Lean Management is a systematic approach to running an organisation that seeks to improve efficiency, reduce waste, and deliver maximum value to the customer. Rooted in the principles of lean manufacturing, which originated from the Toyota Production System (TPS) in the mid-20th century, lean management has since evolved into a widely adopted methodology across diverse industries. Its primary goal is to create more value for customers with fewer resources by optimising workflows, eliminating inefficiencies, and fostering a culture of continuous improvement.
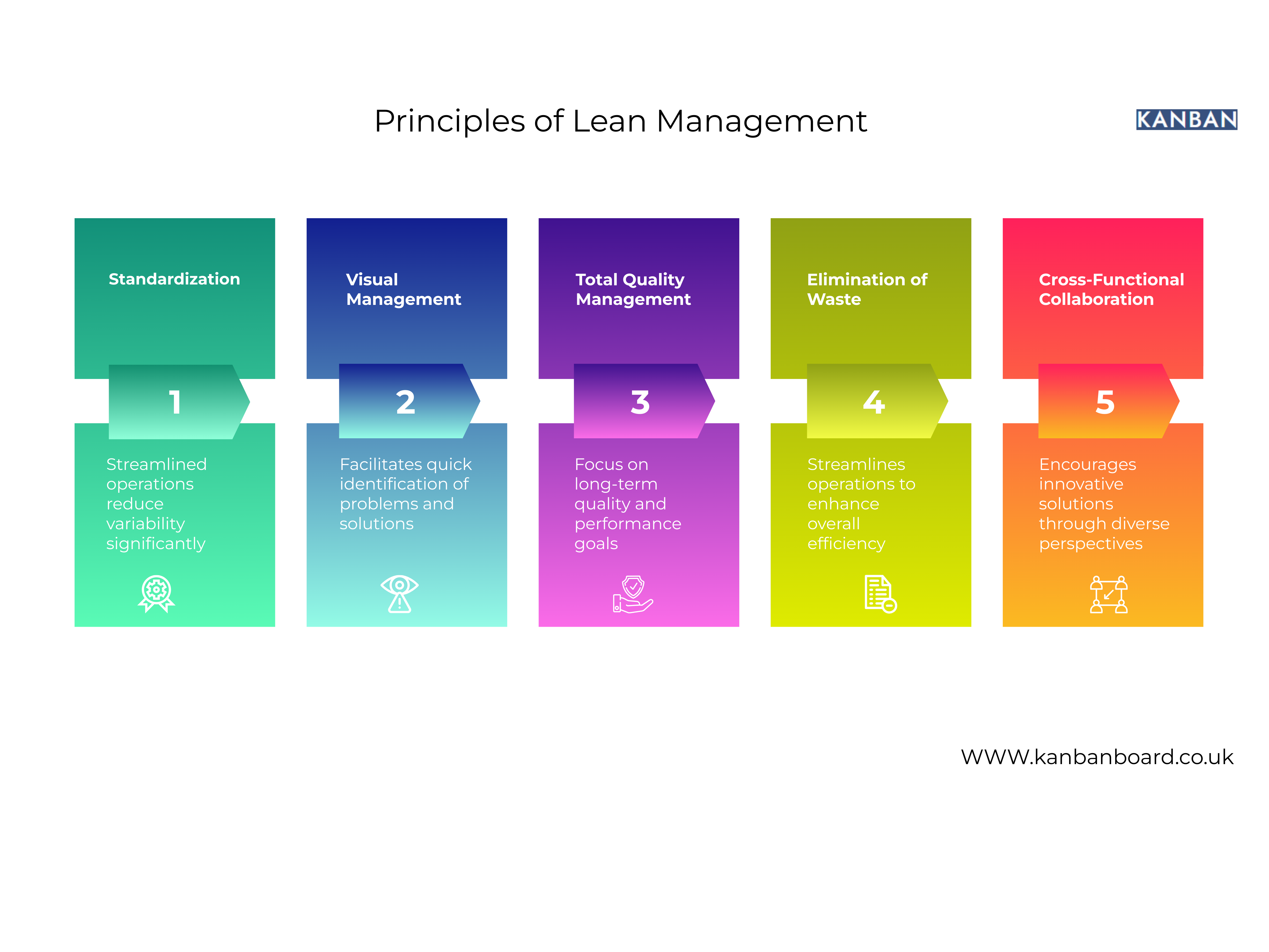
The Core Principles of Lean Management
At the heart of Lean Management are five core principles. These principles guide organisations in transforming their processes to maximise value while minimising waste:
Value Identification
The first step in lean management is identifying what constitutes value from the customer’s perspective. Value is anything that the customer is willing to pay for, such as features, services, or outcomes that meet their needs or solve their problems. Organisations need to focus on delivering these value-added activities while eliminating everything else that does not contribute to the customer's desired outcome.
