Lean Manufacturing is a production strategy designed to minimise waste and maximise efficiency. It seeks to create greater value for customers with fewer resources by streamlining processes, lowering costs, and removing inefficiencies. This approach prioritises continuous improvement, values the involvement of people, and promotes standardised work procedures.
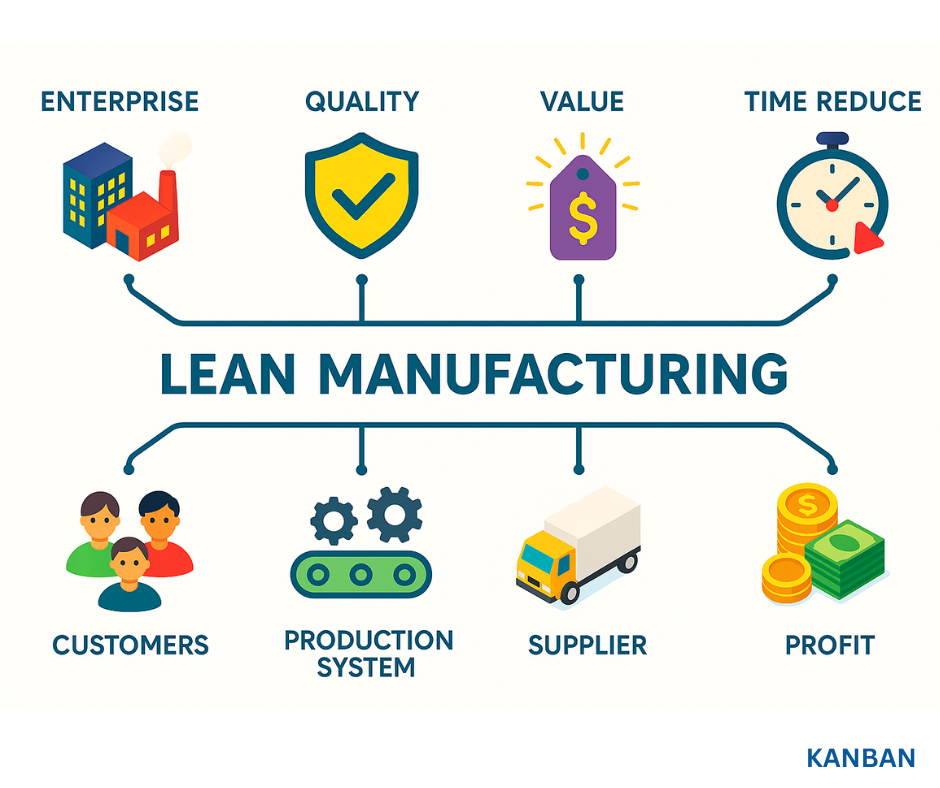
Key Principles of Lean Manufacturing:
Value: Understand what value means to the customer and focus on those activities that add value.
Value Stream: Identify the entire value stream for each product and eliminate waste.
Flow: Ensure that the production process flows smoothly without interruptions.
Pull: Produce only what is needed by the customer, in the amount needed, and when needed.
Perfection: Continuously strive for perfection by improving processes and eliminating waste.
Common Tools and Techniques:
5S: A workplace organisation method that includes Sort, Set in order, Shine, Standardise, and Sustain.
Kaizen: Continuous improvement through small, incremental changes.
Kanban: A scheduling system that helps manage workflow and inventory.
Value Stream Mapping: A visual tool to map out and analyse the flow of materials and information required to bring a product to the customer.
JIT (Just-In-Time): A strategy to increase efficiency by receiving goods only as they are needed in the production process.
Poka-Yoke: A mistake-proofing technique designed to prevent errors in the manufacturing process.
TPM (Total Productive Maintenance): A proactive approach to maintaining and improving production and quality systems through equipment, processes, and employees.
Benefits of Lean Manufacturing:
Reduced Waste: Lower levels of waste in production, leading to cost savings.
Improved Quality: Higher quality products due to continuous improvement and error reduction.
Increased Efficiency: More efficient use of resources and smoother production processes.
Greater Flexibility: Ability to respond more quickly to changes in customer demand.
Enhanced Employee Morale: Involvement in continuous improvement processes can lead to higher job satisfaction and morale.
Lean Manufacturing aims to create more value for customers with fewer resources, driving efficiency and quality in production processes.
What Are the Core Principles of Lean Manufacturing?
