In the manufacturing world, efficiency is paramount. With increasing competition and demand for high-quality products, manufacturers must find ways to optimize their processes and reduce waste. One of the most effective methods for achieving this is by using Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE). OEE is a key performance indicator (KPI) that helps manufacturers understand how well their equipment is performing, identify inefficiencies, and improve productivity. But what exactly is OEE, and how does it work? Let’s break it down.
What Is OEE?
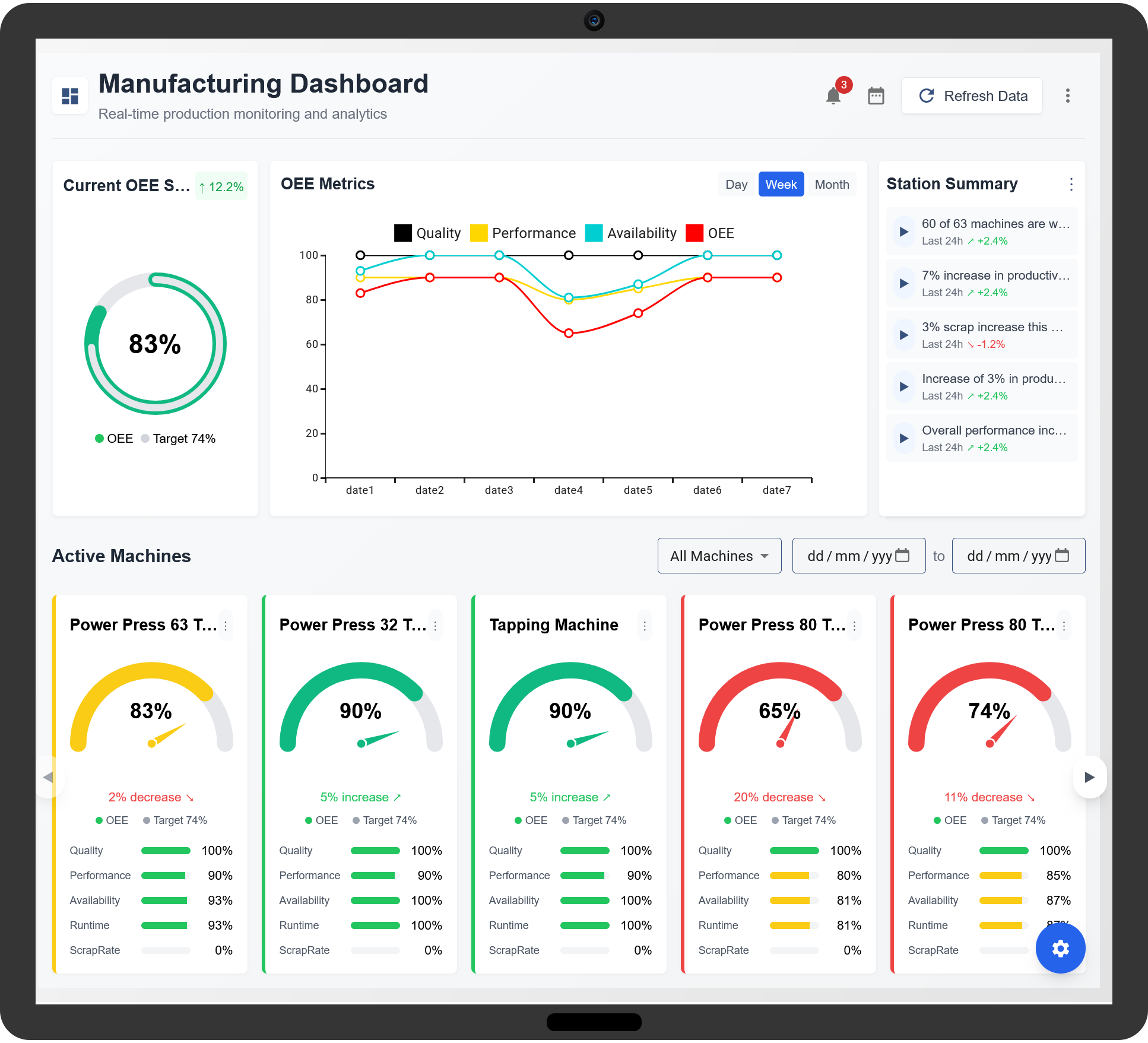
Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) is a comprehensive metric used to measure the effectiveness of manufacturing equipment. It takes into account the three main factors that affect equipment performance: availability, performance, and quality. These three factors are combined into a single percentage, which reflects the overall effectiveness of a production process or piece of equipment. The goal is to identify areas of improvement and help manufacturers increase production efficiency, reduce downtime, and improve product quality.
