In today’s highly competitive and fast-paced business environment, companies are continuously seeking ways to improve efficiency, reduce waste, and enhance customer satisfaction. Lean Six Sigma has emerged as a powerful methodology that helps organisations achieve these goals by combining the principles of Lean and Six Sigma. This approach not only enhances the quality of products and services but also optimises processes, leading to sustainable success.
Understanding Lean Six Sigma
Lean Six Sigma is a methodology that integrates two powerful improvement approaches: Lean and Six Sigma. While Lean focuses on eliminating waste and streamlining processes, Six Sigma aims at reducing variation and improving quality by using statistical methods. Together, Lean Six Sigma combines the strengths of both approaches to create a highly efficient, quality-driven, and customer-focused process improvement system.
- Lean: Lean is primarily concerned with identifying and eliminating non-value-added activities—commonly referred to as waste—in any process. These wastes include unnecessary steps, excessive inventory, waiting time, overproduction, motion, defects, and underutilisation of skills. By removing these inefficiencies, Lean ensures that every step in the process adds value to the end product or service.
- Six Sigma: Six Sigma, on the other hand, focuses on reducing defects and variability in processes. It uses statistical tools and techniques to analyse and measure process performance, identify the root causes of defects, and implement improvements. Six Sigma's ultimate goal is to achieve near-perfect processes with minimal variation, ensuring consistent quality and performance.
The synergy of Lean and Six Sigma allows organisations to achieve more than they could with either methodology alone. The combined approach enables companies to enhance efficiency while simultaneously improving the quality of their products and services.
Core Principles of Lean Six Sigma
At the heart of Lean Six Sigma are several core principles that guide its application. These principles help ensure that improvement initiatives are well-structured, focused, and aligned with the organisation's goals.
1. Focus on the Customer
The primary goal of Lean Six Sigma is to improve processes in ways that directly benefit the customer. Whether it’s reducing defects, improving delivery times, or enhancing product features, the customer’s needs and expectations are always at the forefront. By understanding what customers value most, organisations can design processes that deliver higher quality and meet or exceed customer expectations.
2. Identify and Eliminate Waste
Waste, in the context of Lean Six Sigma, refers to any activity that does not add value to the customer. Through careful analysis, organisations can identify areas of inefficiency and eliminate unnecessary steps or processes. Reducing waste not only improves efficiency but also cuts costs, leading to better financial performance.
3. Use Data and Statistical Analysis
One of the strengths of Lean Six Sigma is its reliance on data and statistical analysis to drive decision-making. This approach ensures that improvements are based on objective, measurable information rather than intuition or guesswork. By using tools such as control charts, root cause analysis, and process mapping, organisations can pinpoint areas of improvement with greater accuracy and confidence.
4. Enhance Process Flow and Quality
Lean Six Sigma emphasises optimising the flow of work and minimising variability. By streamlining processes, organisations can ensure that products and services are delivered consistently, quickly, and with fewer defects. Process improvements are not only about reducing waste but also about ensuring that each process step contributes to a smoother and more efficient operation.
5. Involve and Empower Employees
Successful Lean Six Sigma implementations require the involvement of employees at all levels. Team members are often the ones closest to the process and are in the best position to identify inefficiencies and suggest improvements. By empowering employees to participate in problem-solving and decision-making, organisations foster a culture of continuous improvement.
6. Foster a Culture of Continuous Improvement
Lean Six Sigma is not a one-time project but a long-term commitment to continuous improvement. Organisations that embrace this mindset constantly seek ways to refine processes, enhance quality, and deliver greater value to their customers. This culture of continuous improvement becomes ingrained in the organisation, ensuring ongoing success and adaptation to changing market conditions.