Lean manufacturing is a proven approach to improving efficiency, reducing waste, and delivering value to customers. It is built on a set of core principles that guide organisations in streamlining their processes and maximising productivity. Understanding these principles is essential for any business aiming to improve operations while maintaining high quality standards.

1. Define Value from the Customer’s View
The first principle focuses on understanding what the customer truly values. By identifying this, businesses can ensure that every activity contributes to delivering that value and remove anything that does not.
2. Map the Value Stream
This step involves analysing the full flow of materials and information required to bring a product or service to the customer. It helps identify areas of waste and opportunities for improvement in the process.
3. Create Continuous Flow
Processes should be designed to flow smoothly without delays or interruptions. A steady and predictable flow increases efficiency and reduces the time it takes to complete tasks or deliver products.
4. Establish Pull Systems
Instead of pushing work based on forecasts, Lean encourages pulling products or services based on real demand. This approach minimises overproduction and reduces excess inventory.
5. Pursue Perfection
Lean Manufacturing promotes a culture of ongoing improvement. By regularly reviewing and refining processes, teams aim to move closer to perfection—improving quality, reducing costs, and enhancing customer satisfaction.
These core principles form the foundation of Lean thinking and can lead to long-term success when applied consistently across all levels of an organisation.
How Lean Manufacturing Helps Reduce Waste Across Operations
Lean Manufacturing is a widely used method that focuses on eliminating waste and increasing value in every part of an organisation. By applying Lean principles, companies can identify and remove non-essential activities, leading to greater efficiency, reduced costs, and improved customer satisfaction.
Understanding Waste in Operations
Waste in Lean terms refers to anything that does not add value from the customer’s perspective. This includes excess inventory, overproduction, waiting times, unnecessary movements, defects, and more. These forms of waste slow down operations and use up valuable resources without delivering any benefit to the end user.
Identifying and Eliminating Waste
Lean manufacturing helps teams recognise where waste occurs through tools like value stream mapping. Once identified, these inefficiencies can be targeted for improvement. For example, standardising processes can reduce variation and errors, while organising workspaces can minimise time wasted searching for tools or materials.
Encouraging Continuous Improvement
A key part of Lean is the culture of ongoing improvement. Employees at all levels are encouraged to look for better ways to do their work, report problems, and suggest solutions. This collaborative approach makes it easier to address waste quickly and effectively.
Achieving Long-Term Efficiency
When applied consistently, Lean methods lead to streamlined processes, faster turnaround times, and more effective use of resources. The result is a more efficient operation that delivers higher quality with less effort and expense.
By reducing waste at every level, Lean Manufacturing helps businesses become more productive, agile, and competitive in any industry.
Lean vs Traditional Manufacturing: What’s the Real Difference?
Understanding the difference between Lean and traditional manufacturing is key for businesses looking to improve productivity and reduce waste. Both approaches aim to produce quality products, but their methods and focus vary greatly.
Traditional Manufacturing Explained
In traditional manufacturing, the focus is often on mass production. The goal is to produce large quantities of products to keep unit costs low. This system relies heavily on keeping machines running and stockpiling inventory to meet future demand. While this can lead to economies of scale, it often results in overproduction, long lead times, and higher storage costs.
The Lean Manufacturing Approach
Lean manufacturing takes a different path. It focuses on producing only what is needed, when it is needed, and in the amount needed. It aims to streamline processes, cut waste, and continuously improve operations. This results in quicker turnaround times, lower inventory costs, and better use of resources.
Focus on Value and Flow
One of the key differences is that Lean puts the customer at the centre. Everything is geared towards creating value for the end user. Traditional systems may overlook this by focusing more on internal output targets rather than customer needs.
While traditional manufacturing can still work in certain industries, Lean offers a more flexible and efficient approach. By focusing on flow, value, and waste reduction, Lean Manufacturing helps companies stay competitive in today’s fast-changing markets.
The Five Lean Principles Explained with Everyday Examples
The five Lean principles are simple yet powerful guidelines that help businesses improve efficiency and deliver greater value. These principles can be applied across all industries and even in daily life. Let’s break them down with everyday examples to make them easy to understand.
1. Define Value
Value is what the customer truly needs and is willing to pay for. In a café, for example, a hot, fresh cup of coffee served quickly is the value a customer expects. Anything that does not contribute to this experience, like long waiting times, is not value.