The Three Pillars of OEE
OEE is calculated based on three key factors: availability, performance, and quality. Let’s take a closer look at each of these pillars:
- Availability: This measures the amount of time that equipment is available to produce goods compared to the total scheduled production time. Downtime, such as machine breakdowns, maintenance, or setup changes, reduces the availability score. The formula for availability is:
Availability = (Actual Operating Time / Planned Production Time) x 100
Performance = (Ideal Cycle Time x Total Units Produced / Actual Operating Time) x 100
Quality = (Good Units Produced / Total Units Produced) x 100
Once these factors are calculated, they are multiplied together to determine the OEE score. The formula for OEE is:
OEE = Availability x Performance x Quality
The result is expressed as a percentage, with 100% representing perfect production. In reality, OEE scores above 85% are considered excellent, while scores below 60% typically indicate significant inefficiencies.
How Does OEE Work in Practice?
OEE works by collecting data from equipment and production processes in real-time, which allows manufacturers to assess the effectiveness of their operations. Let’s explore how this works in practice:
1. Monitoring Equipment Performance
The first step in using OEE is to monitor the performance of manufacturing equipment. This involves tracking various aspects of machine operation, such as run time, downtime, cycle times, and product quality. Manufacturers can use sensors, data collection systems, and software solutions to gather this data in real-time. For example, if a machine experiences unexpected downtime, it can be logged as an availability loss, and the system will track the length of the downtime to calculate the availability percentage.
2. Identifying Losses and Inefficiencies
Once the data is collected, it’s analyzed to identify where losses are occurring. These losses are categorized into three types: availability losses, performance losses, and quality losses. Availability losses occur due to unplanned downtime, such as machine breakdowns or maintenance. Performance losses occur when machines are not running at their optimal speed or efficiency. Quality losses happen when defects are produced, or products need to be reworked. By analyzing these losses, manufacturers can pinpoint the root causes of inefficiency and take corrective actions to improve equipment effectiveness.
3. Making Data-Driven Improvements
OEE provides valuable insights into how equipment is being used, helping manufacturers make data-driven decisions. For example, if performance losses are identified due to frequent minor stoppages, the company can look into optimizing the production process or adjusting machine settings to reduce these stoppages. Similarly, if quality losses are high, the manufacturer may need to improve their quality control processes or address issues with materials or equipment calibration. By taking action on the insights provided by OEE data, manufacturers can continuously improve their equipment effectiveness and optimize their production processes.
4. Setting Targets and Benchmarks
OEE also helps manufacturers set performance targets and benchmarks. By calculating the OEE score over time, businesses can track improvements and assess whether their equipment is becoming more effective. For example, if the OEE score for a particular machine is 60%, the goal might be to increase it to 80% over the next six months. This can be achieved by addressing downtime, optimizing performance, and improving quality. OEE provides a clear, measurable way to track progress toward these goals and ensure that equipment is operating at its full potential.
Benefits of Using OEE
OEE is a powerful tool that offers numerous benefits for manufacturers looking to improve efficiency and reduce waste. Some of the key benefits include:
- Increased Productivity: By identifying and addressing equipment inefficiencies, manufacturers can increase production output without adding additional resources or labor.
- Reduced Downtime: OEE helps manufacturers track and reduce downtime by identifying the root causes of unplanned stoppages and enabling proactive maintenance scheduling.
- Improved Quality: OEE allows manufacturers to track quality losses, helping them to improve product quality and reduce defects and rework.
