Lean methodology is a management philosophy derived from the Toyota Production System (TPS) that focuses on enhancing customer value by minimising waste and optimising processes. The core idea behind Lean is to deliver high-quality products and services efficiently by eliminating non-value-added activities, often referred to as waste. Lean methodology can be applied in manufacturing, services, healthcare, and various other sectors, making it a versatile approach to improving operational efficiency.
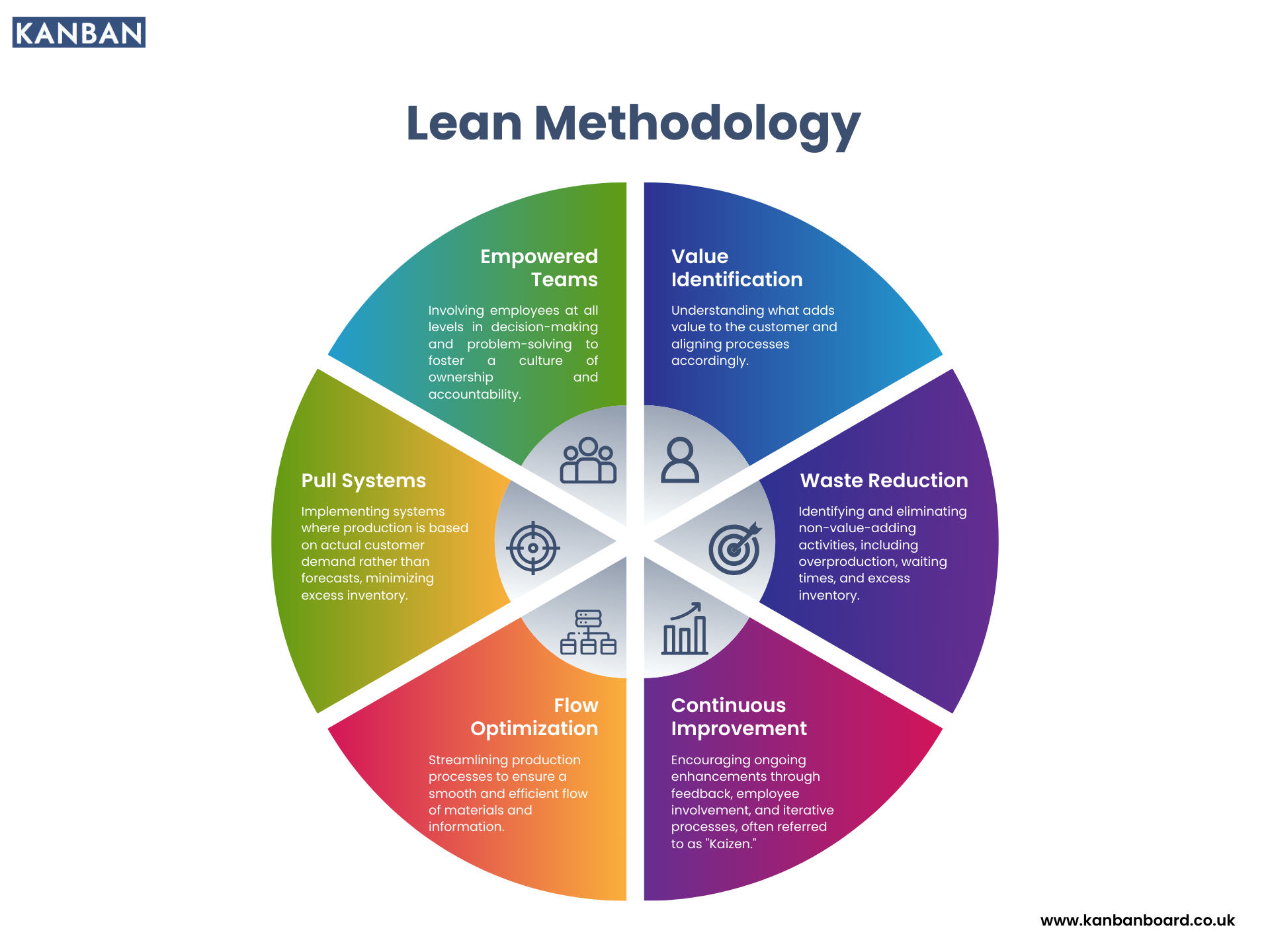
Core Principles of Lean Methodology
Lean methodology is built on several core principles that guide organisations in their pursuit of efficiency and excellence. These principles include:
- Value Identification: Understanding what customers value is the first step in Lean. Organisations must define value from the customer's perspective to align their processes accordingly. This often involves market research, customer feedback, and direct engagement with customers.