2. Map the Value Stream
This step involves looking at every action or step in a process to see which ones add value. In an office, this could mean reviewing the steps involved in approving a document. If there are extra approvals that add no value, they can be removed.
3. Create Flow
Flow means ensuring that work moves smoothly without interruptions. Imagine preparing dinner – if all the ingredients are ready and within reach, the cooking process becomes much faster and easier.
4. Establish Pull
Instead of pushing products or services onto people, pull systems produce only when there is a demand. A bakery, for example, might bake more bread only when the shelves start to empty, avoiding waste.
5. Seek Perfection
Continuous improvement is key. Even small changes, like rearranging tools to be closer at hand, can lead to better performance over time. The goal is to keep improving step by step.
How to Start Your Lean Manufacturing Journey
Starting a Lean manufacturing journey can significantly enhance your company's efficiency, reduce waste, and improve overall performance. However, it’s important to approach it with a well-structured plan. Here’s how to begin.
1. Understand Lean Manufacturing Principles
Before implementing Lean, it’s essential to understand its core principles: value, value stream mapping, flow, pull, and perfection. These principles form the foundation of Lean and guide every improvement effort. Familiarising yourself with these concepts will help you apply them effectively in your organisation.
2. Identify Areas for Improvement
Start by evaluating your current processes. Look for areas where waste occurs—whether it’s overproduction, delays, excess inventory, or unnecessary motion. These inefficiencies will be your starting points for improvement. Engaging employees in this process can also provide valuable insights from those on the shop floor.
3. Engage Your Team
Lean is a team-based approach, and success relies on strong communication and collaboration. Involve your employees at all levels, as they are key to identifying problems and suggesting solutions. Empowering your team ensures the successful implementation of Lean practices across the organisation.
4. Start Small with Pilot Projects
Instead of making sweeping changes all at once, start with a small pilot project. Choose one process or area to apply Lean principles and measure the results. This allows you to refine the approach before expanding it to other areas.
5. Continuously Improve
Lean is about continuous improvement. After implementing Lean practices, regularly review the results and identify further opportunities for optimisation. By building a culture of ongoing improvement, you will ensure long-term success and growth.
Identifying the 8 Types of Waste in Lean Manufacturing
Lean manufacturing focuses on eliminating waste to improve efficiency and maximise value. Understanding the eight types of waste in Lean is crucial for identifying areas of improvement within your processes. Here's a breakdown of each type:
1. Overproduction
Overproduction occurs when products are made before they are needed, leading to excess inventory. This not only ties up resources but can also lead to unnecessary storage costs and potential product spoilage.
2. Waiting
Waiting waste happens when workers, machines, or materials are idle, waiting for the next step in the process. This delays production and reduces overall productivity, contributing to inefficiency.
3. Transport
Excessive movement of materials or products from one location to another is considered waste. Unnecessary transportation increases costs, risks damage, and consumes time that could be spent on value-adding activities.
4. Extra Processing
Extra processing involves performing more work or steps than necessary. This might include adding features or quality checks that are not required, resulting in wasted time and effort.
5. Inventory
Excess inventory ties up capital and space, leading to increased storage costs and potential obsolescence. Keeping inventory levels aligned with demand is critical to reduce waste.
6. Motion
Excess motion refers to unnecessary movement by workers, such as walking long distances or reaching for tools. This type of waste reduces efficiency and can lead to physical strain on workers.
7. Defects
Defects occur when products are made incorrectly, leading to rework or scrap. This waste not only consumes materials but also diverts resources away from productive activities.
8. Unused Talent
Unused talent refers to the waste of human potential when employees' skills and ideas are underutilised. Encouraging team members to contribute their knowledge can help drive continuous improvement.
By identifying and addressing these eight types of waste, organisations can significantly enhance their efficiency and reduce operational costs.
How Lean Supports Sustainability and Cost Savings
Lean manufacturing is not only about improving efficiency but also plays a key role in enhancing sustainability and driving cost savings. By focusing on waste reduction, Lean practices can help organisations reduce their environmental impact while simultaneously lowering operational expenses.
Reducing Waste for Sustainability
One of the core principles of Lean is eliminating waste. This reduction in waste directly contributes to sustainability by minimising the use of resources such as energy, materials, and water. For example, by reducing overproduction and inventory levels, companies can decrease the amount of raw materials that go unused or end up as waste. This leads to fewer discarded products, less landfill waste, and a smaller carbon footprint.
