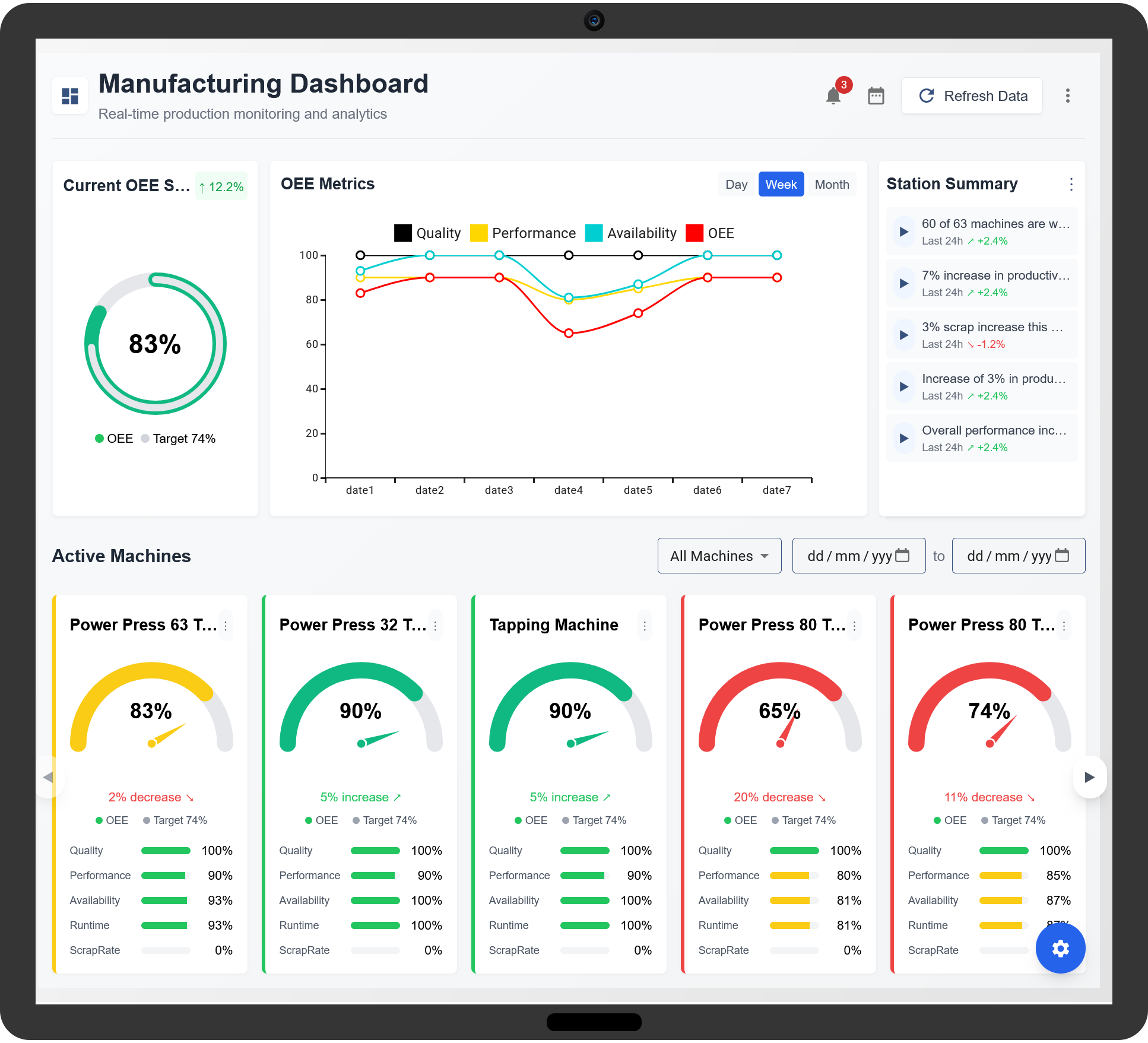
Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) is a crucial performance metric in the manufacturing industry, used to measure how effectively manufacturing equipment is being utilized. OEE combines three important aspects of manufacturing operations: availability, performance, and quality. By calculating and monitoring OEE, manufacturers can identify inefficiencies, reduce downtime, and improve production output, leading to enhanced operational efficiency and cost savings.