Value Stream Mapping
Once value is identified, organisations create a detailed map of the value stream — the entire process flow from raw materials or inputs to the delivery of the final product or service. This map helps to identify areas where waste occurs, such as inefficiencies, bottlenecks, or non-value-adding activities. By analysing the value stream, businesses can pinpoint where improvements are needed.
Flow Optimisation
After mapping the value stream, the next step is to optimise the flow of work through the system. In Lean Management, the aim is to create a seamless flow of activities that move smoothly from one step to the next without delays, interruptions, or bottlenecks. By ensuring that processes flow efficiently, organisations can reduce lead times, improve productivity, and deliver products or services faster.
Pull System Implementation
The pull system is central to lean management. Rather than producing goods or services based on forecasted demand, a pull system ensures that work is only initiated when there is actual customer demand. This helps reduce overproduction, inventory costs, and wasted resources. In practice, organisations adopt just-in-time (JIT) production, where materials or products are produced exactly when needed, in the right quantities, and delivered promptly to customers.
Continuous Improvement (Kaizen)
Lean Management fosters a culture of continuous improvement, also known as Kaizen. This principle emphasises that improvement is an ongoing process, where small, incremental changes are made consistently over time. Employees at all levels are encouraged to contribute ideas for enhancing processes, eliminating waste, and solving problems. Through Kaizen, organisations develop a mindset that strives for perfection, even if it is never fully attainable.
Types of Waste in Lean Management
A key aspect of lean management is identifying and eliminating waste, which is broadly categorised into seven types:
Overproduction
Producing more than what is needed or before it is required leads to excess inventory and wasted resources.
Waiting
Idle time caused by delays, waiting for materials, information, or approvals, disrupts workflow and reduces productivity.
Transportation
Unnecessary movement of materials, products, or people leads to wasted time and energy.
Overprocessing
Performing tasks or adding features that do not add value to the customer is wasteful and inefficient.
Inventory
Excess inventory ties up capital and space and increases the risk of obsolescence.
Motion
Inefficient or unnecessary movements by employees, such as walking, bending, or reaching, reduce efficiency and increase the likelihood of errors or injuries.
Defects
Producing defective products or services leads to rework, repairs, or replacements, wasting time and resources.
Lean Tools and Techniques
To implement Lean Management effectively, organisations utilise a variety of tools and techniques designed to optimise processes and eliminate waste. Some of the most commonly used lean tools include:
5S
This tool focuses on workplace organisation and cleanliness, ensuring that the workspace is organised in a way that promotes efficiency and reduces waste. The five steps of 5S are Sort, Set in order, Shine, Standardise, and Sustain.
Kanban
Kanban is a visual tool that helps manage workflow and inventory by signaling when tasks are ready to be started or when materials need to be replenished. It helps teams prioritise work based on customer demand and reduces overproduction.
Value Stream Mapping (VSM)
VSM is a detailed analysis tool that helps organisations visualise the flow of materials and information throughout the production process. It highlights inefficiencies and areas where waste can be reduced.
Kaizen Events
These are focused, short-term improvement projects that involve cross-functional teams working together to address specific issues or inefficiencies. Kaizen events are designed to achieve rapid results and promote continuous improvement.
Just-In-Time (JIT)
JIT is a production system that reduces inventory and waste by ensuring that materials are delivered only when they are needed in the production process. This helps organisations avoid overproduction and reduce storage costs.
