Kanban is a popular task management system that originated from the Toyota Production System (TPS) in the 1940s. Initially used in manufacturing for just-in-time production, it has since been adapted for various industries, including software development, project management, and personal task organisation. Kanban emphasises visualising workflow, limiting work in progress (WIP), and continuous improvement.
Details of Kanban task management:
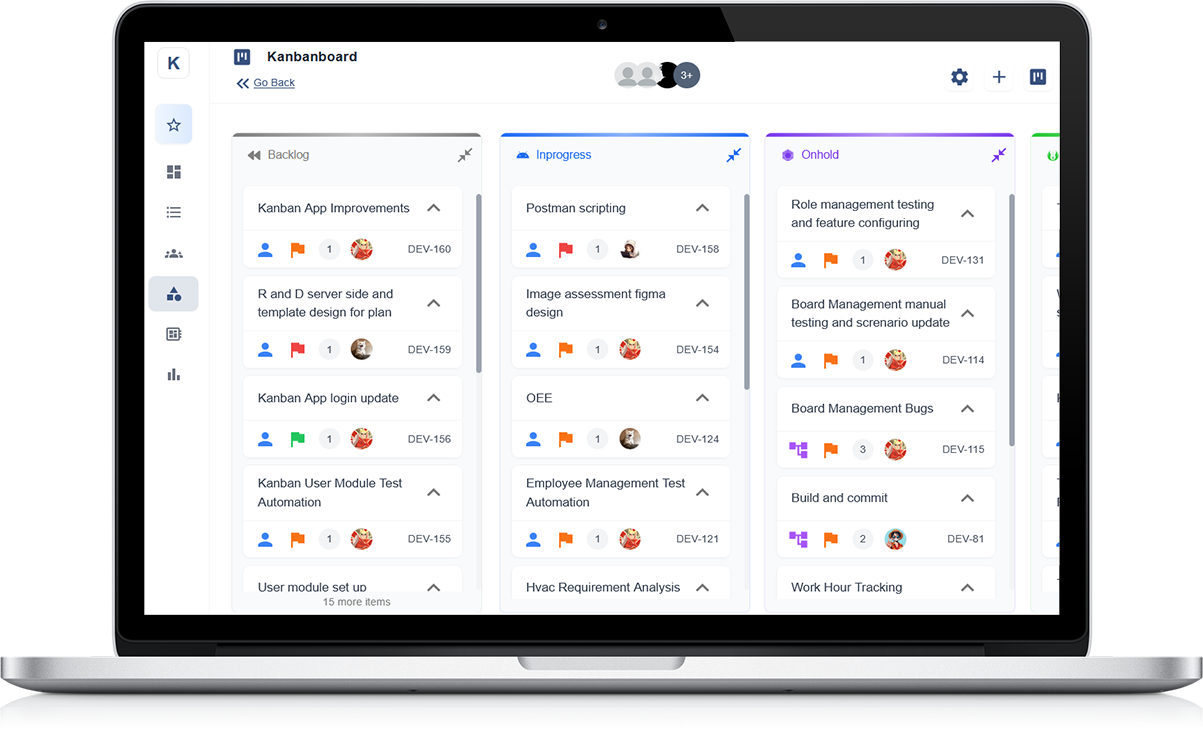
Visual Board: At the core of Kanban is a visual board divided into columns representing different stages of the workflow. Common columns include "To Do," "In Progress," and "Done." Each column contains cards representing tasks or work items.
Work Items (Cards): These are the individual tasks or units of work. They can be physical cards on a physical board or digital cards in software tools. Each card typically includes details such as task description, assignee, due date, and any relevant attachments or links.
Workflow: The workflow represents the steps that a work item goes through from creation to completion. By visualising this process on the Kanban board, team members can easily see the status of each task and identify bottlenecks or areas for improvement.
Limiting Work in Progress (WIP): One of Kanban's key principles is limiting the number of tasks allowed in each column at any given time. This helps prevent overloading team members and ensures that work flows smoothly through the system. WIP limits encourage focus, reduce multitasking, and improve overall efficiency.