- Value Stream Mapping: Once value is defined, organisations map out the entire value stream—the series of steps and activities that contribute to delivering a product or service to the customer. This mapping helps identify wasteful activities, delays, and bottlenecks within the process.
- Elimination of Waste: Lean methodology focuses on eliminating the seven types of waste: overproduction, waiting, transportation, over-processing, excess inventory, unnecessary motion, and defects. By systematically identifying and removing these wastes, organisations can streamline operations and improve efficiency.
- Continuous Flow: Lean emphasises creating a smooth, uninterrupted flow of work through processes. This involves restructuring workflows, minimising handoffs, and ensuring that work-in-progress moves seamlessly from one stage to the next.
- Pull System: Unlike traditional push systems, where production is based on forecasts, Lean employs a pull system. This means that work is produced based on actual customer demand, ensuring that resources are allocated effectively and reducing excess inventory.
- Continuous Improvement (Kaizen): Kaizen, or continuous improvement, is a fundamental aspect of Lean. It encourages a culture of ongoing evaluation and enhancement of processes, promoting small, incremental changes that lead to significant long-term benefits.
Key Tools and Techniques in Lean Methodology
Lean methodology employs various tools and techniques to facilitate the principles mentioned above. Some of the most commonly used tools include:
- 5S: This is a workplace organisation method that includes five steps: Sort, Set in Order, Shine, Standardise, and Sustain. The goal is to create a clean, efficient workspace that promotes productivity and safety.
- Kanban: Kanban is a visual scheduling system that helps manage workflow by signaling when new tasks should be started based on demand. It promotes a pull-based system and reduces work-in-progress inventory.
- Value Stream Mapping (VSM): VSM is a visual representation of the flow of materials and information in a process. It helps teams identify areas of waste and inefficiency, enabling them to develop targeted improvement strategies.
- Poka-Yoke: This is a mistake-proofing technique designed to prevent errors in processes. Poka-Yoke involves implementing simple, inexpensive mechanisms to detect and correct mistakes before they result in defects.
- A3 Problem-Solving: The A3 method is a structured approach to problem-solving that involves a one-page report detailing the problem, analysis, proposed solutions, and action plans. It encourages collaboration and a deep understanding of the issues at hand.
Benefits of Lean Methodology
Implementing Lean methodology offers numerous benefits for organisations, including:
- Increased Efficiency: By eliminating waste and streamlining processes, Lean helps organisations operate more efficiently, leading to faster turnaround times and reduced costs.
- Enhanced Quality: Lean methodologies focus on delivering high-quality products and services. By preventing defects and encouraging continuous improvement, organisations can achieve higher levels of quality and customer satisfaction.
- Greater Flexibility: Lean organisations are better equipped to respond to changes in customer demand and market conditions. The pull system and continuous improvement processes enable quicker adjustments to production and service delivery.
- Employee Engagement: Lean promotes a culture of involvement and empowerment among employees. By encouraging staff to participate in identifying improvements and making decisions, organisations can foster a more engaged and motivated workforce.
- Customer Satisfaction: Ultimately, Lean methodology centers around delivering value to customers. By aligning processes with customer needs and reducing lead times, organisations can enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Challenges in Implementing Lean Methodology
While Lean methodology offers significant benefits, organisations may face challenges when implementing it. Some common challenges include:
- Resistance to Change: Employees and management may be resistant to changing established processes and practices. Overcoming this resistance requires effective communication and leadership support.
- Lack of Understanding: Without a clear understanding of Lean principles and tools, organisations may struggle to implement them effectively. Training and education are crucial for successful implementation.
- Cultural Barriers: Lean requires a cultural shift towards continuous improvement and collaboration. Organisations with deeply ingrained hierarchical structures may find it challenging to adopt a Lean mindset.
- Inconsistent Application: Lean methodology requires consistent application across all levels of the organisation. Inconsistent practices can lead to confusion and undermine the effectiveness of Lean initiatives.
Applications of Lean Methodology
Lean methodology is versatile and can be applied in various industries, including:
- Manufacturing: Originally developed in manufacturing, Lean is widely used to optimise production processes, reduce waste, and improve quality.