Benefits of Lean Management
Implementing Lean Management brings numerous benefits to organisations across industries:
Improved Efficiency
By eliminating waste and optimising workflows, lean management helps organisations increase efficiency and productivity. Processes become smoother, faster, and more predictable.
Enhanced Customer Satisfaction
Lean Management emphasises delivering maximum value to customers by focusing on their needs and reducing inefficiencies. This results in faster delivery times, higher-quality products or services, and improved customer experiences.
Cost Reduction
Reducing waste, inventory, and overproduction leads to lower operating costs. Lean management helps organisations allocate resources more effectively and avoid unnecessary expenses.
Employee Engagement
Lean Management fosters a culture of continuous improvement, where employees are empowered to contribute ideas and solutions. This leads to increased employee engagement, job satisfaction, and collaboration.
Flexibility and Adaptability
Lean organisations are better equipped to respond to changes in customer demand or market conditions. By focusing on creating flexible and adaptable processes, Lean Management enables organisations to adjust quickly and efficiently.
Challenges of Implementing Lean Management
Despite its many benefits, implementing lean management can be challenging. Common challenges include:
Cultural Resistance
Lean management requires a cultural shift towards continuous improvement, which can be met with resistance from employees who are accustomed to traditional ways of working.
Sustaining Improvements
Achieving initial improvements through lean initiatives is often easier than sustaining them over the long term. Organisations need to ensure that lean practices become ingrained in the company culture.
Leadership Commitment
Lean management requires strong commitment and support from leadership to drive change and ensure that improvements are implemented consistently.
Training and Development
Employees need proper training in lean tools and methodologies to implement lean management effectively. Organisations must invest in ongoing training and development to build a skilled and knowledgeable workforce.
What is Lean Management? A Practical Introduction for Businesses
Lean management is a business approach focused on creating more value for customers while using fewer resources. It aims to streamline operations, remove waste, and improve overall efficiency. Originally developed to improve manufacturing processes, lean management principles are now widely used across all types of industries, helping businesses stay competitive and deliver better results.

Core Principles of Lean Management
At its heart, lean management is built on several key principles. The first is defining value from the customer's perspective. Businesses must understand exactly what their customers value and focus their processes on delivering this efficiently. The second principle is identifying and removing waste—anything that does not add value to the product or service. Continuous improvement, respect for people, and creating a flow of work without delays are also central to lean management.
Benefits for Businesses
Implementing lean management offers many advantages. It leads to faster production times, reduced costs, and higher quality products and services. Teams become more engaged as they are encouraged to participate in problem-solving and process improvements. By focusing on efficiency and customer satisfaction, businesses can achieve sustainable growth and a strong competitive advantage in the market.
Lean management is not just a one-time project; it is a continuous journey. Companies that embrace lean thinking create a culture of ongoing improvement, making them better equipped to face challenges and meet the ever-changing needs of their customers.
Core Principles of Lean Management: What Every Organisation Should Know
Lean management is built on a set of simple but powerful principles that guide organisations towards greater efficiency, better quality, and higher customer satisfaction. Understanding these principles is key for any business looking to improve performance and stay competitive in a fast-moving market.
Defining Value
The first step in lean management is to clearly define value from the customer's point of view. Organisations must understand what their customers really want and focus on delivering exactly that, without adding unnecessary steps or features that do not add value.
Mapping the Value Stream
Once value is defined, businesses need to map out all the actions and processes involved in delivering it. This helps to identify waste—activities that consume resources but do not add value. Removing waste leads to leaner, more efficient operations.
Creating Flow
Lean management aims to ensure that work flows smoothly through processes without delays or interruptions. By organising workspaces, streamlining tasks, and removing barriers, organisations can improve flow and reduce production times.
Establishing Pull Systems
Rather than producing goods based on forecasts, lean systems operate on pull, meaning production is driven by actual customer demand. This reduces overproduction and minimises inventory costs.
Pursuing Perfection
Lean management encourages continuous improvement at every level. By fostering a culture where teams regularly review and improve processes, organisations can move closer to perfection, boosting efficiency and delivering greater value to customers.