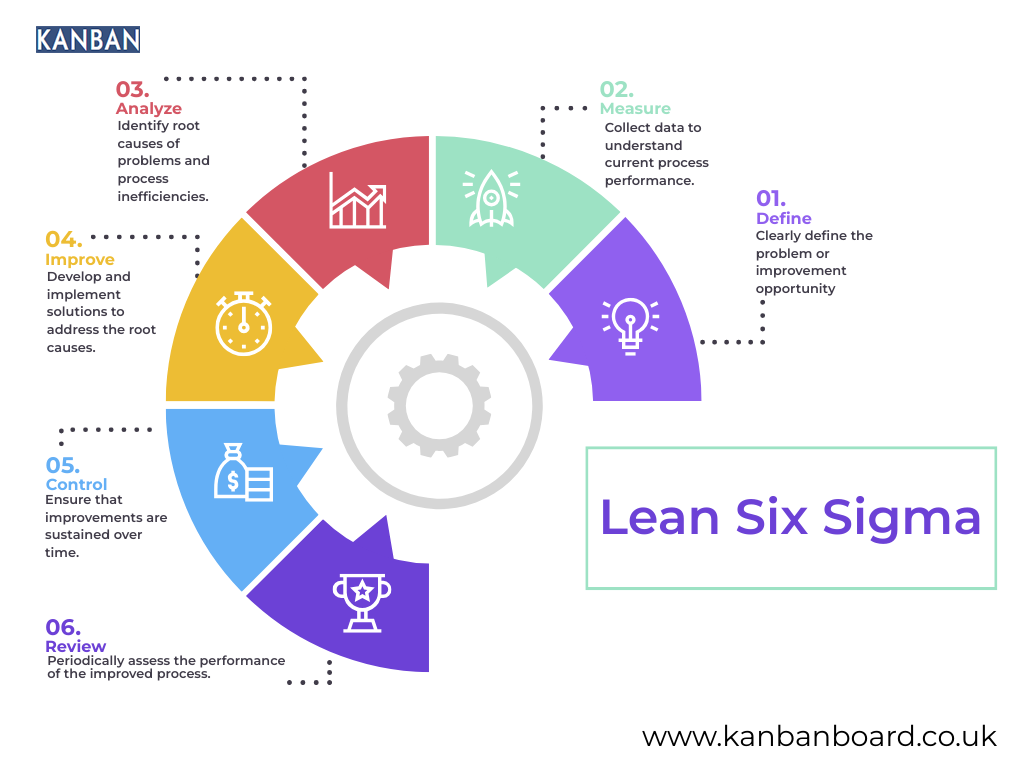
The DMAIC Process
A key aspect of Lean Six Sigma is the DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyse, Improve, Control) process, which provides a structured framework for identifying and addressing process inefficiencies:
- Define: Identify the problem, the goals of the improvement project, and the customer’s needs.
- Measure: Collect data to establish a baseline and quantify the current performance of the process.
- Analyse: Examine the data to identify the root causes of inefficiencies and defects.
- Improve: Implement changes designed to eliminate the root causes and improve process performance.
- Control: Monitor the improved process to ensure that the gains are sustained over time.
The DMAIC process is a systematic approach that ensures improvements are targeted, data-driven, and sustainable. It encourages continuous monitoring and control to prevent regression to previous levels of performance.
Benefits of Lean Six Sigma
The successful implementation of Lean Six Sigma brings a wide array of benefits to organisations across industries:
- Improved Quality: By reducing defects and variability, Lean Six Sigma ensures that products and services meet higher standards of quality, resulting in fewer customer complaints and returns.
- Increased Efficiency: The elimination of waste and streamlining of processes lead to faster production times, improved delivery, and reduced operational costs.
- Cost Reduction: With fewer defects and more efficient processes, organisations can achieve significant cost savings.
- Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: A focus on delivering value to customers means that organisations are better positioned to meet customer expectations and improve their overall experience.
- Employee Engagement: Empowering employees to participate in continuous improvement fosters a sense of ownership and engagement, leading to a more motivated and productive workforce.
Understanding Lean Six Sigma: A Powerful Combination for Business Excellence
Lean Six Sigma is a powerful methodology used by businesses to improve performance, reduce waste, and enhance efficiency. Combining two key principles—Lean, which focuses on minimising waste, and Six Sigma, which aims to reduce variation and improve quality—this approach provides a structured framework for continuous improvement across all areas of an organisation.

1. The Lean Approach
The Lean principle focuses on eliminating non-value-added activities, or waste, from business processes. By streamlining operations and removing inefficiencies, organisations can improve the flow of work, reduce costs, and provide more value to customers. Lean tools, such as value stream mapping and Kaizen, help teams identify waste and optimise processes for maximum efficiency.
2. The Six Sigma Approach
Six Sigma, on the other hand, aims to reduce defects and variation in processes to achieve near-perfect results. The Six Sigma methodology uses data-driven techniques like DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyse, Improve, Control) to identify and eliminate the root causes of problems. By reducing variation, businesses can achieve more consistent and reliable outcomes, leading to higher customer satisfaction and reduced costs.