- Healthcare: Lean principles are increasingly applied in healthcare settings to streamline patient care processes, reduce wait times, and improve overall patient outcomes.
- Service Industry: Service-oriented organisations utilise Lean to enhance customer service, optimise workflows, and improve service delivery efficiency.
- Software Development: Lean principles are adapted in software development through methodologies like Lean Software Development, which emphasises rapid delivery and continuous feedback.
- Supply Chain Management: Lean methodologies help optimise supply chain processes, reduce lead times, and enhance overall efficiency in the delivery of goods and services.
What Is Lean Methodology and How Does It Help Your Business Operate Smarter?
Lean methodology is a business approach focused on maximising value while minimising waste. It helps organisations operate more efficiently by improving processes, cutting out non-essential steps, and delivering better results with fewer resources. Originally developed for manufacturing, Lean principles are now widely used across various industries to improve performance and customer satisfaction.

1. Focusing on Customer Value
At the heart of Lean methodology is the idea of providing more value to the customer. This means understanding what the customer truly needs and tailoring processes to meet those needs without unnecessary extras. By focusing on what matters most, businesses can streamline their efforts and deliver better outcomes.
2. Identifying and Reducing Waste
Lean helps businesses identify different types of waste—such as time delays, overproduction, or excess inventory—that add no value. Once identified, these wastes are systematically removed from the process. The result is a faster, smoother, and more cost-effective workflow that benefits both the business and the customer.
3. Encouraging Continuous Improvement
Another key principle of Lean is continuous improvement. Teams are encouraged to regularly review their processes, spot issues, and suggest changes. This ongoing effort to improve helps businesses stay agile, respond quickly to changes, and keep operations running smoothly over time.
In summary, Lean methodology supports smarter business operations by focusing on value, cutting waste, and fostering a culture of improvement. When implemented effectively, it leads to higher efficiency, better customer service, and stronger overall performance.
The 5 Core Principles of Lean and Why They Matter
Lean methodology is built on five core principles that guide organisations in creating more value while using fewer resources. These principles help improve efficiency, reduce waste, and focus on what truly matters to the customer. Understanding and applying these principles can lead to smarter operations and long-term success.
1. Define Value
The first principle is to clearly define what value means from the customer's point of view. This helps organisations focus only on what adds real value and avoid spending time and effort on activities that don’t meet customer needs.
2. Map the Value Stream
This step involves looking at the entire process and identifying every action that contributes to delivering the product or service. By mapping the value stream, businesses can spot areas of waste and highlight opportunities for improvement.
3. Create Flow
Once waste has been removed, the next step is to ensure that work flows smoothly from start to finish without delays or interruptions. A steady flow allows products or services to move quickly through the process, improving lead times and reducing bottlenecks.
4. Establish Pull
In Lean, work is driven by demand rather than forecasts. This means that production or service delivery begins only when there is a clear need, helping to avoid overproduction and reduce inventory costs.
5. Seek Perfection
The final principle encourages continuous improvement. Organisations should always look for ways to improve processes, reduce waste, and deliver greater value. This creates a culture focused on long-term growth and quality.
By following these five principles, businesses can build stronger processes that are efficient, customer-focused, and adaptable to change.
Understanding the 8 Wastes in Lean and How to Eliminate Them
In Lean methodology, the concept of waste refers to any activity that does not add value to the customer. By identifying and removing waste, organisations can improve efficiency, reduce costs, and deliver better results. There are eight common types of waste in Lean, and understanding them is key to improving business processes.
1. Overproduction
Making more than what is needed or before it is needed can lead to excess inventory, storage costs, and wasted effort. To eliminate this, produce only what is required, when it is required.
2. Waiting
Delays between steps in a process slow down production and waste valuable time. Streamline workflows to reduce downtime and ensure tasks move forward without unnecessary pauses.
3. Transport
Unnecessary movement of materials or products can cause delays and increase the risk of damage. Layout improvements and better planning can help reduce transport waste.
4. Extra Processing
Doing more work than necessary, such as using more materials or performing unneeded steps, adds no value. Review processes to ensure each step is essential and efficient.
5. Inventory
Excess inventory ties up resources and space. Keep inventory levels in check and use a pull-based system to align stock with demand.
6. Motion
Unnecessary movement by people, such as reaching, walking, or bending, can be tiring and inefficient. Organise workspaces to minimise these actions.