How Lean Management Drives Operational Efficiency and Reduces Waste
Lean management offers a practical and powerful way for organisations to improve operational efficiency while reducing waste. By focusing on what truly adds value for the customer, businesses can streamline their processes and eliminate activities that consume time, money, and resources unnecessarily.
Focusing on Customer Value
Lean management begins by identifying what customers genuinely value. This clear focus ensures that every task and process is aligned with delivering that value, helping organisations avoid wasting efforts on activities that do not contribute to customer satisfaction.
Eliminating Waste
Waste can come in many forms, such as overproduction, excess inventory, unnecessary movement, and defects. Lean techniques help teams spot and remove these inefficiencies. By doing so, businesses can operate faster, more cost-effectively, and with fewer errors.
Streamlining Processes
Lean management encourages the simplification of processes. Standardising work procedures, reorganising workflows, and improving layouts help tasks to flow smoothly, cutting down on delays and making it easier for employees to do their jobs effectively.
Empowering Employees
In a lean environment, employees are given the tools and authority to solve problems and make improvements. Their insights lead to smarter ways of working and faster responses to issues, strengthening operational efficiency across the organisation.
Building a Culture of Continuous Improvement
Lean management fosters an ongoing commitment to review and enhance operations. This continuous improvement mindset keeps businesses flexible, competitive, and ready to meet changing customer needs with minimal waste and maximum efficiency.
The Benefits of Implementing Lean Management Across Departments
Implementing lean management across departments offers organisations the opportunity to optimise processes, reduce waste, and enhance overall performance. By applying lean principles in every area of the business, companies can create a more streamlined and efficient environment that drives both short-term and long-term success.
Improved Efficiency
One of the key benefits of lean management is improved efficiency. By identifying and eliminating inefficiencies across departments, such as redundant tasks, bottlenecks, or excessive paperwork, businesses can reduce the time and resources needed to complete tasks. This allows teams to focus on high-value activities that directly contribute to company goals.
Cost Reduction
By cutting out unnecessary steps in workflows and reducing waste, lean management helps organisations lower operational costs. For example, by reducing excess inventory or improving processes to prevent errors and defects, businesses can avoid costly mistakes and increase profitability without compromising on quality.
Increased Collaboration
Lean management encourages cross-departmental collaboration by aligning all areas of the business around shared goals. Departments that work together more effectively are able to communicate better, share resources, and solve problems faster, leading to faster decision-making and smoother operations.
Enhanced Customer Satisfaction
When departments work more efficiently, the organisation can deliver products and services to customers more quickly and reliably. By focusing on continuous improvement, lean management ensures that businesses remain adaptable and responsive to customer needs, which boosts overall satisfaction.
Employee Engagement and Empowerment
Lean management promotes employee involvement by encouraging them to suggest improvements and contribute to problem-solving. This empowers employees, boosting morale and fostering a culture of innovation and ownership across departments.
Top Lean Management Tools You Should Be Using for Efficiency
Lean management focuses on optimising processes, reducing waste, and improving efficiency across an organisation. To achieve these goals, businesses can benefit from using a variety of lean management tools. These tools help identify inefficiencies, streamline workflows, and drive continuous improvement.
1. Value Stream Mapping
Value stream mapping is a powerful tool for visualising and analysing the flow of materials and information through a process. It helps identify areas of waste, such as delays, bottlenecks, or redundant steps, allowing businesses to make informed decisions on where improvements can be made. By creating a value stream map, organisations can prioritise areas that need attention and develop targeted solutions.
2. 5S System
The 5S system is a methodology for organising and standardising the workplace. It stands for Sort, Set in order, Shine, Standardise, and Sustain. This tool helps eliminate clutter, improve organisation, and create a cleaner, more efficient working environment. The 5S system not only boosts productivity but also enhances safety and employee morale.
3. Kaizen
Kaizen is the practice of continuous, incremental improvements. It encourages employees at all levels to identify small, manageable changes that lead to more efficient processes. The Kaizen approach fosters a culture of improvement by making everyone in the organisation accountable for finding opportunities to enhance performance.
4. Kanban
Kanban is a visual tool used to manage workflow and inventory. By using boards, cards, or digital tools, businesses can track tasks, monitor progress, and ensure that work is evenly distributed. Kanban helps to eliminate waste by highlighting areas where resources are being overburdened or underutilised, enabling better management of workload.