3. The Synergy of Lean Six Sigma
When combined, Lean and Six Sigma complement each other by focusing on both process efficiency and quality. Lean improves speed and flow, while Six Sigma ensures that processes are stable and consistently produce high-quality results. This combination helps businesses achieve optimal performance, reduce waste, and improve overall profitability.
Lean Six Sigma is a proven approach to business excellence, offering a comprehensive solution for organisations looking to optimise their operations, reduce costs, and achieve long-term success.
How Lean Six Sigma Improves Operational Efficiency and Reduces Waste
Lean Six Sigma is a powerful methodology that combines two proven approaches to improve operational efficiency and reduce waste within businesses. By integrating Lean’s focus on eliminating non-value-added activities and Six Sigma’s emphasis on reducing variation, organisations can streamline processes, optimise resources, and deliver better outcomes.
1. Streamlining Processes with Lean
Lean focuses on identifying and eliminating waste in business processes. This waste can take many forms, such as excess inventory, unnecessary steps, or waiting times. By applying Lean principles like value stream mapping and continuous improvement (Kaizen), organisations can optimise workflows and reduce inefficiencies. This leads to faster operations, lower costs, and better resource utilisation.
2. Enhancing Quality with Six Sigma
Six Sigma aims to reduce process variation and defects, ensuring that products and services meet the highest quality standards. Using tools like the DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyse, Improve, Control) methodology, businesses can identify the root causes of inefficiencies and implement data-driven solutions. By minimising defects, organisations can improve customer satisfaction, reduce rework, and lower costs associated with poor quality.
3. Achieving Long-Term Success
When combined, Lean and Six Sigma create a comprehensive approach to improving operational efficiency. Lean helps speed up processes and reduce waste, while Six Sigma ensures that the outcomes are consistently high-quality. Together, these methodologies drive continuous improvement, enhance productivity, and reduce costs, leading to long-term business success.
Lean Six Sigma offers a proven way to boost operational efficiency, eliminate waste, and enhance quality. Businesses that adopt this approach can improve their bottom line while delivering greater value to customers.
The Key Principles Behind Lean Six Sigma Methodology
Lean Six Sigma is a methodology that combines two powerful concepts—Lean and Six Sigma—to improve operational efficiency, reduce waste, and enhance quality in business processes. By applying these principles, organisations can achieve significant improvements in their performance and customer satisfaction.
1. Focus on Customer Value
At the heart of Lean Six Sigma is the focus on delivering value to customers. This principle emphasises understanding customer needs and aligning business processes to meet those expectations. By reducing waste and improving quality, businesses can deliver better products and services, increasing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
2. Eliminate Waste
The Lean aspect of the methodology focuses on identifying and removing waste—any activity that does not add value to the customer. This could include excess inventory, unnecessary steps in a process, or delays in workflow. By eliminating these wastes, businesses can streamline operations, reduce costs, and improve efficiency.
3. Reduce Variation
Six Sigma’s primary focus is on reducing variation and defects in processes. By using data-driven techniques and tools like DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyse, Improve, Control), organisations can identify the root causes of inconsistencies and implement improvements. Reducing variation ensures more predictable, high-quality outcomes, which leads to fewer defects and greater customer satisfaction.
4. Continuous Improvement
Lean Six Sigma promotes a culture of continuous improvement. Organisations using this methodology constantly monitor their processes, identify areas for improvement, and implement changes to enhance performance. This ongoing effort helps businesses remain competitive and responsive to market changes.
The key principles of Lean Six Sigma—focusing on customer value, eliminating waste, reducing variation, and fostering continuous improvement—enable organisations to optimise their processes, improve quality, and drive long-term success.
What Are the Main Benefits of Lean Six Sigma for Your Organisation?
Implementing Lean Six Sigma in your organisation can drive significant improvements in efficiency, quality, and customer satisfaction. By combining the principles of Lean (eliminating waste) and Six Sigma (reducing variation), organisations can achieve better results, optimise resources, and foster a culture of continuous improvement. Here are the main benefits of adopting Lean Six Sigma:
1. Increased Efficiency
One of the primary benefits of Lean Six Sigma is the ability to streamline processes. By identifying and eliminating waste in operations, businesses can reduce unnecessary steps, minimise delays, and improve the flow of work. This leads to faster processes, lower operational costs, and a more efficient use of resources.