7. Defects
Errors lead to rework and wasted materials. Focus on quality at every stage to reduce mistakes and maintain high standards.
8. Underutilised Skills
Not using employees’ full potential means missing out on ideas and talents. Encourage involvement and use people’s skills wisely.
By spotting and removing these eight wastes, organisations can work smarter, reduce costs, and deliver greater value to their customers.

How Lean Methodology Improves Process Efficiency and Flow
Lean methodology is a powerful approach that helps businesses improve process efficiency and create a smooth, uninterrupted flow of work. By focusing on value and reducing waste, Lean ensures that every step in a process contributes meaningfully to the final result. This leads to faster delivery, better quality, and lower costs.
1. Removing Waste for Streamlined Processes
One of the key ways Lean improves efficiency is by identifying and eliminating waste. This includes time delays, unnecessary steps, extra movement, or overproduction. By cutting out these non-value-adding activities, businesses can shorten lead times and use resources more effectively. The result is a cleaner, simpler process that delivers better outcomes with less effort.
2. Creating Smooth Workflows
Lean also focuses on creating continuous flow. This means designing processes so that work moves steadily from one step to the next without delays or interruptions. A smooth workflow reduces waiting time, keeps tasks moving forward, and prevents backlogs. This not only boosts productivity but also makes it easier to meet deadlines and maintain quality.
3. Standardising and Improving
Lean encourages standardising best practices so that everyone works consistently and efficiently. Once a process is stable, teams can look for small, ongoing improvements. This commitment to continuous improvement helps ensure long-term success and adaptability.
In summary, Lean methodology improves process efficiency and flow by cutting waste, simplifying steps, and promoting steady progress. These improvements support better performance, stronger teamwork, and more satisfied customers.
Lean vs Traditional Management: What’s the Real Difference?
Lean management and traditional management approaches offer different philosophies when it comes to improving business operations. While both aim for efficiency and productivity, their methods and mindsets differ significantly. Understanding the key differences can help businesses choose the approach that best fits their goals and culture.
1. Focus on Value vs. Efficiency
One of the primary differences between Lean and traditional management is their focus. Lean management centres around delivering maximum value to the customer by eliminating waste at every stage of the process. It promotes a customer-centric approach where every action is measured by its ability to add value. Traditional management, on the other hand, typically focuses more on efficiency through process standardisation, often at the expense of flexibility and continuous improvement.
2. Flexibility vs. Rigidity
Lean management encourages flexibility, adaptability, and ongoing improvement. It values the input of all employees, fostering a culture where continuous feedback is used to improve processes. Traditional management tends to be more rigid, relying on fixed procedures and top-down decision-making, which can limit innovation and responsiveness to changes in the market.
3. Empowerment vs. Control
Lean management empowers employees by involving them in problem-solving and decision-making. It promotes teamwork and trust, with the belief that those closest to the work are best positioned to improve processes. Traditional management, however, often relies on centralised control, where decisions are made at higher levels and employees are expected to follow instructions.
In conclusion, Lean management is about delivering value, flexibility, and continuous improvement, while traditional management often focuses on efficiency and control. By understanding these key differences, organisations can adopt the approach that best aligns with their strategic goals.
Real-World Benefits of Applying Lean Thinking in the Workplace
Lean thinking has become a transformative approach for businesses looking to optimise their operations, reduce waste, and increase overall efficiency. By focusing on value and eliminating non-value-adding activities, organisations can achieve significant improvements in productivity, customer satisfaction, and cost-effectiveness. Here are some of the real-world benefits of applying Lean thinking in the workplace.
1. Increased Efficiency and Productivity
One of the most immediate benefits of Lean thinking is the significant improvement in efficiency. By streamlining processes and removing unnecessary steps, businesses can accomplish more with fewer resources. This leads to faster production times, quicker response times, and improved service delivery, all contributing to enhanced productivity across the organisation.
2. Cost Savings
Lean thinking helps businesses identify and reduce waste, which in turn leads to cost savings. From minimising excess inventory to eliminating redundant processes, Lean encourages smarter use of resources. By cutting out wasteful activities, companies can lower operational costs, increase profit margins, and reinvest savings into growth or innovation.
3. Enhanced Quality and Customer Satisfaction
Focusing on continuous improvement and reducing defects ensures higher quality products and services. With Lean thinking, businesses can reduce errors and enhance the customer experience. By meeting customer needs faster and with greater accuracy, businesses can build stronger customer relationships and improve retention rates.
