Manufacturing workflow management is a systematic approach that coordinates, controls, and optimizes the flow of production activities in a manufacturing environment. It integrates various processes, resources, and technologies to ensure efficient and effective production operations. This comprehensive guide covers the essential components and benefits of manufacturing workflow management, providing valuable insights for manufacturers looking to streamline their operations.
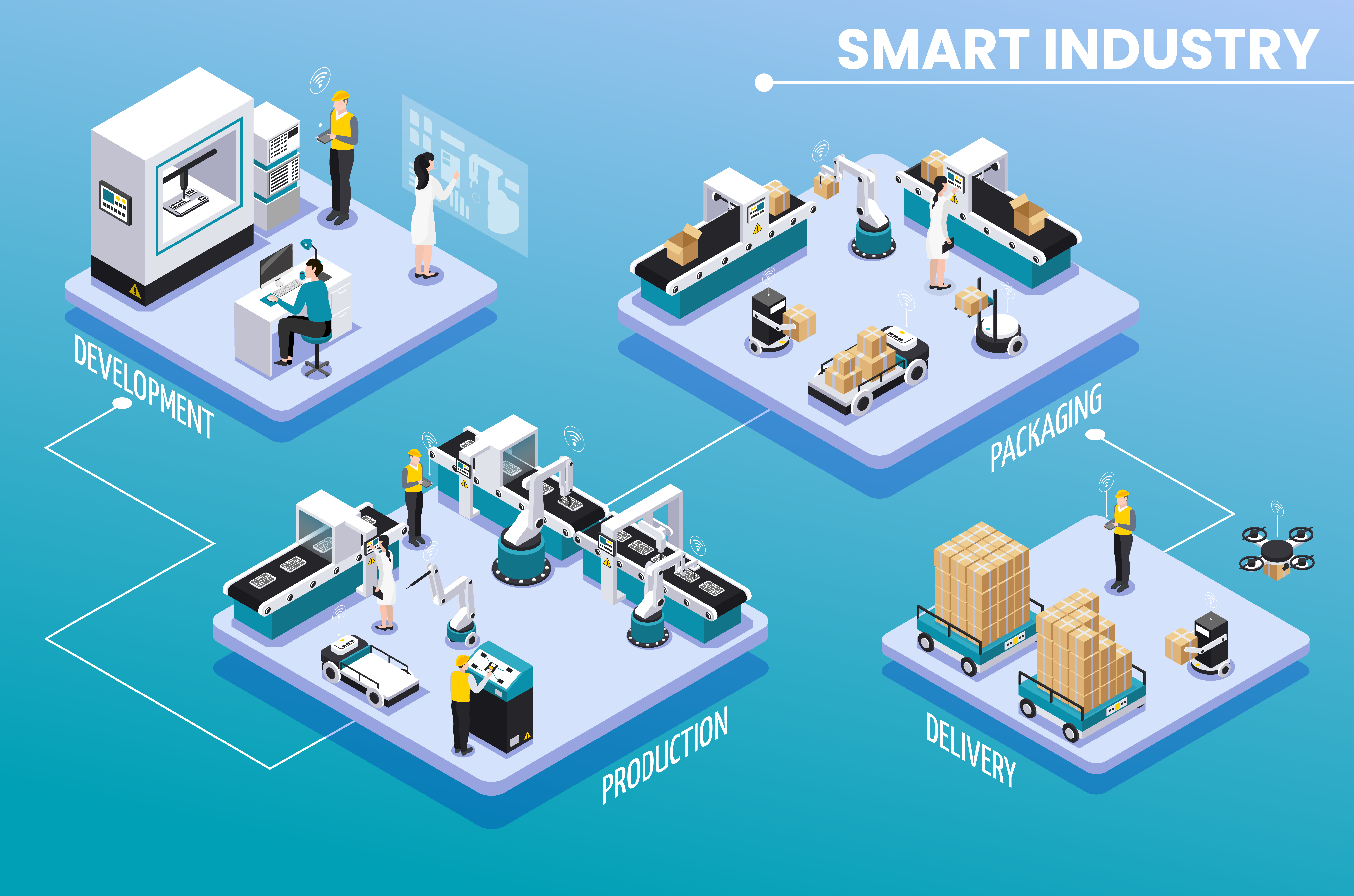
Key Components of Manufacturing Workflow Management
Process Design and Mapping: The foundation of effective manufacturing workflow management is a well-designed process map. This involves creating detailed diagrams of production processes, including each step, sequence, and dependency. Process optimization helps identify bottlenecks and inefficiencies, enabling streamlined operations and improved productivity.
Task management: Task management involves planning, tracking, and organizing tasks to ensure efficient completion. It includes setting priorities, deadlines, assigning responsibilities, and monitoring progress to achieve goals effectively. Task management tools and techniques help streamline workflows, enhance productivity, and improve collaboration within teams.
Resource Management: Efficient resource management is crucial for manufacturing success. This involves allocating tasks to machines, equipment, and personnel based on their availability and capacity. Additionally, inventory management ensures raw materials, work-in-progress items, and finished goods are tracked and available when needed, preventing production delays.
Production Scheduling: Production scheduling is the heart of workflow management. Job scheduling plans and sequences production activities to optimize machine usage and minimize downtime. Capacity planning assesses production capabilities to meet demand without overloading resources, ensuring a balanced and efficient production process.
Quality Control: Maintaining high-quality standards is vital in manufacturing. Quality control involves implementing inspection and testing procedures at various production stages to ensure products meet required standards. Defect management tracks and addresses any issues promptly, reducing waste and enhancing product quality.
Real-Time Monitoring and Control: Real-time monitoring is essential for proactive management. Production tracking systems provide real-time visibility into the status of production activities, ensuring adherence to schedules and identifying potential issues early. Data collection from machines and processes allows for detailed analysis and informed decision-making.
Integration with Other Systems: Integrating manufacturing workflow management with other systems enhances efficiency. ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) integration ensures seamless data flow and coordination across departments. MES (Manufacturing Execution Systems) integration manages and controls shop floor production, optimizing overall operations.
Reporting and Analytics: Data-driven insights are crucial for continuous improvement. Tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) such as cycle time, throughput, and yield provides valuable insights into production performance. Analyzing production data helps identify trends, patterns, and areas for improvement, supporting strategic planning.
Benefits of Manufacturing Workflow Management
Increased Efficiency: Streamlined workflows and optimized processes reduce production time and costs, enhancing overall efficiency.
Improved Quality: Consistent quality control ensures high-quality products, reducing defects and enhancing customer satisfaction.
Enhanced Flexibility: Adaptable workflows allow quick responses to changes in demand or production conditions, maintaining productivity.
Better Resource Utilization: Efficient resource allocation minimizes waste and maximizes productivity, optimizing the use of machines and personnel.
Real-Time Visibility: Continuous monitoring provides insights into production status and performance, enabling proactive management and quick issue resolution.
Data-Driven Decision Making: Comprehensive data collection and analysis support informed decision-making, driving strategic planning and operational improvements.
Reduced Downtime: Effective scheduling and maintenance planning reduce machine downtime, increasing overall uptime and productivity.
How to create Workflow Management
Define Objectives: Identify workflow goals and scope.
Map Workflow: Break down tasks, sequence them, and create visual diagrams.
Assign Roles: Allocate tasks to team members based on skills and define responsibilities.
Set Timelines: Estimate task durations, create schedules, and set deadlines.
Monitor Progress: Track tasks in real-time, update statuses, and address issues.
Review and Optimize: Gather feedback, analyze performance, and refine the workflow for continuous improvement.