2. Improved Quality
Six Sigma’s focus on reducing variation and defects ensures that products and services meet the highest quality standards. By using data-driven tools like DMAIC, businesses can identify the root causes of issues and implement solutions that result in more consistent, high-quality outcomes. This ultimately leads to greater customer satisfaction and fewer returns or complaints.
3. Enhanced Customer Satisfaction
By delivering higher quality products and services faster, organisations can improve customer satisfaction. Lean Six Sigma helps businesses align their processes with customer needs, ensuring they provide value with minimal waste. As a result, organisations can build stronger relationships with their customers, leading to greater loyalty and repeat business.
4. Continuous Improvement
Lean Six Sigma encourages a culture of continuous improvement. Organisations regularly assess their processes, identify areas for improvement, and implement changes to achieve better results. This focus on constant enhancement helps businesses remain competitive and agile in today’s fast-paced market.
Lean Six Sigma offers a wide range of benefits, including increased efficiency, improved quality, enhanced customer satisfaction, and a commitment to continuous improvement. By adopting this methodology, organisations can position themselves for long-term success.
The Role of DMAIC in Lean Six Sigma Projects
DMAIC is a critical framework within the Lean Six Sigma methodology, used to drive process improvements and achieve optimal results. Standing for Define, Measure, Analyse, Improve, and Control, this data-driven approach provides a structured path for problem-solving and continuous improvement. By following the DMAIC process, organisations can systematically identify issues, eliminate waste, and enhance efficiency.
1. Define
The first step in the DMAIC process is to define the problem or process that needs improvement. This phase involves clearly identifying the goals, objectives, and scope of the project. By defining the problem, teams can ensure they focus on the right issues and align their efforts with business goals. It also helps to establish measurable outcomes that will demonstrate the project’s success.
2. Measure
In the Measure phase, data is collected to understand the current performance of the process. This involves identifying key metrics, such as cycle time, defect rates, or customer satisfaction, and gathering relevant data. Measuring the process allows organisations to understand its baseline performance, identify areas of waste, and pinpoint opportunities for improvement.
3. Analyse
The Analyse phase focuses on identifying the root causes of problems. Data collected in the Measure phase is analysed to uncover patterns, correlations, and underlying issues that contribute to process inefficiencies or defects. By understanding the cause of the problem, teams can develop targeted solutions to address it.
4. Improve
Once the root causes are identified, the Improve phase involves developing and testing solutions. Teams implement changes to optimise the process, reduce waste, and enhance quality. Solutions are then evaluated to ensure they effectively address the identified issues and deliver measurable improvements.
5. Control
The final phase, Control, ensures that improvements are sustained over time. In this phase, organisations establish monitoring systems to track performance and make adjustments as needed. Control mechanisms help prevent the process from reverting to its previous state and ensure long-term success.
The DMAIC framework is essential for Lean Six Sigma projects, providing a systematic, data-driven approach to process improvement. By following each phase, organisations can achieve sustainable results, improve efficiency, and drive long-term success.

How Lean Six Sigma Drives Continuous Improvement Across Industries
Lean Six Sigma is a methodology that promotes continuous improvement by combining the principles of Lean and Six Sigma. This approach helps businesses across various industries enhance operational efficiency, reduce waste, and improve quality. By focusing on data-driven decision-making and process optimisation, Lean Six Sigma drives long-term success and sustainability.
1. Streamlining Processes
One of the primary benefits of Lean Six Sigma is its ability to streamline processes. In any industry, inefficiencies can slow down operations and increase costs. Lean Six Sigma identifies and eliminates waste, such as unnecessary steps in a process or delays, ensuring smoother workflows. This not only improves productivity but also enhances resource utilisation and reduces operational costs.
2. Enhancing Quality
Six Sigma’s focus on reducing variation and defects plays a crucial role in enhancing product and service quality. By using tools such as DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyse, Improve, Control), organisations can identify root causes of defects and implement improvements. This ensures that products and services consistently meet high standards, leading to better customer satisfaction and fewer errors or returns.
3. Fostering a Culture of Continuous Improvement
Lean Six Sigma encourages a culture of continuous improvement by empowering employees to contribute to problem-solving and process optimisation. As organisations adopt this mindset, they continually assess and improve their operations, ensuring they stay competitive in the market. This ongoing effort to improve helps businesses adapt to changing customer needs and market conditions.