In summary, applying Lean thinking in the workplace brings tangible benefits such as improved efficiency, cost savings, and enhanced customer satisfaction. These advantages help businesses remain competitive, adapt to market changes, and maintain long-term success.
How to Identify and Remove Non-Value-Adding Activities
In any organisation, identifying and removing non-value-adding activities is crucial for improving efficiency and maximising productivity. These activities consume resources without contributing to the final product or service. By eliminating them, businesses can streamline processes, reduce costs, and focus on what truly matters to customers. Here’s how to identify and remove these activities effectively.
1. Map Out Your Processes
The first step in identifying non-value-adding activities is to map out your current processes. Visualising each step helps you see the entire workflow and pinpoint areas where waste occurs. You can create process flow diagrams or use value stream mapping to capture every activity involved in delivering your product or service.
2. Categorise Each Activity
Once you have a clear map of your processes, categorise each activity based on whether it adds value or not. Value-adding activities directly contribute to meeting customer needs, while non-value-adding activities are tasks that don’t enhance the product or service. Common examples of non-value-adding activities include excessive paperwork, waiting times, and redundant approvals.
3. Eliminate Wasteful Activities
After identifying the non-value-adding activities, the next step is to eliminate or streamline them. This may involve automating tasks, reorganising workflows, or removing unnecessary steps. Encourage continuous improvement by empowering your team to suggest further optimisations.
In conclusion, by mapping out processes, categorising activities, and removing waste, businesses can significantly improve their efficiency and provide better value to their customers.
The Role of Continuous Improvement (Kaizen) in Lean Methodology
Continuous improvement, or Kaizen, is a fundamental concept in Lean methodology that drives organisations to constantly strive for better efficiency, quality, and value. The idea behind Kaizen is simple: make small, incremental changes over time that lead to significant improvements in processes, products, and services. This approach not only enhances operational performance but also creates a culture of teamwork and innovation.
1. Encouraging Small, Consistent Changes
Kaizen encourages organisations to focus on making small, manageable changes rather than large-scale overhauls. These incremental improvements can be applied to any part of the organisation, from production lines to administrative processes. Over time, these small changes accumulate, leading to significant advancements in efficiency, cost reduction, and quality.
2. Empowering Employees to Contribute
One of the key principles of Kaizen is that everyone, from top management to frontline employees, has a role in improving the business. Employees are encouraged to identify inefficiencies, suggest improvements, and take ownership of making changes in their work areas. This inclusive approach fosters a sense of ownership and commitment, leading to higher morale and a more motivated workforce.
3. Building a Culture of Continuous Improvement
Incorporating Kaizen into Lean methodology is not just about applying improvement techniques; it’s about creating a mindset that values ongoing optimisation. This culture of continuous improvement ensures that organisations are always looking for ways to refine their processes and stay competitive in the marketplace.
In summary, Kaizen plays a crucial role in Lean methodology by driving constant, small improvements that add up over time. This commitment to continuous improvement leads to higher efficiency, better quality, and a more engaged workforce.
Lean Tools Explained: Value Stream Mapping, 5S, Kanban & More
Lean methodology is built around several powerful tools that help businesses streamline operations, reduce waste, and improve efficiency. Among these tools are Value Stream Mapping, 5S, Kanban, and others, each designed to tackle specific aspects of the workflow. Let’s explore how these tools work and how they can help enhance business processes.
1. Value Stream Mapping (VSM)
Value Stream Mapping is a visual tool used to analyse and design the flow of materials and information required to bring a product or service to the customer. It helps identify value-adding and non-value-adding activities, allowing businesses to eliminate waste and improve efficiency. VSM highlights bottlenecks and delays in the process, helping teams focus on areas for improvement.
2. 5S System
The 5S system is a workplace organisation method that focuses on sorting, setting in order, shining, standardising, and sustaining. This tool helps create a clean, organised, and efficient work environment, reducing waste and improving productivity. By following the 5S principles, businesses can ensure that everything is in its place, making it easier for employees to do their work effectively.
3. Kanban
Kanban is a visual scheduling system used to manage work and inventory. It helps regulate the flow of materials, ensuring that tasks are completed just in time and that inventory levels are kept to a minimum. By using Kanban boards or cards, teams can visually track work in progress and make adjustments when needed, promoting efficiency and preventing overproduction.