5. Root Cause Analysis (RCA)
Root cause analysis is a problem-solving technique used to identify the underlying cause of issues in processes. By addressing the root cause rather than just the symptoms, organisations can implement long-term solutions to prevent recurrence. This tool helps businesses identify opportunities for system-wide improvements and reduces recurring problems.
By incorporating these lean management tools into your business operations, you can streamline processes, reduce waste, and enhance overall efficiency.

Steps to Successfully Implement Lean Management in Your Organisation
Implementing lean management is a strategic approach to improving efficiency, reducing waste, and maximising value in any organisation. To successfully introduce lean practices, it's important to follow a structured approach that engages all levels of the business. Here are the key steps to implement lean management effectively:
1. Understand Lean Principles
Before implementing lean management, it’s crucial for leadership and key employees to fully understand the core principles of lean. This includes eliminating waste, improving processes, and delivering value to customers. Understanding these principles helps ensure alignment across the organisation and sets a clear direction for the transformation.
2. Identify Areas of Improvement
Conduct a thorough analysis of current processes to identify areas of inefficiency. Use tools like value stream mapping to visualise workflows and pinpoint where waste occurs, whether in time, materials, or effort. Focus on processes that have the most significant impact on performance and customer satisfaction.
3. Engage Employees at All Levels
Lean management thrives when all employees are involved in the process. Encourage collaboration and open communication throughout the organisation. Engage employees in suggesting improvements and be open to their ideas. When employees feel empowered, they are more likely to contribute to the success of lean initiatives.
4. Start with Small Changes
Implement lean practices incrementally, starting with small, manageable changes that can demonstrate quick wins. Focus on a single process or department to pilot lean management and refine the approach before scaling it across the organisation. This step allows for adjustments without overwhelming the team.
5. Measure and Monitor Progress
Establish key performance indicators (KPIs) to track progress and measure the success of lean initiatives. Regularly assess the impact of changes and ensure that improvements are being maintained. Use feedback and data to refine processes further and identify new opportunities for improvement.
By following these steps, your organisation can create a culture of continuous improvement and enhance operational efficiency through lean management.
Lean Thinking vs Traditional Management: Key Differences Explained
Lean thinking and traditional management are two distinct approaches to business operations, each with its own set of principles and strategies for achieving success. While traditional management focuses on hierarchical structures and control, lean thinking emphasises efficiency, continuous improvement, and the elimination of waste. Understanding these differences can help businesses choose the right approach for their needs.
1. Focus on Waste Elimination vs. Control
In lean thinking, the primary goal is to eliminate waste in all forms – whether it's time, resources, or effort. Lean practices encourage businesses to streamline processes, improve flow, and maximise value for customers. In contrast, traditional management often focuses on maintaining control over resources and processes, which can lead to inefficiencies and missed opportunities for improvement.
2. Employee Empowerment vs. Top-Down Control
Lean thinking promotes employee involvement at all levels, encouraging them to identify inefficiencies and contribute to continuous improvement. It creates a culture of shared responsibility where everyone works together to improve processes. Traditional management, however, tends to have a top-down approach where decision-making is centralised, and employees are often not encouraged to suggest changes.
3. Continuous Improvement vs. Stability
Lean thinking operates on the principle of continuous improvement, or “Kaizen,” where small, incremental changes are made regularly to enhance efficiency. This ensures that processes are constantly evolving and adapting. On the other hand, traditional management is often more focused on maintaining stability and control, which can hinder innovation and slow down improvement efforts.
4. Long-Term Value vs. Short-Term Goals
Lean thinking prioritises long-term value creation by focusing on customer satisfaction and process efficiency. It encourages businesses to invest in long-term improvements that will pay off over time. Traditional management, however, may be more focused on achieving short-term goals and meeting immediate performance targets.
lean thinking offers a more flexible, collaborative, and efficiency-driven approach compared to the more structured and control-based traditional management style.