4. Driving Innovation
By focusing on data and performance, Lean Six Sigma fosters innovation. As companies identify opportunities for improvement, they also uncover new ways to innovate and add value to their customers. This focus on continuous enhancement helps businesses stay ahead of the competition.
Lean Six Sigma drives continuous improvement across industries by optimising processes, enhancing quality, fostering innovation, and creating a culture of ongoing development. Organisations that implement these principles can achieve long-term success and sustainability in an ever-changing marketplace.
Lean Six Sigma vs Traditional Process Improvement: What’s the Difference?
When it comes to improving business processes, organisations often face the decision between adopting Lean Six Sigma or sticking with traditional process improvement methods. Both approaches aim to enhance efficiency and quality, but they differ in their methodologies, tools, and outcomes. Understanding these differences can help businesses choose the best approach for their needs.
1. Focus on Waste and Variation
Lean Six Sigma combines two powerful approaches: Lean, which focuses on eliminating waste, and Six Sigma, which targets reducing variation and defects. This dual focus makes Lean Six Sigma highly effective in streamlining processes while maintaining consistent quality. In contrast, traditional process improvement methods may focus more on general optimisation without the specific emphasis on waste reduction and variation control.
2. Data-Driven Decision-Making
One of the key strengths of Lean Six Sigma is its data-driven approach. It relies heavily on gathering and analysing data to identify root causes of inefficiencies or defects. The use of tools like DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyse, Improve, Control) ensures that decisions are based on solid evidence. Traditional methods may not always prioritise data collection, often relying more on experience or intuition in decision-making.
3. Continuous Improvement Culture
Lean Six Sigma promotes a culture of continuous improvement, encouraging employees at all levels to identify problems and propose solutions. This culture is ingrained in the methodology, ensuring long-term improvements. Traditional methods may not always foster this ongoing effort, with improvements often being seen as one-off projects rather than part of an ongoing organisational culture.
4. Measurable Outcomes
Lean Six Sigma focuses on achieving measurable results, such as reduced cycle times, improved quality, and lower costs. The effectiveness of the improvements can be tracked using key performance indicators (KPIs). Traditional process improvement methods may not always have clear metrics or may focus more on subjective improvements.
While both Lean Six Sigma and traditional process improvement methods aim to optimise processes, Lean Six Sigma offers a more structured, data-driven, and sustainable approach. By focusing on both waste elimination and variation reduction, it drives continuous improvement with measurable results.
How Lean Six Sigma Can Enhance Quality Control in Your Business
Quality control is essential for any business looking to improve products and services, meet customer expectations, and reduce waste. Lean Six Sigma is a powerful methodology that can significantly enhance quality control by focusing on reducing defects and improving process efficiency. By integrating Lean principles with Six Sigma tools, businesses can achieve higher quality standards while also increasing operational efficiency.
1. Identifying and Eliminating Defects
One of the primary goals of Lean Six Sigma is to identify and eliminate defects that negatively impact quality. By using data-driven tools and techniques, such as the DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyse, Improve, Control) process, businesses can identify the root causes of quality issues. This targeted approach ensures that problems are resolved at their source, reducing the likelihood of recurring defects and improving the overall quality of products and services.
2. Standardising Processes
Standardising processes is a key aspect of Lean Six Sigma. By defining best practices and ensuring consistency across operations, businesses can maintain a higher level of quality control. Standardisation helps to minimise variation, which is crucial for ensuring that every product or service meets the desired quality standards. This consistency also helps to reduce errors and enhance customer satisfaction.
3. Improving Efficiency
Lean Six Sigma’s focus on eliminating waste and improving efficiency plays a significant role in enhancing quality control. By streamlining processes and removing unnecessary steps, businesses can reduce errors, minimise delays, and ensure smoother workflows. This increased efficiency leads to more reliable products and services, ultimately improving quality control outcomes.
4. Continuous Monitoring and Improvement
Lean Six Sigma fosters a culture of continuous improvement. Once quality control improvements are implemented, the process doesn’t stop there. Regular monitoring and analysis ensure that businesses can maintain and further enhance quality over time. By continuously assessing performance and making adjustments, companies can ensure that their quality control systems stay effective and aligned with changing customer needs.
Lean Six Sigma is an invaluable tool for enhancing quality control. Through its structured, data-driven approach, it helps businesses identify defects, standardise processes, improve efficiency, and maintain a culture of continuous improvement—all of which lead to superior product and service quality.