Lowering Costs through Lean Principles
By identifying and eliminating inefficiencies, Lean practices can result in significant cost savings. Whether it’s cutting down on excess inventory, reducing defects, or minimising unnecessary movement, Lean manufacturing ensures that resources are utilised more effectively. This not only lowers production costs but also increases profit margins. Additionally, by streamlining processes, companies can improve their cash flow and reduce the need for large amounts of capital tied up in unused inventory or equipment.
Improved Resource Utilisation
Lean focuses on the efficient use of resources, which can lead to improved productivity and reduced consumption of materials. By enhancing employee involvement and promoting continuous improvement, Lean manufacturing also fosters innovation, helping companies find new ways to reduce their environmental impact and improve operational efficiency.
Lean manufacturing offers significant benefits for both sustainability and cost savings by creating more efficient, resource-conscious processes that help companies reduce waste and enhance long-term profitability.
Lean Tools Every Manufacturer Should Know About
Lean manufacturing tools are essential for streamlining processes, reducing waste, and improving efficiency. These tools focus on eliminating unnecessary steps and optimising production, which helps manufacturers achieve better quality, lower costs, and faster turnaround times. Here are some of the most important Lean tools every manufacturer should consider:
1. 5S System
The 5S system is a fundamental Lean tool that focuses on workplace organisation. It stands for Sort, Set in Order, Shine, Standardise, and Sustain. Implementing 5S helps keep workspaces clean and organised, leading to higher efficiency and safety. By maintaining an organised environment, employees can easily access tools and materials, reducing downtime and errors.
2. Value Stream Mapping (VSM)
Value Stream Mapping is used to visually represent the flow of materials and information in the production process. It helps identify waste and inefficiencies, allowing manufacturers to streamline operations and enhance value creation. VSM is an excellent tool for highlighting bottlenecks and areas that need improvement.
3. Kanban
Kanban is a visual scheduling system that helps manage inventory and production flow. It ensures that materials are replenished just in time, reducing overstocking and minimising waste. Kanban uses signals, such as cards or boards, to track progress and prevent production delays.
4. Kaizen
Kaizen is a philosophy of continuous improvement. It encourages small, incremental changes that lead to long-term improvements in efficiency and quality. By involving all employees in the process of identifying and solving problems, Kaizen fosters a culture of continuous learning and innovation.
5. Just-in-Time (JIT)
Just-in-Time is a production strategy that aims to produce goods only when they are needed. This reduces inventory costs and minimises waste by aligning production with demand, ensuring that raw materials and components are available at the right time.
By integrating these Lean tools into daily operations, manufacturers can optimise their processes, reduce waste, and increase overall productivity.
The Role of Continuous Improvement in Lean Success
Continuous improvement is a core principle of Lean manufacturing and plays a crucial role in driving long-term success. The concept focuses on making small, incremental changes to processes, which together lead to significant improvements in efficiency, quality, and productivity. By embedding continuous improvement in the organisational culture, manufacturers can achieve ongoing growth and adaptability.
Enhancing Efficiency Through Small Changes
Continuous improvement encourages employees at all levels to identify and address inefficiencies in their daily tasks. These small changes, when consistently applied, accumulate over time, resulting in substantial reductions in waste and cost. By fostering a culture where everyone is responsible for improving processes, businesses can become more agile and responsive to challenges.
Encouraging Employee Engagement
One of the key benefits of continuous improvement is its ability to engage employees. When workers are empowered to suggest improvements and contribute to problem-solving, it increases their sense of ownership and job satisfaction. This involvement boosts morale and creates a more collaborative work environment, which is essential for Lean success.
Supporting Lean Tools and Practices
Continuous improvement supports the effective implementation of Lean tools like Kaizen, 5S, and Kanban. These tools rely on an environment where small, consistent improvements are valued and integrated into everyday operations. As a result, businesses that embrace continuous improvement are better equipped to sustain Lean principles and achieve lasting success.
In summary, continuous improvement is not just a strategy but a mindset that drives Lean success by fostering innovation, reducing waste, and enhancing efficiency throughout an organisation.
How to Train Your Team in Lean Thinking
Training your team in Lean thinking is essential for creating a culture of continuous improvement and efficiency. Lean principles focus on eliminating waste, improving processes, and empowering employees to contribute to the success of the business. Here's how to get started with Lean training for your team.