Real-Life Success Stories: Companies Thriving with Lean Management
Lean management has transformed numerous businesses worldwide, helping them increase efficiency, reduce waste, and deliver greater value to their customers. Many organisations, both large and small, have embraced lean principles to streamline their processes and improve their bottom line. Here are a few real-life examples of companies thriving with lean management.
1. Manufacturing Excellence
A global manufacturing company implemented lean management to optimise production processes, reduce downtime, and improve product quality. By introducing standardised work processes, visual management tools, and a culture of continuous improvement, the company saw a significant reduction in defects and a marked increase in productivity. The lean approach allowed them to better meet customer demands and stay ahead of competitors in a fast-paced market.
2. Retail Industry Success
A retail giant applied lean principles to its supply chain, focusing on inventory management and order fulfilment. Through waste elimination techniques, such as reducing excess stock and improving stock replenishment systems, they enhanced operational efficiency and reduced costs. This allowed them to keep prices competitive while maintaining high levels of customer satisfaction, resulting in increased sales and market share.
3. Healthcare Improvements
A leading healthcare provider adopted lean management in its hospital operations to improve patient care and reduce waiting times. By streamlining processes in the emergency department, implementing better communication practices, and focusing on eliminating non-value-adding activities, the hospital significantly improved patient outcomes and reduced costs, all while maintaining high-quality care standards.
These real-life success stories show that lean management is not just a buzzword but a practical approach that delivers tangible benefits across various industries. By focusing on waste reduction, continuous improvement, and customer value, businesses can achieve long-term success and operational excellence.
Overcoming Common Challenges When Introducing Lean Management
Introducing lean management into an organisation can be highly beneficial, but it often comes with its set of challenges. Understanding these obstacles and how to overcome them can ensure a smoother implementation and greater success in the long run. Here are some common challenges faced when adopting lean management and tips on overcoming them.
1. Resistance to Change
One of the biggest hurdles in implementing lean management is resistance from employees. People may be set in their ways or fearful of change. To overcome this, it is essential to involve employees early in the process. Provide training, communicate the benefits of lean practices, and encourage a culture of collaboration. This helps to reduce resistance and fosters a sense of ownership over the new processes.
2. Lack of Leadership Support
Without strong leadership support, lean initiatives can fail to gain traction. Leaders must demonstrate commitment to lean principles by actively participating in training, setting a clear vision, and leading by example. When leadership is fully engaged, it sets a positive tone and drives the organisation toward success.
3. Insufficient Training and Resources
Lean management requires a solid understanding of its tools and techniques. Providing employees with adequate training is crucial for success. Ensure that your team has access to the necessary resources and support to implement lean practices effectively. Regular workshops and refresher courses can keep everyone aligned and skilled in lean methods.
4. Measuring Success
Tracking the success of lean initiatives can be difficult, especially in the early stages. Set clear, measurable goals from the outset and use key performance indicators (KPIs) to track progress. Regular reviews and adjustments will help ensure that lean practices continue to improve efficiency and reduce waste over time.
By addressing these challenges head-on, organisations can successfully introduce lean management and experience its full benefits of improved efficiency and waste reduction.
The Role of Leadership in Building a Lean Culture
Leadership plays a pivotal role in building and sustaining a lean culture within an organisation. A strong commitment from leaders is essential for implementing lean management successfully and ensuring it becomes embedded in the company’s values and everyday operations. Here's how leadership drives the success of lean initiatives.
1. Leading by Example
For a lean culture to thrive, leaders must model the behaviours they wish to see in their teams. By actively engaging in lean processes, identifying areas of improvement, and continuously focusing on waste reduction, leaders set the tone for the entire organisation. This hands-on approach encourages employees to follow suit and adopt lean practices themselves.
2. Fostering Open Communication
Effective leadership ensures there is open communication across all levels of the organisation. Encouraging feedback and input from employees allows leaders to identify challenges, concerns, and opportunities for improvement. Leaders should be approachable, listen to their teams, and support them in implementing lean strategies that drive efficiency and quality.
3. Providing Training and Resources
Leaders must ensure that their teams are equipped with the right tools, skills, and knowledge to succeed with lean practices. Providing ongoing training and access to resources enables employees to understand lean principles and apply them effectively in their daily tasks. Investing in employee development fosters a culture of continuous improvement.