The Importance of Data-Driven Decisions in Lean Six Sigma
In today’s competitive business environment, making informed decisions is crucial for success. Lean Six Sigma is a methodology that relies heavily on data to drive decisions, ensuring that improvements are based on facts rather than assumptions. This data-driven approach is one of the core strengths of Lean Six Sigma, enabling organisations to achieve measurable results and sustainable improvements in their processes.
1. Identifying Root Causes
One of the primary benefits of using data in Lean Six Sigma is its ability to identify the root causes of problems. Instead of relying on guesswork or subjective opinions, data is gathered and analysed to pinpoint exactly where inefficiencies or defects occur. Tools like statistical analysis and process mapping are used to reveal patterns, helping businesses make more accurate decisions about where to focus their improvement efforts.
2. Reducing Variability
Lean Six Sigma focuses on reducing variation, which can lead to defects and inconsistent results. By using data to monitor and measure performance, businesses can identify areas where variability occurs and implement strategies to reduce it. This data-driven approach ensures that processes are more consistent, leading to higher quality outcomes and greater customer satisfaction.
3. Continuous Improvement
Data-driven decisions support the continuous improvement cycle in Lean Six Sigma. By constantly collecting data and monitoring performance, businesses can track progress over time. This allows for timely adjustments to be made when necessary, ensuring that improvements are sustained and that the organisation remains competitive in the long run.
4. Optimising Resources
Data also plays a key role in resource optimisation. By analysing process data, businesses can identify areas where resources are being wasted, whether it’s time, materials, or labour. Lean Six Sigma helps to streamline operations, ensuring that resources are used efficiently and that costs are minimised.
Data-driven decisions are at the heart of Lean Six Sigma. By using data to identify root causes, reduce variability, support continuous improvement, and optimise resources, businesses can achieve better outcomes and long-term success.
Real-World Applications of Lean Six Sigma in Manufacturing and Services
Lean Six Sigma is a versatile methodology that has proven to be effective in both manufacturing and service industries. By combining the principles of Lean, which focuses on waste reduction, and Six Sigma, which aims to reduce variation, businesses can achieve substantial improvements in quality, efficiency, and customer satisfaction. Below, we explore how Lean Six Sigma is applied in real-world scenarios across manufacturing and services.
1. Manufacturing Industry: Reducing Waste and Improving Quality
In the manufacturing sector, Lean Six Sigma is widely used to streamline processes, eliminate waste, and enhance product quality. For example, a company might apply Lean Six Sigma to improve assembly line efficiency by identifying bottlenecks and reducing cycle times. By eliminating unnecessary steps and optimising workflows, manufacturers can produce higher-quality products at lower costs. Furthermore, Six Sigma’s data-driven approach helps pinpoint defects and improve consistency in production, ensuring that products meet strict quality standards.
2. Service Industry: Enhancing Customer Experience
In the service industry, Lean Six Sigma is employed to improve customer satisfaction and operational efficiency. For instance, a call centre might use Lean Six Sigma to reduce call handling times without sacrificing the quality of customer service. By analysing data, the centre can identify areas for improvement and train staff to handle customer queries more effectively. Similarly, healthcare providers use Lean Six Sigma to streamline patient care processes, reducing waiting times and improving patient outcomes.
3. Cross-Industry Applications: Driving Continuous Improvement
Across both sectors, Lean Six Sigma drives a culture of continuous improvement. By collecting data, analysing performance, and making informed decisions, businesses can achieve long-term success. Whether it’s through faster production times or improved customer service, Lean Six Sigma provides organisations with the tools to optimise operations and deliver superior results consistently.
Lean Six Sigma offers significant benefits across manufacturing and service industries. Its ability to reduce waste, improve quality, and increase efficiency makes it an invaluable tool for organisations seeking to enhance performance and drive growth.
How to Get Started with Lean Six Sigma in Your Organisation
Implementing Lean Six Sigma in your organisation can bring about significant improvements in efficiency, quality, and customer satisfaction. However, successfully integrating this methodology requires careful planning and a structured approach. Below are key steps to get started with Lean Six Sigma in your business.
1. Gain Leadership Support
Before embarking on a Lean Six Sigma journey, it's essential to gain buy-in from senior leadership. Their support will ensure that the necessary resources, training, and commitment are in place. Leadership should understand the value Lean Six Sigma brings and champion its implementation across all levels of the organisation.