1. Start with the Basics
Before diving into specific Lean tools and techniques, ensure that your team understands the fundamental principles of Lean thinking. These include focusing on value, reducing waste, and improving flow. Use real-world examples to explain how Lean can enhance efficiency and quality in their daily work. A clear understanding of these principles will help them apply Lean in a practical way.
2. Focus on Hands-on Learning
Lean training is most effective when it involves hands-on learning. Incorporate exercises, simulations, and workshops where team members can practice Lean tools like 5S, Kaizen, and Value Stream Mapping. This approach allows them to see the impact of these techniques in real-time and understand how they can be applied to their roles.
3. Foster a Culture of Continuous Improvement
Encourage your team to continuously look for areas to improve. Lean thinking thrives in an environment where employees feel empowered to suggest and implement improvements. Create a space for open communication and feedback, where team members can share their ideas and work together to refine processes.
4. Provide Ongoing Support
Lean training doesn't stop after the initial sessions. Continuously support your team by providing resources, offering refresher courses, and recognising improvements. This ongoing commitment to Lean will keep the momentum going and lead to lasting change.
By training your team in Lean thinking, you create a more efficient, engaged workforce focused on delivering value and improving processes.
Creating a Lean Culture: Tips for Long-Term Success
Creating a Lean culture within your organisation is essential for achieving long-term success. Lean thinking focuses on continuous improvement, waste reduction, and optimising value for both customers and employees. Here are some practical tips for fostering a Lean culture that thrives over time.
1. Lead by Example
To build a Lean culture, leadership must fully embrace and embody Lean principles. Managers and supervisors should lead by example, demonstrating commitment to continuous improvement, waste reduction, and efficiency. When leaders consistently prioritise these values, it sets the tone for the rest of the organisation.
2. Encourage Employee Involvement
Lean culture thrives when employees at all levels are actively involved in problem-solving and process improvements. Encourage employees to identify waste, suggest solutions, and contribute to decision-making. By empowering staff, you build ownership and a sense of responsibility for the success of Lean initiatives.
3. Provide Ongoing Training and Support
A successful Lean culture requires continuous learning. Provide your team with regular training on Lean tools and techniques, such as 5S, Kaizen, and Value Stream Mapping. Ongoing support helps employees stay engaged and understand how Lean practices can be applied to their daily tasks.
4. Celebrate Small Wins
Recognising and celebrating small improvements can have a significant impact on morale and motivation. Acknowledge the efforts of your team in making incremental improvements, and use these successes as examples to inspire further action across the organisation.
By following these tips, you can cultivate a Lean culture that fosters continuous improvement, encourages employee engagement, and ultimately leads to sustained success.
How Lean Manufacturing Impacts Quality Control
Lean manufacturing is a powerful approach that not only improves efficiency but also significantly impacts quality control. By focusing on waste reduction, continuous improvement, and process optimisation, Lean principles create a framework that supports better product quality and enhanced operational performance.
1. Waste Reduction Leads to Higher Quality
One of the core principles of Lean is the elimination of waste. In the context of quality control, waste can include defective products, rework, or unnecessary inspections. By eliminating these inefficiencies, Lean manufacturing ensures that products are produced right the first time, reducing the need for corrective actions and increasing overall quality.
2. Standardised Work for Consistency
Lean encourages standardised work procedures, which help ensure consistency across production processes. Standardisation leads to fewer errors and variations, improving the consistency of the final product. This consistency directly impacts quality control by making it easier to identify and address any deviations from the desired standards.
3. Continuous Improvement Drives Quality Enhancement
Kaizen, a Lean concept focused on continuous improvement, promotes regular evaluation and refinement of processes. This culture of ongoing improvements allows businesses to consistently identify areas for quality enhancement, whether through small process tweaks or larger system overhauls, resulting in higher-quality products and fewer defects.
4. Empowering Employees to Identify Issues
Lean manufacturing encourages employees to take an active role in identifying and resolving quality issues. By giving workers the tools and authority to address problems as they arise, Lean fosters a proactive approach to quality control, helping to maintain high standards throughout the production process.
Lean manufacturing creates a solid foundation for quality control by focusing on waste reduction, process standardisation, and continuous improvement, ultimately leading to higher-quality products and greater customer satisfaction.