4. Aligning Goals and Vision
Leaders should align lean initiatives with the organisation's broader goals and vision. By doing so, they ensure that lean practices are not viewed as a separate or temporary effort but as an integral part of the organisation’s long-term success. Clear direction and purpose create a shared understanding of why lean management matters.
leadership is crucial in fostering a lean culture. Through leading by example, open communication, and providing resources, leaders can drive sustained improvements and ensure that lean principles become ingrained in the organisation’s DNA.
Using Visual Management Techniques to Support Lean Practices
Visual management techniques are powerful tools that can enhance lean practices by providing clear, immediate visual cues to employees, improving communication and decision-making processes. By making key information visible, visual management helps eliminate confusion, boosts efficiency, and aligns teams towards common goals.
1. Simplifying Information Display
One of the core principles of visual management is simplicity. Information such as key performance indicators (KPIs), process statuses, and work progress can be displayed using clear, easy-to-understand visuals like charts, graphs, and colour-coded systems. This reduces the time spent searching for information, helping teams focus on tasks that add value.
2. Enhancing Process Transparency
Visual tools like flowcharts and process maps provide a visual representation of workflows, making it easier for employees to understand how tasks should be completed. This transparency helps to identify bottlenecks or inefficiencies in the process, enabling teams to make real-time adjustments to improve performance.
3. Supporting Standardisation and Consistency
Standard work instructions and visual controls help ensure that everyone follows the same processes. For example, visual aids such as shadow boards or colour-coded tools can help maintain consistency across tasks and shift changes, reducing errors and increasing quality control.
4. Engaging Employees in Continuous Improvement
Visual management also encourages employee engagement by making performance easily measurable. By visually tracking progress and displaying goals, employees are more motivated to contribute to improvements, fostering a culture of continuous improvement.
Incorporating visual management techniques into lean practices is an effective way to enhance clarity, improve communication, and drive performance. With visual cues, organisations can create an environment that supports lean principles, optimising workflows and ensuring better outcomes.
Continuous Improvement (Kaizen) as the Heart of Lean Management
At the core of lean management is the principle of continuous improvement, or Kaizen. This Japanese philosophy focuses on making small, incremental changes that lead to significant improvements in efficiency, quality, and overall performance. Kaizen encourages everyone in the organisation, from leadership to frontline employees, to actively participate in the improvement process.
1. Fostering a Culture of Improvement
Kaizen is not a one-time effort; it’s an ongoing approach that embeds a culture of continuous improvement within the organisation. By making small, regular improvements, businesses can adapt more quickly to changes in the market, enhance processes, and provide better value to customers. Every employee becomes a part of the process, driving improvements in their daily work environment.
2. Empowering Employees to Drive Change
Kaizen empowers employees by encouraging them to identify problems and suggest improvements. This helps to develop a sense of ownership and responsibility towards the organisation’s success. Employees at all levels are encouraged to contribute their ideas, leading to a more collaborative, engaged workforce.
3. Eliminating Waste and Increasing Efficiency
Through small, continuous improvements, Kaizen targets waste reduction in all its forms. Whether it’s minimising excess inventory, reducing unnecessary steps in a process, or streamlining communication, the goal is always to eliminate waste. This leads to better resource utilisation, quicker turnaround times, and lower costs.
By embracing Kaizen, organisations can create a sustainable environment of continuous improvement, where efficiency, quality, and employee engagement continually evolve, driving lean management to success.
How to Measure the Success of Lean Management Initiatives
Measuring the success of lean management initiatives is crucial to ensure continuous improvement and achieve desired outcomes. It involves assessing various metrics and KPIs that reflect efficiency, waste reduction, and overall performance improvement. Below are some key strategies to measure success effectively.
1. Monitor Process Efficiency
One of the most important indicators of lean success is process efficiency. This can be measured by tracking cycle time, the time it takes to complete a task or produce a product. A reduction in cycle time often indicates that the lean practices have streamlined operations and eliminated unnecessary steps.