In summary, Lean tools like Value Stream Mapping, 5S, and Kanban are essential for improving workflow, reducing waste, and creating a more efficient and productive workplace. When used together, these tools form the foundation of a Lean organisation.
Creating a Lean Culture: Engaging Teams in Waste Reduction
Building a Lean culture within an organisation is essential for achieving long-term success and operational efficiency. By involving teams in waste reduction and process optimisation, businesses can create a culture of continuous improvement. Here’s how to engage your team in Lean practices and foster a waste-reducing environment.
1. Foster Awareness of Waste
The first step in creating a Lean culture is to make employees aware of the different types of waste that can occur within processes. This includes overproduction, waiting time, unnecessary movement, excess inventory, defects, overprocessing, and unused talent. By educating your team on these wastes, you empower them to identify and address inefficiencies in their daily work.
2. Encourage Team Involvement
Engage your team by involving them in identifying areas where waste can be reduced. Hold regular meetings or workshops where employees can discuss potential improvements and suggest solutions. When team members are actively involved in problem-solving, they are more likely to embrace Lean practices and contribute to process improvements.
3. Empower with Lean Tools
Equip your team with the right Lean tools, such as Value Stream Mapping, 5S, or Kanban, to identify and eliminate waste in their workflows. Provide training and encourage employees to use these tools to find areas for improvement. Empowering your team with the right tools builds confidence and enables them to take ownership of the improvement process.
In conclusion, creating a Lean culture involves raising awareness, engaging teams, and providing the tools to eliminate waste. By fostering a continuous improvement mindset, your organisation can achieve greater efficiency, better quality, and improved customer satisfaction.
How to Start a Lean Transformation in Your Organisation
Starting a Lean transformation in your organisation requires careful planning, commitment, and a clear strategy to eliminate waste and improve processes. Lean principles focus on maximising value for customers while minimising resources and effort. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to begin your Lean transformation journey.
1. Define Your Vision and Objectives
Before implementing Lean, it's important to have a clear vision of what you want to achieve. Identify the key areas where Lean can make a difference, such as improving efficiency, reducing waste, or enhancing customer satisfaction. Set measurable objectives that align with your organisation’s overall goals to ensure a successful transformation.
2. Educate and Involve Employees
For Lean transformation to be successful, it must involve all levels of the organisation. Begin by educating employees on Lean principles, such as eliminating waste, continuous improvement, and creating value. Encourage a culture where everyone feels empowered to contribute ideas and improvements. This collective involvement will help drive change from within.
3. Start with Pilot Projects
Rather than implementing Lean across the entire organisation all at once, start with pilot projects. Focus on a specific department or process that could benefit from Lean tools and methods. By testing Lean in smaller areas, you can refine your approach and build momentum before expanding it throughout the organisation.
In summary, starting a Lean transformation involves defining clear objectives, educating employees, and testing the process with pilot projects. As you progress, continuously assess the results and make improvements to embed Lean practices throughout your organisation for long-term success.
Lean for Service-Based Businesses: Not Just for Manufacturing
While Lean methodology is often associated with manufacturing, its principles can be effectively applied to service-based businesses as well. By focusing on reducing waste and improving efficiency, service-based organisations can enhance customer satisfaction, reduce costs, and boost operational performance. Here’s how Lean can benefit service industries such as healthcare, finance, and customer support.
1. Eliminating Non-Value-Adding Activities
In service-based businesses, there are many processes that do not directly add value to the customer experience. Lean encourages the identification and elimination of these non-value-adding activities, such as unnecessary paperwork, long waiting times, and redundant steps in service delivery. By streamlining processes, businesses can reduce costs and improve service speed.
2. Improving Customer Experience
Lean focuses on creating value for the customer. By reducing waste and improving efficiency, service-based businesses can deliver faster, more reliable, and higher-quality services. For example, streamlining the process for handling customer queries or simplifying booking systems can lead to improved satisfaction and loyalty.
3. Continuous Improvement with Kaizen
Kaizen, the principle of continuous improvement, is a key aspect of Lean. In service-based businesses, this means constantly evaluating and improving processes to ensure they meet customer needs. Regularly seeking employee feedback, implementing small improvements, and encouraging a culture of innovation are all ways to integrate Kaizen into your service operations.