Case Studies: Lean in Action Across UK Industries
Lean manufacturing principles have been successfully applied across various industries in the UK, leading to significant improvements in efficiency, cost reduction, and product quality. Here are a few case studies that highlight Lean in action:
1. Automotive Industry: Reducing Production Time
In the UK automotive sector, Lean principles have been implemented to streamline production lines and reduce lead times. By applying techniques like Just-in-Time (JIT) inventory management and Kaizen (continuous improvement), manufacturers have significantly reduced the time it takes to assemble vehicles. This not only cuts costs but also improves the overall production flow, resulting in faster delivery times to customers and better alignment with demand.
2. Food Manufacturing: Waste Reduction and Efficiency Gains
Food manufacturing companies in the UK have embraced Lean to reduce waste and improve operational efficiency. Through practices like 5S (Sort, Set in order, Shine, Standardise, Sustain), companies have optimised their production environments, leading to a reduction in material waste and higher product consistency. By reducing unnecessary movement and improving workstation layouts, productivity has increased, and product quality has been enhanced, all while cutting down on operational costs.
3. Healthcare Sector: Streamlining Processes for Better Patient Care
Lean techniques have also made a significant impact in the UK's healthcare sector. By applying Lean to streamline administrative and clinical processes, hospitals have improved patient care and reduced waiting times. By using tools such as Value Stream Mapping, healthcare providers have identified and eliminated bottlenecks, ensuring faster and more efficient service delivery. This has not only improved patient satisfaction but also resulted in cost savings and better resource utilisation.
These case studies demonstrate how Lean manufacturing principles can be adapted across various industries in the UK, driving continuous improvement, operational efficiency, and enhanced product quality.
Digital Lean: Using Technology to Enhance Lean Processes
In today’s fast-paced business environment, integrating digital tools with Lean manufacturing principles has become essential for organisations looking to stay competitive. Digital Lean is the fusion of traditional Lean methodologies with advanced technologies, allowing businesses to optimise processes, reduce waste, and improve efficiency in ways that were not possible before.
1. Data-Driven Decision Making
One of the key advantages of digital Lean is the ability to gather and analyse data in real-time. Technologies like sensors and IoT (Internet of Things) devices enable companies to track equipment performance, monitor production rates, and detect anomalies before they turn into major issues. By leveraging this data, businesses can make informed decisions, quickly identify areas for improvement, and implement solutions to streamline their operations.
2. Automation and Robotics
Automation plays a crucial role in enhancing Lean processes. By automating repetitive tasks, companies can reduce human error, improve consistency, and free up workers to focus on higher-value tasks. Robotics and automated systems help maintain a steady production flow, which aligns with Lean’s goal of minimising downtime and maximising productivity.
3. Lean Software Tools
There are several software tools that complement Lean processes by offering solutions for project management, inventory control, and workflow optimisation. These digital tools allow for better collaboration, more accurate forecasting, and more efficient resource management, all while reducing costs and waste.
Incorporating digital technologies into Lean practices not only enhances operational performance but also fosters a culture of continuous improvement. As businesses embrace Digital Lean, they can achieve greater flexibility, faster response times, and long-term sustainability.
Common Pitfalls in Lean Implementation and How to Avoid Them
While Lean manufacturing offers numerous benefits, its implementation can be challenging. Many businesses encounter common pitfalls that can hinder the success of Lean initiatives. Understanding these challenges and knowing how to avoid them is key to achieving lasting improvements.
1. Lack of Leadership Support
A common mistake in Lean implementation is the lack of commitment from senior leadership. Without strong leadership and a clear vision, Lean efforts can falter. Leaders must actively champion Lean principles, provide resources, and ensure alignment across all departments to drive success.
2. Failing to Engage Employees
Lean is most effective when it involves everyone in the organisation, from top management to frontline workers. When employees are not engaged or do not understand the rationale behind Lean practices, they are less likely to buy into the process. Regular communication, training, and empowerment are essential to foster a culture of continuous improvement.
3. Inadequate Training and Resources
Implementing Lean practices requires a well-trained workforce. Without proper training, employees may struggle to adopt new processes or understand how to identify and eliminate waste. Providing ongoing training and access to Lean tools is crucial for sustaining improvements.
4. Focusing Too Much on Tools, Not on Mindset
While Lean tools like 5S and value stream mapping are important, Lean is ultimately about a mindset of continuous improvement. Organisations can fall into the trap of focusing too heavily on tools and techniques without embracing the underlying principles. It’s vital to cultivate a mindset that values efficiency, respect for people, and problem-solving.
By recognising and addressing these pitfalls, businesses can successfully implement Lean and achieve sustained improvements in productivity and efficiency.