks that are currently active or upcoming.
2. Not Updating the Board Regularly
A Scrum board is only effective when it is updated regularly. If tasks aren't moved through the columns or updated as they progress, it can lead to confusion and miscommunication. Ensure that the board reflects the current status of the tasks to keep everyone on the same page.
3. Ignoring the Definition of Done
Another mistake is not clearly defining what "done" means for each task. Without a clear definition, tasks may linger in the "Done" column without being fully completed. Set clear criteria for task completion to maintain quality and prevent incomplete work from slipping through the cracks.
4. Lack of Team Involvement
Scrum boards should be a collaborative tool, not something managed by one person. If only one team member is responsible for updating the board, it can result in inaccurate information. Encourage all team members to contribute and ensure they actively engage with the board.
By avoiding these common mistakes, teams can maximise the effectiveness of their Scrum boards and improve their workflow, leading to better project outcomes.
How Scrum Boards Facilitate Continuous Improvement in Agile Workflows
Scrum boards are a vital tool in agile workflows, helping teams visualise, organise, and optimise their work processes. One of the key benefits of using a Scrum board is how it facilitates continuous improvement, a fundamental principle of agile methodology.
1. Visualising Workflow and Identifying Bottlenecks
Scrum boards offer a clear visual representation of tasks, making it easier to track progress in real-time. By categorising tasks into columns like "To Do," "In Progress," and "Done," teams can quickly spot bottlenecks or areas where work is piling up. Identifying these obstacles early allows teams to take proactive steps to remove them and improve the flow of work.
2. Promoting Regular Reflection
Scrum boards naturally encourage regular team reflection during stand-up meetings and retrospectives. Teams review completed tasks, assess what's working, and identify areas for improvement. This continuous feedback loop enables teams to make small adjustments regularly, ensuring that they are constantly evolving and enhancing their processes.
3. Improving Task Prioritisation
With a Scrum board, tasks are often prioritised based on their importance and urgency. As priorities shift, teams can adapt quickly, ensuring that the most critical tasks are completed first. This flexibility ensures that teams stay aligned with business goals and can respond to changes in customer needs or market conditions.