Understanding the Components of OEE
OEE is derived from three key components that assess different aspects of equipment performance. These components are:
- Availability: This measures the percentage of scheduled production time that the equipment is available for production. It accounts for all unplanned downtime, such as machine breakdowns, maintenance, or delays in the production process.
- Performance: This measures the speed at which equipment operates relative to its designed capacity. It takes into account factors like slower cycle times, minor stops, and inefficiencies that reduce the actual performance of the equipment compared to its optimal output.
- Quality: This component measures the proportion of products produced that meet quality standards, as opposed to those that are defective or require rework. Quality is critical in ensuring that the output from the equipment contributes to the final product specifications without any waste or defects.
The OEE score is calculated by multiplying the three components together:
OEE = Availability × Performance × Quality
Why is OEE Important in Manufacturing?
OEE is important because it provides a comprehensive view of manufacturing efficiency. By tracking OEE, companies can pinpoint areas of inefficiency and take proactive steps to address them. This leads to several benefits in manufacturing:
- Improved Efficiency: By focusing on improving availability, performance, and quality, OEE helps manufacturers optimize their production processes and reduce wasted time and resources.
- Increased Productivity: Tracking OEE can identify bottlenecks and performance gaps in production, enabling manufacturers to enhance throughput and increase the overall output of their operations.
- Better Maintenance Practices: OEE data helps identify patterns of downtime, allowing for predictive maintenance strategies that reduce unplanned downtime and extend the lifespan of equipment.
- Cost Reduction: By reducing inefficiencies, OEE helps reduce costs associated with wasted time, resources, and materials. A higher OEE score correlates with a more cost-effective manufacturing process.
- Continuous Improvement: OEE encourages a continuous improvement culture by providing measurable data on performance. By regularly monitoring and acting upon OEE results, manufacturers can make incremental improvements that accumulate over time, leading to greater operational effectiveness.
How to Calculate OEE
OEE calculation involves three main steps, which are derived from the availability, performance, and quality components. Below is a breakdown of each calculation:
1. Availability
Availability measures the percentage of time that equipment is available for production. It is calculated by dividing the actual production time by the planned production time. The formula for availability is:
Availability = (Planned Production Time - Downtime) / Planned Production Time
2. Performance
Performance measures how fast the equipment is running compared to its maximum possible speed. The formula for performance is:
Performance = (Ideal Cycle Time × Total Units Produced) / Actual Production Time
Where the Ideal Cycle Time refers to the time it takes for a machine to produce one unit when running at its optimal speed. If the performance ratio is less than 100%, it indicates that the equipment is running slower than its maximum capacity.
3. Quality
Quality measures the percentage of products that meet quality standards without defects. The formula for quality is:
Quality = Good Units / Total Units Produced
Where Good Units are those that meet quality specifications, and Total Units Produced refers to the total number of units produced, including both good and defective units.
OEE Benchmarks and Targets
In manufacturing, OEE benchmarks vary depending on the type of industry, equipment, and production processes. However, a general guideline for OEE performance is:
- 100% OEE: This represents perfect production, where equipment operates at full availability, performance, and quality without any issues or downtime.
- 85% OEE: This is considered world-class performance in most manufacturing industries. Achieving an 85% OEE score indicates that a facility is operating efficiently and effectively.
- 60% OEE: This is typically considered an average OEE score. While not ideal, it suggests that there is significant room for improvement in terms of availability, performance, or quality.
- Below 60% OEE: A score below 60% indicates that the facility is underperforming, with substantial inefficiencies present that need to be addressed.
Setting OEE targets helps manufacturers strive for continuous improvement, aligning operational goals with financial outcomes. Regular OEE monitoring can help assess the effectiveness of improvement initiatives and identify areas where additional focus is needed.
Improving OEE in Manufacturing
To improve OEE, manufacturers need to address the factors that affect availability, performance, and quality. Below are some strategies to optimize each of these components:
1. Improving Availability
Availability can be improved by minimizing downtime. Some strategies to achieve this include:
- Preventive Maintenance: Implementing a strong preventive maintenance program ensures that equipment is regularly serviced and potential issues are identified before they cause unplanned downtime.
- Quick Changeovers: Reducing changeover times between production runs can help improve equipment availability by ensuring that machines are operating at full capacity for longer periods.
- Root Cause Analysis: When downtime occurs, performing a root cause analysis helps identify underlying issues that can be addressed to prevent future occurrences.