Pull System: Kanban operates on a pull system, where new work is pulled into the workflow only when there is capacity to handle it. This contrasts with push systems, where work is pushed onto team members regardless of their capacity. The pull system helps maintain a steady workflow and prevents work from piling up.
Continuous Improvement: Kanban encourages teams to continuously evaluate and improve their processes. By regularly reviewing metrics such as lead time, cycle time, and throughput, teams can identify areas for optimisation and make incremental changes to their workflow.
Visualisation: The visual nature of the Kanban board makes it easy for team members to understand the status of work at a glance. This transparency promotes collaboration, alignment, and accountability within the team.

Continuous Improvement:Kanban is highly flexible and can be adapted to suit the specific needs and preferences of different teams. Whether it's customising column names, adding swimlanes for different types of work, or integrating with other tools and systems, Kanban can be tailored to fit virtually any workflow.
Metrics and Analytics: Kanban provides valuable metrics and analytics that enable teams to track performance and identify areas for improvement.
Analytics and Reporting: Software provides tools for data analysis, generating reports on key performance indicators, patient outcomes, resource utilisation, and financial metrics to support decision-making and compliance with regulatory requirements.
Kanban is a powerful task management system that emphasises visualising workflow, limiting work in progress, and continuously improving processes. By implementing Kanban, teams can increase efficiency, transparency, and collaboration, ultimately delivering higher-quality work in less time.
What Is Kanban Task Management and Why Does It Work?
Kanban task management is a visual approach to organising work, designed to help teams manage tasks more efficiently and transparently. The method uses a board divided into columns that represent different stages of a workflow, such as “To Do”, “In Progress”, and “Done”. Tasks are represented as cards that move through these stages from left to right.

Clear Visual Structure
The strength of Kanban lies in its visual clarity. At a glance, anyone can see the status of tasks, identify bottlenecks, and understand team priorities. This transparency helps improve communication and collaboration among team members, as everyone can stay aligned on progress and expectations.
Improved Workflow Control
Kanban encourages continuous flow and limits the number of tasks in progress at any one time. This focus on “work in progress” (WIP) limits ensures that teams do not overload themselves and can concentrate on completing tasks before starting new ones. This leads to better quality, fewer errors, and faster delivery times.
Flexibility and Simplicity
One of the main reasons Kanban works well for many organisations is its simplicity and adaptability. It can be used in any industry and scaled to suit teams of any size. Whether managing daily tasks or full-scale projects, Kanban makes it easier to prioritise, manage workloads, and make continuous improvements.
In summary, Kanban task management works because it makes tasks visible, keeps teams focused, and promotes a smooth, balanced workflow. It’s a practical solution for teams looking to work smarter and more effectively.
How to Set Up a Kanban Board for Your Team’s Daily Tasks
A Kanban board is a simple and effective tool for managing daily tasks. It helps teams stay organised, improves task visibility, and supports steady progress. Setting up a Kanban board for daily use is easy and highly flexible, making it ideal for any team or department.
Step 1: Define the Workflow Stages
Start by deciding the key stages your tasks go through each day. A common setup includes three basic columns: “To Do”, “In Progress”, and “Done”. You can add more columns if needed, such as “Waiting” or “Review”, to match your team’s actual workflow.
Step 2: Choose a Format
You can create your board physically using a whiteboard and sticky notes, or go digital with an online tool. The format should suit your team’s working style and allow easy updates. Make sure it’s accessible to everyone who needs to use it.
Step 3: Create Task Cards
Each task should be written on a card and placed in the appropriate column. Include clear task names, deadlines, and assigned team members. Cards can also include notes or tags to indicate priority or task type.
Step 4: Use Daily Updates
Hold a short daily meeting where team members update the board by moving tasks to the right stage. This keeps everyone informed, highlights blockers early, and supports better collaboration throughout the day.
By setting up a clear, easy-to-use Kanban board, your team can focus better, work more efficiently, and keep daily goals on track.