2. Train Key Employees
Lean Six Sigma relies on well-trained employees to drive improvement initiatives. Start by training key staff members in the fundamentals of Lean and Six Sigma. Employees can then become "Champions," "Black Belts," or "Green Belts" based on their level of expertise. These trained individuals will lead and guide Lean Six Sigma projects, ensuring that they are carried out effectively.
3. Define Clear Goals and Objectives
It’s crucial to set clear, measurable goals for your Lean Six Sigma projects. These goals should align with your organisation’s overall business objectives, whether it’s improving product quality, reducing waste, or increasing customer satisfaction. Defining these objectives at the outset helps ensure that your efforts are focused and result in tangible improvements.
4. Start with Pilot Projects
To get started, it’s helpful to implement Lean Six Sigma on a small scale through pilot projects. Choose areas with significant room for improvement, and use them as test cases for applying Lean Six Sigma principles. This allows you to refine your approach before scaling it up across the organisation.
5. Measure and Analyse Results
Data-driven decision-making is at the core of Lean Six Sigma. Regularly measure and analyse the results of your improvement initiatives. This helps you track progress, identify areas for further improvement, and make informed decisions to optimise processes.
Getting started with Lean Six Sigma involves securing leadership support, training employees, setting clear objectives, running pilot projects, and continually measuring results. With a structured approach, your organisation can unlock the full potential of Lean Six Sigma and drive continuous improvement.
Training and Certification in Lean Six Sigma: What You Need to Know
Lean Six Sigma is a powerful methodology that helps organisations improve processes, reduce waste, and enhance quality. To effectively implement Lean Six Sigma within your organisation, it's essential to have well-trained professionals who are knowledgeable in its principles. Training and certification in Lean Six Sigma can empower individuals and teams to drive meaningful improvements. Here’s what you need to know about Lean Six Sigma training and certification.
1. Understanding the Different Levels of Certification
Lean Six Sigma certifications come in different levels, each representing a deeper understanding and expertise in the methodology. The most common levels are:
- Yellow Belt: This entry-level certification is ideal for those new to Lean Six Sigma. It focuses on the basic principles and tools.
- Green Belt: A Green Belt professional is typically responsible for managing projects and supporting Black Belts in process improvement initiatives.
- Black Belt: Black Belt professionals are experts in Lean Six Sigma and lead complex projects. They possess a deep understanding of the tools and techniques required for process optimisation.
- Master Black Belt: The highest level, Master Black Belts oversee Lean Six Sigma strategies across an organisation and mentor other belts.
2. Choosing the Right Training Program
When selecting a Lean Six Sigma training program, it's important to choose one that is recognised for its quality and credibility. Look for training courses that offer a combination of theoretical knowledge and practical, hands-on experience. A good program should also provide real-world examples and case studies to reinforce learning.
3. Benefits of Lean Six Sigma Certification
Obtaining a Lean Six Sigma certification can offer numerous benefits. It enhances your skillset, making you more valuable to your organisation. It also increases your ability to lead projects, improve efficiency, and solve complex problems. Moreover, certification can help boost career opportunities and provide recognition as a process improvement expert.
Training and certification in Lean Six Sigma are crucial steps in equipping individuals with the skills necessary to drive continuous improvement. Whether you’re just starting or looking to deepen your expertise, Lean Six Sigma certification offers valuable insights and a path to professional growth.
How Lean Six Sigma Supports Cost Reduction and Profit Growth
Lean Six Sigma is a methodology designed to improve business processes by reducing waste, minimising defects, and enhancing efficiency. By implementing Lean Six Sigma principles, organisations can achieve significant cost reductions and promote sustainable profit growth. Here’s how Lean Six Sigma supports cost reduction and profit growth in businesses.
1. Eliminating Waste and Inefficiency
One of the core principles of Lean Six Sigma is waste reduction. Lean focuses on identifying and eliminating non-value-added activities that consume time and resources without contributing to the final product or service. By streamlining processes, businesses can reduce operational costs, cut down on excess inventory, and minimise unnecessary steps in production. This leads to greater efficiency and lower operational expenses.
2. Reducing Defects and Improving Quality
Six Sigma focuses on reducing variation and defects in processes. By improving process quality, organisations can reduce rework, scrap, and customer complaints, leading to cost savings. Fewer defects also mean less time and money spent on fixing problems, resulting in more consistent and reliable products or services. This directly contributes to higher customer satisfaction, repeat business, and long-term profitability.