2. Evaluate Waste Reduction
Lean management aims to reduce waste in all forms, including time, materials, and energy. Measuring waste reduction involves tracking the elimination of non-value-added activities and resources. This can be done through direct observation, value stream mapping, and waste audits. If waste is significantly reduced, it's a clear sign that lean initiatives are working.
3. Assess Employee Engagement and Involvement
Another critical success factor is the level of employee involvement in the lean process. High engagement indicates that the lean culture is taking root. You can measure this through surveys, feedback sessions, and the number of suggestions or improvements submitted by employees. Increased participation often leads to better problem-solving and innovation.
4. Track Customer Satisfaction
Lean management ultimately aims to improve the value delivered to customers. Monitoring customer feedback, satisfaction levels, and repeat business is vital in evaluating lean success. Improved quality, faster delivery times, and reduced costs typically lead to greater customer satisfaction.
By tracking these key metrics, organisations can effectively measure the success of their lean management initiatives and continue making improvements to achieve long-term operational excellence.
Lean Management for SMEs: Why Small Businesses Can Benefit Too
Lean management is often associated with large corporations, but small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) can benefit significantly from adopting its principles. By focusing on efficiency, waste reduction, and continuous improvement, lean practices can help SMEs boost productivity, cut costs, and improve customer satisfaction.
1. Streamlined Processes
One of the key advantages of lean management for SMEs is the ability to streamline operations. Small businesses typically have fewer resources, so it’s essential to maximise efficiency. By eliminating wasteful practices and focusing on value-adding activities, SMEs can improve their processes without the need for major investments in new technology or equipment.
2. Cost Reduction
Lean management helps SMEs identify and eliminate unnecessary expenses. Whether it’s reducing stock levels, improving production flow, or reducing downtime, lean practices allow small businesses to operate with fewer resources while maintaining or improving product quality. This translates directly to cost savings and improved profitability.
3. Improved Customer Satisfaction
Lean management focuses on delivering value to customers, which is critical for small businesses looking to grow and maintain a loyal customer base. By improving lead times, enhancing product quality, and reducing errors, SMEs can offer a better overall experience for their customers, leading to increased satisfaction and repeat business.
4. Greater Employee Engagement
In lean organisations, employees are encouraged to contribute ideas for improvement. This sense of involvement fosters a culture of continuous improvement and helps employees feel more engaged. For small businesses, this can lead to better morale and a more motivated workforce.
lean management offers SMEs the tools to optimise their operations, reduce waste, and deliver better value to their customers. By adopting lean principles, small businesses can compete more effectively in today’s fast-paced market.
Future Trends: How Lean Management is Evolving with Technology
As technology continues to advance, lean management is evolving to incorporate digital tools and innovations that enhance efficiency and streamline processes. In the coming years, the integration of new technologies will further optimise lean principles, enabling businesses to reduce waste, improve decision-making, and boost overall performance.
1. Automation and Robotics
Automation plays a crucial role in lean management by reducing manual tasks, improving speed, and minimising errors. With the increasing use of robotics in manufacturing and logistics, businesses can automate repetitive tasks and optimise workflows. This not only reduces waste but also allows human resources to focus on higher-value activities.
2. Data Analytics and Predictive Insights
Data analytics is becoming a key enabler of lean management. By collecting and analysing data in real-time, businesses can identify inefficiencies and opportunities for improvement faster than ever before. Predictive analytics can forecast demand, optimise inventory levels, and improve maintenance scheduling, leading to a more agile and responsive organisation.
3. Cloud-Based Lean Tools
Cloud-based software is transforming lean management by enabling real-time collaboration, continuous monitoring, and data sharing across teams. These tools allow businesses to track key performance indicators (KPIs), manage projects, and maintain transparency, leading to faster decision-making and more efficient operations.
4. Internet of Things (IoT)
The Internet of Things (IoT) enables devices and machines to communicate with each other, providing businesses with real-time data on equipment performance, inventory, and operational conditions. This connectivity helps businesses stay proactive in their lean management approach by quickly identifying and addressing potential issues before they escalate.
The future of lean management is being shaped by technological advancements that enable businesses to work smarter, not harder. By embracing these trends, companies can continue to enhance their operational efficiency, reduce waste, and maintain a competitive edge.