From To-Do to Done: Visualising Workflow with Kanban Columns
Kanban columns are a simple yet powerful way to visualise the progress of tasks from start to finish. They give a clear picture of how work flows through each stage, helping teams stay organised, avoid delays, and improve productivity. With just a few columns, you can turn a long task list into a structured and manageable workflow.
Start with the Basics
The most common Kanban board uses three main columns: “To Do”, “In Progress”, and “Done”. Each column represents a different stage of the workflow. Tasks are added to the “To Do” column when they are ready to be started, moved to “In Progress” when work begins, and placed in “Done” once completed.
Customise to Fit Your Team
While the basic setup works for many teams, you can add extra columns to better reflect your process. For example, you might add “Waiting for Review” or “On Hold” to show tasks that need input from others. The key is to keep the board simple and clear so everyone understands the flow.
Keep Work Moving
By using Kanban columns, your team can easily spot where tasks are getting stuck and take action. This helps prevent bottlenecks and keeps work moving smoothly from one stage to the next. Visualising your workflow makes it easier to plan, prioritise, and communicate.
In short, Kanban columns turn task management into a visual process that supports focus, teamwork, and steady progress from “To Do” to “Done”.

Boosting Team Accountability with Transparent Task Tracking
Transparent task tracking plays a vital role in building team accountability. When everyone can see what needs to be done, who is doing it, and what progress has been made, it creates a clear sense of ownership. Teams work better when expectations are visible and shared across the group.
Visibility Builds Responsibility
By using a visual task tracker, such as a board or digital tool, each task is linked to a team member. This visibility encourages individuals to take responsibility for their work, as everyone can see their assigned tasks and progress. It also reduces confusion and avoids duplication of effort.
Improves Communication and Clarity
Transparent tracking supports open communication within the team. It’s easier to see when someone is overloaded or stuck, making it simple to offer support or adjust priorities. This improves teamwork and ensures everyone is working towards the same goal.
Tracks Progress in Real Time
With regular updates, a task tracker provides a real-time view of what’s moving forward and what’s falling behind. This helps managers and team leads address issues early, keeping the project on track and meeting deadlines more reliably.
Overall, transparent task tracking creates a more accountable and collaborative working environment. It builds trust, encourages responsibility, and leads to better results by keeping everyone aligned and aware of their role in the team’s success.
The Power of Visual Cues: How Kanban Improves Focus and Flow
Kanban is a simple yet powerful method that uses visual cues to improve task management, focus, and workflow. By displaying tasks clearly on a board, it helps teams and individuals stay organised and productive without feeling overwhelmed. It works by making work visible and easy to follow.
Visual Organisation Boosts Clarity
Kanban boards use cards and columns to show tasks and their progress. This visual layout makes it easier to see what needs doing, what’s in progress, and what’s already done. By having a clear view of the workload, team members can focus on the most important tasks without distraction.
Reduces Overload and Improves Flow
With Kanban, teams can set limits on how many tasks are allowed in each stage of work. These limits prevent people from taking on too much at once, which keeps the workflow steady. This leads to fewer delays and smoother handovers between tasks or team members.
Supports Quick Decisions and Action
Visual cues on a Kanban board allow for quicker understanding and action. For example, if a task is stuck too long in one column, it’s easy to spot and resolve. This helps teams act quickly, solve problems, and keep work moving efficiently.
In summary, Kanban uses the power of visual cues to bring structure, reduce clutter, and keep teams focused. It’s a flexible system that helps improve the flow of work and keeps everyone on the same page.
Customising Your Kanban Board for Agile Project Management
Kanban is a versatile tool for agile project management, and customising your Kanban board can help enhance productivity and streamline processes. By adjusting the board to match your team’s specific needs, you can improve workflow, reduce bottlenecks, and ensure tasks are handled efficiently.
Tailor Columns to Your Workflow
Customising the columns on your Kanban board is a great first step. While many boards use basic columns like "To Do," "In Progress," and "Done," you can adjust these stages to reflect your team's unique workflow. For example, you might include "Waiting for Review" or "Blocked" columns if your team needs to track approval stages or identify obstacles more clearly.