- Cost Savings: Optimizing equipment effectiveness reduces operational costs by improving resource utilization, decreasing waste, and minimizing downtime.
- Continuous Improvement: OEE provides a continuous feedback loop, allowing manufacturers to constantly monitor, measure, and improve their equipment and processes over time.
Challenges of Implementing OEE
While OEE is a powerful metric, there are challenges involved in implementing it effectively. One of the main challenges is ensuring accurate data collection. Without accurate, real-time data, OEE calculations can be misleading, making it difficult to identify inefficiencies. Additionally, implementing OEE requires a culture of continuous improvement, where employees are empowered to take action based on the data. This requires training, collaboration, and a commitment to data-driven decision-making at all levels of the organization.
What Is OEE and How Does It Work?
What is OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness)?
OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness) is a performance metric used in manufacturing to measure the efficiency of equipment. It helps identify losses, track performance, and provide actionable insights into improving productivity.
How does OEE work in manufacturing?
OEE works by tracking three main components—Availability, Performance, and Quality. By measuring how well equipment is performing compared to its full potential, manufacturers can identify inefficiencies and areas for improvement.
Why is OEE important for manufacturing operations?
OEE is crucial for manufacturing because it provides a clear picture of how well machines are utilized. By identifying the reasons for lost time, performance issues, and defects, it helps businesses improve productivity, reduce waste, and increase profitability.
What are the key components of OEE?
The three key components of OEE are Availability, Performance, and Quality. Availability measures equipment uptime, Performance measures how fast the equipment operates relative to its capacity, and Quality measures the number of good products produced compared to the total produced.
How is OEE calculated?
OEE is calculated by multiplying the three components—Availability, Performance, and Quality. The formula is: OEE = (Availability) × (Performance) × (Quality).
What is the formula for calculating OEE?
The formula for calculating OEE is: OEE = (Availability × Performance × Quality). This gives a percentage value representing the overall effectiveness of equipment.
What does each OEE component (Availability, Performance, Quality) mean?
Availability refers to the time equipment is available for production. Performance refers to how efficiently the equipment operates. Quality measures the proportion of good-quality products produced versus total production.
How can OEE help improve manufacturing efficiency?
OEE helps improve manufacturing efficiency by identifying areas where equipment is underperforming. It highlights losses due to downtime, slow speeds, or defects, providing manufacturers with data to implement corrective actions that increase productivity and reduce waste.
What is considered a good OEE score?
A good OEE score typically ranges from 85% to 100%. A score of 85% or higher is considered world-class, indicating that the equipment is operating efficiently and producing high-quality output with minimal downtime.
What are the common causes of low OEE?
Common causes of low OEE include equipment breakdowns (low Availability), slower-than-expected production speeds (low Performance), and quality defects (low Quality). These factors lead to inefficiencies that can be identified and corrected through OEE analysis.
How can you improve OEE in manufacturing?
Improving OEE involves reducing downtime (increasing Availability), optimizing machine speeds (improving Performance), and minimizing defects (enhancing Quality). Techniques such as preventive maintenance, operator training, and process improvements can all contribute to a better OEE score.
How does OEE track machine availability?
OEE tracks machine availability by monitoring downtime events. The time when equipment is not running due to breakdowns, maintenance, or setup changes is deducted from the total available time, providing an accurate measure of equipment uptime.
How does OEE measure production speed?
OEE measures production speed by comparing the actual production rate to the theoretical maximum rate of the equipment. If a machine is running slower than its full potential, it will reduce the Performance score and indicate areas for improvement.
How does OEE measure product quality?
OEE measures product quality by comparing the number of good products to the total number produced. Defective or reworked products are considered losses, reducing the Quality component of OEE and highlighting areas for quality control improvements.
What role does OEE play in continuous improvement processes?
OEE plays a key role in continuous improvement by providing insights into equipment performance and identifying areas where losses occur. By regularly monitoring OEE, manufacturers can track improvements, adjust processes, and implement strategies that drive ongoing productivity enhancements.