In summary, Lean is not just for manufacturing; service-based businesses can also benefit from its principles. By eliminating waste, improving processes, and focusing on continuous improvement, service organisations can achieve greater efficiency and enhance customer satisfaction.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Implementing Lean Principles
Implementing Lean principles can bring significant improvements to your organisation, but it's important to approach the process with care. Many businesses make common mistakes during Lean implementation that can hinder success. Here’s a look at some of these pitfalls and how to avoid them.
1. Failing to Involve Employees
One of the most common mistakes in Lean implementation is not involving employees at all levels. Lean is a team-based approach, and without buy-in from everyone, it’s hard to create a culture of continuous improvement. Ensure that employees are educated about Lean principles and are given the opportunity to contribute ideas and solutions.
2. Focusing Only on Short-Term Results
Lean is a long-term strategy, and expecting immediate results can lead to disappointment. Many organisations focus on quick wins but fail to maintain Lean practices over time. Successful Lean transformation requires a sustained commitment to continuous improvement and long-term planning.
3. Ignoring the Bigger Picture
Sometimes, businesses focus on eliminating waste in one area but ignore the bigger picture. Lean should be implemented across all processes, not just isolated parts of the organisation. A holistic approach ensures that improvements in one area don’t create new problems elsewhere.
In conclusion, avoid these common mistakes by involving your team, focusing on long-term success, and taking a holistic approach to Lean. With the right strategy, Lean principles can transform your organisation and drive lasting improvements.
How Lean Supports Agile, Six Sigma, and Other Improvement Methods
Lean methodology, with its focus on reducing waste and improving efficiency, is often used in conjunction with other improvement methods like Agile and Six Sigma. These methodologies complement each other and, when combined, can lead to even greater operational success. Here’s how Lean supports and enhances these popular methods.
1. Lean and Agile
Lean and Agile both prioritise customer value, flexibility, and efficiency. While Lean focuses on eliminating waste, Agile emphasises adaptive planning and delivering incremental value. Lean supports Agile by streamlining processes, eliminating delays, and ensuring that teams can focus on delivering value quickly. Together, they help organisations become more responsive to customer needs and market changes.
2. Lean and Six Sigma
Six Sigma aims to reduce defects and variation in processes to improve quality. Lean complements Six Sigma by eliminating non-value-adding activities, which often contribute to inefficiency and defects. By combining Lean’s waste-reduction techniques with Six Sigma’s focus on quality and process improvement, organisations can achieve both efficiency and high-quality results.
3. Lean and Other Improvement Methods
Lean can also be integrated with other methodologies like Total Quality Management (TQM) and the Theory of Constraints (TOC). The shared focus on improving processes, increasing efficiency, and reducing waste allows Lean to support various improvement methods. By using Lean in tandem with these approaches, organisations can create a more comprehensive strategy for continuous improvement.
In conclusion, Lean supports and enhances other improvement methods like Agile and Six Sigma by streamlining processes, eliminating waste, and ensuring more efficient operations. Combining these methods can help organisations achieve greater success and drive sustainable growth.
Success Stories: How UK Businesses Increased Efficiency with Lean
Lean methodology has proven to be a game-changer for many UK businesses, helping them streamline operations, reduce waste, and improve efficiency. Here are a few success stories of how Lean transformed operations and drove significant improvements across various sectors.
1. Manufacturing: Streamlining Production Processes
A well-established UK manufacturing company was struggling with inefficiencies in its production line, leading to delays and excess inventory. After adopting Lean principles, the company implemented techniques such as Value Stream Mapping and 5S to identify waste and improve workflows. As a result, production time was reduced, inventory costs dropped, and product quality improved, leading to increased customer satisfaction and higher profits.
2. Healthcare: Reducing Patient Waiting Times
A UK-based healthcare provider faced long patient waiting times and inefficiencies in its processes. By applying Lean tools like Kaizen and Kanban, the hospital streamlined its patient flow, improved resource allocation, and reduced delays. This transformation led to shorter waiting times for patients and better utilisation of staff and equipment, ultimately enhancing patient care and operational efficiency.
3. Retail: Improving Stock Management
A retail chain in the UK implemented Lean to address issues with stock management and inventory turnover. Using Lean tools, the business was able to eliminate excess stock, reduce out-of-stock incidents, and optimise its supply chain. As a result, the company experienced smoother operations, reduced costs, and improved customer satisfaction.
These success stories demonstrate that Lean can benefit businesses in various sectors, from manufacturing to healthcare and retail. By focusing on continuous improvement, organisations can boost efficiency, reduce waste, and enhance customer value.