Set WIP Limits for Better Focus
Work-in-progress (WIP) limits are a key feature in Kanban. By setting a maximum number of tasks that can be in a column at any given time, you ensure that your team doesn’t get overloaded. This also helps maintain focus on finishing tasks before starting new ones, which keeps the workflow steady and prevents backlogs.
Colour-Coding for Prioritisation
Colour-coding tasks can add another layer of customisation to your board. Assign different colours to tasks based on priority or department, so team members can easily identify what requires immediate attention. This simple visual aid makes it easier to spot urgent tasks at a glance and helps teams stay on track.
In conclusion, customising your Kanban board for agile project management allows you to tailor the system to fit your team's needs, enhance focus, and improve overall efficiency. By adjusting columns, setting WIP limits, and using colour-coding, your Kanban board becomes a powerful tool for successful project management.
Digital vs Physical Kanban Boards: Which One Is Right for You?
Kanban boards are an essential tool for managing tasks and improving workflow. Both digital and physical Kanban boards offer distinct advantages, but choosing the right one for your team depends on your needs, preferences, and work environment.
Advantages of Physical Kanban Boards
Physical Kanban boards are simple to set up and ideal for teams that work in the same location. These boards are often displayed on a large whiteboard or wall, allowing team members to interact directly with the board. They provide a tangible way to visualise work and track progress. Physical boards are particularly effective for teams that need to have quick, in-person discussions and enjoy hands-on task management.
Benefits of Digital Kanban Boards
Digital Kanban boards, on the other hand, offer the flexibility to work from anywhere, making them perfect for remote or distributed teams. They can be accessed in real-time, enabling faster updates and collaboration. Digital boards also allow for more customisation, such as adding deadlines, labels, and attachments. Many platforms also integrate with other tools, making it easier to streamline workflows across various applications.
Which One Should You Choose?
If your team works in the same office and prefers a hands-on approach, a physical Kanban board may be the best option. However, if your team is remote or requires more flexibility and collaboration features, a digital board could provide the ideal solution. Ultimately, the right choice depends on your team's workflow, communication style, and organisational needs.
How to Limit Work in Progress (WIP) and Avoid Bottlenecks
Managing work in progress (WIP) is essential for optimising productivity and avoiding bottlenecks in any workflow. By limiting WIP, teams can improve focus, maintain steady progress, and prevent delays, ensuring that tasks are completed efficiently and on time.
Set Clear WIP Limits for Each Stage
One of the most effective ways to limit WIP is by setting clear limits for each stage of your process. This means deciding how many tasks can be in each column or category at any given time. For example, in a Kanban board, you could set a limit of three tasks in the "In Progress" column. This encourages teams to complete tasks before taking on new ones, reducing the risk of overburdening any part of the process.
Prioritise Tasks Based on Importance
Prioritising tasks ensures that your team focuses on the most critical tasks first, preventing bottlenecks. Use clear labelling or colour coding to indicate priority, helping team members quickly identify what needs to be addressed immediately and what can wait. Prioritisation helps manage the flow of work, ensuring high-priority tasks are not delayed.
Encourage Continuous Communication and Collaboration
Regular communication between team members is vital for tracking progress and identifying potential bottlenecks early. By maintaining open channels of communication, teams can resolve issues quickly and ensure tasks move smoothly from one stage to the next. Collaboration helps keep everyone aligned, reducing delays and improving overall efficiency.
By setting WIP limits, prioritising tasks, and encouraging communication, you can effectively manage work in progress and avoid bottlenecks, leading to a more streamlined and productive workflow.
Using Colour Codes and Labels to Prioritise Tasks Visually
Prioritising tasks visually is a simple yet powerful way to increase productivity and enhance workflow management. By using colour codes and labels, teams can quickly identify which tasks need immediate attention and which can be deferred, all at a glance. This method not only streamlines decision-making but also reduces the chances of overlooked tasks.