3. Increasing Efficiency and Productivity
Lean Six Sigma fosters a culture of continuous improvement, encouraging teams to consistently look for ways to improve efficiency and productivity. As processes become more efficient, employees can focus on value-added activities, leading to faster turnaround times and more output. This increased productivity contributes to higher profit margins, as businesses can produce more with fewer resources.
4. Data-Driven Decision Making
Lean Six Sigma relies on data to identify areas of improvement and measure success. By using data to make informed decisions, businesses can implement targeted improvements that lead to both cost reduction and profit growth. This approach ensures that resources are used optimally, reducing waste and enhancing overall profitability.
Lean Six Sigma provides businesses with the tools to reduce costs, improve quality, and drive efficiency. By eliminating waste, reducing defects, and improving productivity, organisations can achieve sustainable profit growth and maintain a competitive edge in their industry.
Measuring Success with Lean Six Sigma: KPIs and Metrics
Measuring success is a vital aspect of any Lean Six Sigma initiative. To track improvements, organisations rely on key performance indicators (KPIs) and metrics. These help to assess the effectiveness of process changes, identify areas for further improvement, and demonstrate the financial impact of Lean Six Sigma projects. Here’s how KPIs and metrics play a crucial role in measuring success with Lean Six Sigma.
1. Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for Lean Six Sigma
KPIs are critical to understanding the performance of business processes and aligning them with organisational goals. In Lean Six Sigma, KPIs focus on metrics like process efficiency, defect rates, and customer satisfaction. Common KPIs include:
- Defects Per Million Opportunities (DPMO): This measures the number of defects in a process and helps identify areas that require improvement.
- Cycle Time: The total time taken to complete a process, from start to finish. Reducing cycle time increases efficiency and reduces costs.
- First Pass Yield (FPY): The percentage of products that pass through the process without needing rework or correction.
2. Process Metrics for Continuous Improvement
Alongside KPIs, process metrics such as throughput, efficiency, and cost per unit provide valuable insights into the performance of specific processes. These metrics help track improvements over time and determine the success of Lean Six Sigma initiatives. They also allow organisations to make data-driven decisions to optimise processes further.
3. Linking Metrics to Business Outcomes
To truly measure success, Lean Six Sigma metrics should be linked to business outcomes such as increased profitability, reduced operational costs, and higher customer satisfaction. By monitoring these metrics, organisations can ensure that Lean Six Sigma projects deliver tangible, long-term benefits.
KPIs and metrics are essential in measuring the success of Lean Six Sigma initiatives. By using these tools, businesses can track improvements, identify areas for further optimisation, and ultimately achieve better outcomes, driving sustainable growth and operational excellence.
Common Challenges When Implementing Lean Six Sigma (And How to Overcome Them)
Implementing Lean Six Sigma can bring about significant improvements in business processes, but it is not without its challenges. Organisations often face various obstacles when trying to adopt this methodology. Understanding these challenges and knowing how to overcome them can make the implementation process smoother and more effective.
1. Resistance to Change
One of the most common challenges when implementing Lean Six Sigma is resistance to change. Employees may be hesitant to adopt new processes or methods, fearing disruption or a loss of control. To overcome this, it is essential to foster a culture of continuous improvement and involve employees early in the process. Training and clear communication about the benefits of Lean Six Sigma can help reduce resistance and encourage buy-in from all levels of the organisation.
2. Lack of Proper Training
Without proper training, Lean Six Sigma can be difficult to implement successfully. Employees need to be equipped with the right skills and knowledge to carry out process improvements effectively. Organisations should invest in comprehensive training programmes, from Yellow Belt to Black Belt certifications, ensuring that staff have the tools to identify inefficiencies and make data-driven decisions.
3. Inadequate Leadership Support
Lean Six Sigma requires strong leadership to guide and support the initiative. If senior management is not fully committed to the project, it can lead to lack of resources, direction, and enthusiasm. Ensuring leadership is fully engaged and provides the necessary resources is key to a successful implementation.
4. Difficulty in Measuring Progress
Another challenge is measuring the effectiveness of Lean Six Sigma initiatives. To overcome this, organisations should establish clear KPIs and metrics from the outset. These will help track improvements and keep the team focused on achieving measurable results.
While implementing Lean Six Sigma comes with challenges, these obstacles can be overcome with the right approach. By fostering a culture of change, investing in training, ensuring leadership support, and measuring progress, businesses can successfully integrate Lean Six Sigma and drive lasting improvements.