2. Improving Performance
To improve performance, the focus should be on increasing the speed of production while minimizing waste and inefficiencies. Strategies include:
- Optimizing Machine Settings: Adjusting machine settings to maximize output while maintaining product quality can improve performance.
- Minimizing Minor Stops: Identifying and addressing minor stops, such as jams or interruptions, helps reduce the time lost during production.
- Training Operators: Well-trained operators are more efficient in running machines at optimal performance levels, reducing slowdowns and errors.
3. Improving Quality
Improving quality is key to ensuring that products meet specifications and reduce waste. Some approaches to improve quality include:
- Quality Control Systems: Implementing rigorous quality control processes helps ensure that defects are identified early and corrected before they affect production.
- Employee Involvement: Involving employees in quality improvement initiatives helps create a culture of accountability and attention to detail.
- Automated Inspections: Using automated inspection systems can help identify defects early in the production process, ensuring that only high-quality products are produced.
What is OEE in the manufacturing industry?
What is OEE in the manufacturing industry?
OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness) is a metric used to measure the efficiency of manufacturing equipment by considering factors like availability, performance, and quality. It helps identify losses, inefficiencies, and areas for improvement in the production process.
Why is OEE important for manufacturers?
OEE is crucial for manufacturers because it provides insight into how effectively production equipment is being used. It helps optimize production processes, reduce waste, improve product quality, and increase profitability by minimizing downtime and inefficiencies.
How is OEE calculated?
OEE is calculated using the following formula: OEE = Availability × Performance × Quality. Each component is calculated based on specific metrics, such as operating time, cycle time, and defective products.
What are the components of OEE?
The components of OEE include:
- Availability: Measures the percentage of time equipment is available for production.
- Performance: Measures how well equipment operates compared to its maximum capacity.
- Quality: Measures the percentage of good products produced compared to the total output.
What does a good OEE score look like?
A world-class OEE score is typically 85% or higher. Scores below 60% indicate a need for significant improvement, while a score between 60% and 85% reflects a production process that could benefit from optimization.
How can OEE help identify production inefficiencies?
OEE helps identify production inefficiencies by breaking down equipment performance into three key areas: availability, performance, and quality. By tracking these metrics, manufacturers can pinpoint where losses are occurring and focus efforts on improvement.
How can OEE be improved in a manufacturing environment?
OEE can be improved by addressing the root causes of downtime, optimizing machine speeds, reducing defects, and implementing preventive maintenance. Continuous monitoring and data analysis help identify improvement opportunities in real time.
What is the difference between OEE and productivity?
OEE measures the effectiveness of equipment usage in production, while productivity measures the overall output of the manufacturing process. OEE focuses on machine performance, while productivity considers the entire process efficiency, including labor and materials.
How does OEE impact overall production costs?
OEE directly impacts production costs by highlighting inefficiencies and equipment issues that lead to increased downtime, slow production speeds, and defective products. By improving OEE, manufacturers can reduce operational costs and increase profitability.
What role does OEE play in continuous improvement processes?
OEE plays a key role in continuous improvement processes by providing data on performance gaps. It enables manufacturers to identify areas for improvement, prioritize actions, and track the effectiveness of improvement initiatives over time.
Can OEE be used to benchmark manufacturing performance?
Yes, OEE is often used to benchmark manufacturing performance by comparing it across shifts, production lines, or even facilities. It helps set performance standards and track progress toward achieving optimal equipment efficiency.
How does OEE help with downtime management?
OEE helps with downtime management by tracking and categorizing downtime events. This enables manufacturers to identify the causes of downtime, such as equipment failures or setup issues, and take corrective actions to reduce its frequency and impact.
What is the relationship between OEE and equipment reliability?
OEE is closely linked to equipment reliability because frequent breakdowns or performance issues reduce availability and performance, lowering OEE scores. Improving equipment reliability through maintenance and monitoring increases OEE and ensures smoother operations.
Can OEE be applied to both new and old equipment?
Yes, OEE can be applied to both new and old equipment. However, older machines may experience more frequent breakdowns and require more maintenance, which can affect OEE scores. Proper monitoring and maintenance can help improve their effectiveness.
How does OEE contribute to overall operational efficiency?
OEE contributes to overall operational efficiency by identifying and addressing inefficiencies in equipment usage. By improving OEE, manufacturers can increase productivity, reduce waste, improve product quality, and lower production costs, leading to greater operational efficiency.