Colour Coding for Quick Identification
Colour coding is one of the most effective ways to prioritise tasks. Different colours can represent varying levels of urgency or importance. For example, red could signify high-priority tasks that require immediate action, while green could indicate tasks that are low priority or completed. By applying these colour codes to task cards or entries, team members can instantly identify where their focus is needed, without having to read through lengthy descriptions.
Using Labels for Clearer Task Categorisation
In addition to colours, labels can be used to categorise tasks by type or specific focus. For instance, labels such as "Urgent", "In Progress", or "Waiting on Feedback" help break down tasks even further. This allows for better organisation and clearer communication between team members. Labels also allow for easy filtering, so team members can focus on specific categories of tasks without distraction.
Benefits of Visual Task Prioritisation
Using colour codes and labels not only enhances visibility but also reduces cognitive load. Teams spend less time figuring out task priorities and can instead focus on executing them efficiently. This approach encourages accountability, helps manage workloads, and ensures deadlines are met.
Incorporating colour coding and labels into your task management system will significantly improve workflow clarity, reduce errors, and boost overall team productivity.
Tracking Performance and Progress with Kanban Metrics
Kanban is an excellent tool for visualising workflows, but to truly optimise performance, you need to track key metrics. Kanban metrics help teams monitor progress, identify bottlenecks, and improve overall efficiency. By focusing on specific metrics, you can gain valuable insights into how your workflow is functioning and where improvements can be made.
Key Kanban Metrics to Monitor
There are several metrics that provide insight into the efficiency of your Kanban system. One of the most important is lead time, which measures the total time it takes for a task to move from start to finish. Reducing lead time can greatly improve the speed of your workflow.
Cycle Time: How Long Does It Take to Complete a Task?
Another important metric is cycle time, which tracks how long it takes for a task to move through the process once work has started. Monitoring cycle time helps identify delays and areas where tasks may be stuck. By understanding cycle times, teams can optimise the flow of work and improve overall efficiency.
WIP (Work in Progress): Limiting Overload
Work in Progress (WIP) limits play a crucial role in Kanban systems. WIP limits ensure that no team member is overloaded with too many tasks, preventing bottlenecks and improving focus. By setting and adhering to WIP limits, teams can prevent task congestion and ensure work moves smoothly through the process.
By regularly reviewing these Kanban metrics, teams can pinpoint areas for improvement, increase productivity, and streamline workflows. Monitoring performance and progress with Kanban metrics ensures continuous improvement and allows teams to stay agile in responding to changing needs.
Kanban for Remote Teams: Staying Aligned Across Locations
As remote teams become increasingly common, maintaining alignment and productivity across locations can be challenging. Kanban, a visual workflow management system, provides an effective solution for ensuring that remote teams stay organised and focused. By adopting Kanban, teams can easily track progress, identify bottlenecks, and collaborate more effectively, no matter where they are located.
Visual Task Management for Remote Collaboration
Kanban’s visual nature makes it ideal for remote teams, as it allows everyone to see the status of tasks in real time. By using digital Kanban boards, team members can quickly understand what needs to be done, who is working on what, and where tasks are in the process. This visibility reduces the need for constant updates and helps prevent miscommunication.
Clear Workflow and Prioritisation
Kanban also helps remote teams prioritise tasks. By organising work into categories like "To Do," "In Progress," and "Completed," teams can ensure that tasks are completed in order of importance. Remote workers can update the board as they progress, ensuring that everyone is on the same page regarding project status and priorities.
Real-Time Collaboration and Flexibility
Kanban boards allow for seamless real-time collaboration. Team members can add comments, attach files, and make updates, making it easier for remote teams to work together without time zone constraints. With flexible features such as WIP (Work in Progress) limits and task labels, teams can customise the board to suit their needs and adapt to changing priorities.
Incorporating Kanban into your remote team’s workflow will help streamline communication, improve task management, and ensure consistent progress, no matter where team members are working from.
Case Study: How a UK Team Improved Productivity with Kanban
A leading UK-based team faced challenges with managing tasks efficiently, leading to delays and miscommunication. To address these issues, they adopted Kanban, a visual task management system that allowed them to track progress in real time. This case study explores how Kanban transformed their workflow and improved productivity.
Challenges Faced Before Implementing Kanban
Before implementing Kanban, the team struggled with disorganised task tracking, unclear priorities, and frequent delays. Work was often completed out of order, which created bottlenecks and inefficiencies. With multiple team members working on different tasks, tracking progress and ensuring alignment was a constant challenge.
Implementing Kanban for Visual Task Management
The team adopted a Kanban board to visualise their workflow. They created columns to represent various stages of their tasks, including “To Do,” “In Progress,” and “Completed.” This visual tool helped team members easily see what tasks needed attention, who was working on them, and where each task was in the process.
Results Achieved
Within just a few weeks, the team saw a significant improvement in productivity. Tasks were completed more quickly and in the correct order, reducing the frequency of bottlenecks. With clearer visibility into task progress, communication improved, and team members were more aligned with project goals. Additionally, the team was able to identify inefficiencies in their workflow and address them promptly.
By adopting Kanban, the team experienced a more streamlined and efficient approach to task management, leading to a boost in overall productivity and a smoother workflow.
How to Integrate Kanban with Lean and Continuous Improvement Tools
Kanban is a powerful visual tool for managing workflow and improving efficiency. When integrated with Lean principles and continuous improvement tools, it can significantly enhance productivity, reduce waste, and streamline processes. This integration ensures that tasks flow smoothly, bottlenecks are addressed, and teams are empowered to achieve their goals more effectively.
Aligning Kanban with Lean Principles
Lean methodology focuses on eliminating waste and optimising value by improving process flow. Kanban supports these principles by visualising the workflow, allowing teams to identify inefficiencies quickly. By setting Work in Progress (WIP) limits, Kanban helps teams focus on completing tasks before starting new ones, thereby reducing overproduction and unnecessary delays.
Using Kanban for Continuous Improvement
Continuous improvement, or Kaizen, is an essential part of Lean. By incorporating Kanban, teams can monitor and track their processes in real time, making it easier to identify areas for improvement. The visual nature of Kanban boards allows teams to spot trends and bottlenecks, leading to better decision-making and prioritisation of tasks that drive value.
Combining Kanban with Other Lean Tools
Kanban can be further enhanced by integrating it with other Lean tools, such as value stream mapping and 5S. Value stream mapping helps teams visualise the flow of materials and information, while 5S focuses on organising the workspace for maximum efficiency. Together, these tools enable teams to optimise workflows, reduce waste, and continuously improve their processes.
Integrating Kanban with Lean and continuous improvement tools fosters a culture of ongoing progress, helping teams deliver high-quality results more efficiently and effectively.
Getting Started with Kanban: Tips for First-Time Users
Kanban is a highly effective tool for managing tasks and improving workflow. It helps teams visually track their work, manage priorities, and identify bottlenecks. If you're new to Kanban, here are some essential tips to get started and make the most of this powerful system.
1. Set Up a Simple Kanban Board
The first step is to create a Kanban board, which can be physical (using sticky notes) or digital (using software). The board should have columns representing different stages of your workflow, such as “To Do,” “In Progress,” and “Completed.” This will allow you to easily track the progress of each task.
2. Define Your Workflow
Before you start adding tasks to your board, take the time to define your workflow. Break down your tasks into manageable stages and map them onto your Kanban board. Be sure to include clear definitions for each column so everyone on the team knows what stage each task is in.
3. Use Work-in-Progress (WIP) Limits
One of Kanban's key principles is setting Work-in-Progress (WIP) limits. These limits prevent team members from taking on too many tasks at once, helping to maintain focus and reduce the risk of bottlenecks. Start with modest WIP limits and adjust as you become more familiar with the system.
4. Regularly Review and Adjust
Kanban is all about continuous improvement. Regularly review your board and workflows to identify areas for optimisation. Hold brief meetings to discuss any bottlenecks and decide on improvements that can make the process more efficient.
By following these simple steps, you can successfully implement Kanban and start improving your task management from day one.