What is a Balanced Scorecard?
A Balanced Scorecard (BSC) is a strategic management tool that provides a comprehensive framework for monitoring and managing an organisation's performance. Developed by Robert Kaplan and David Norton in the early 1990s, the BSC goes beyond traditional financial metrics to include non-financial aspects, giving a holistic view of an organisation's health and progress. This approach helps organisations align their activities to the vision and strategy, improve internal and external communications, and monitor performance against strategic goals.
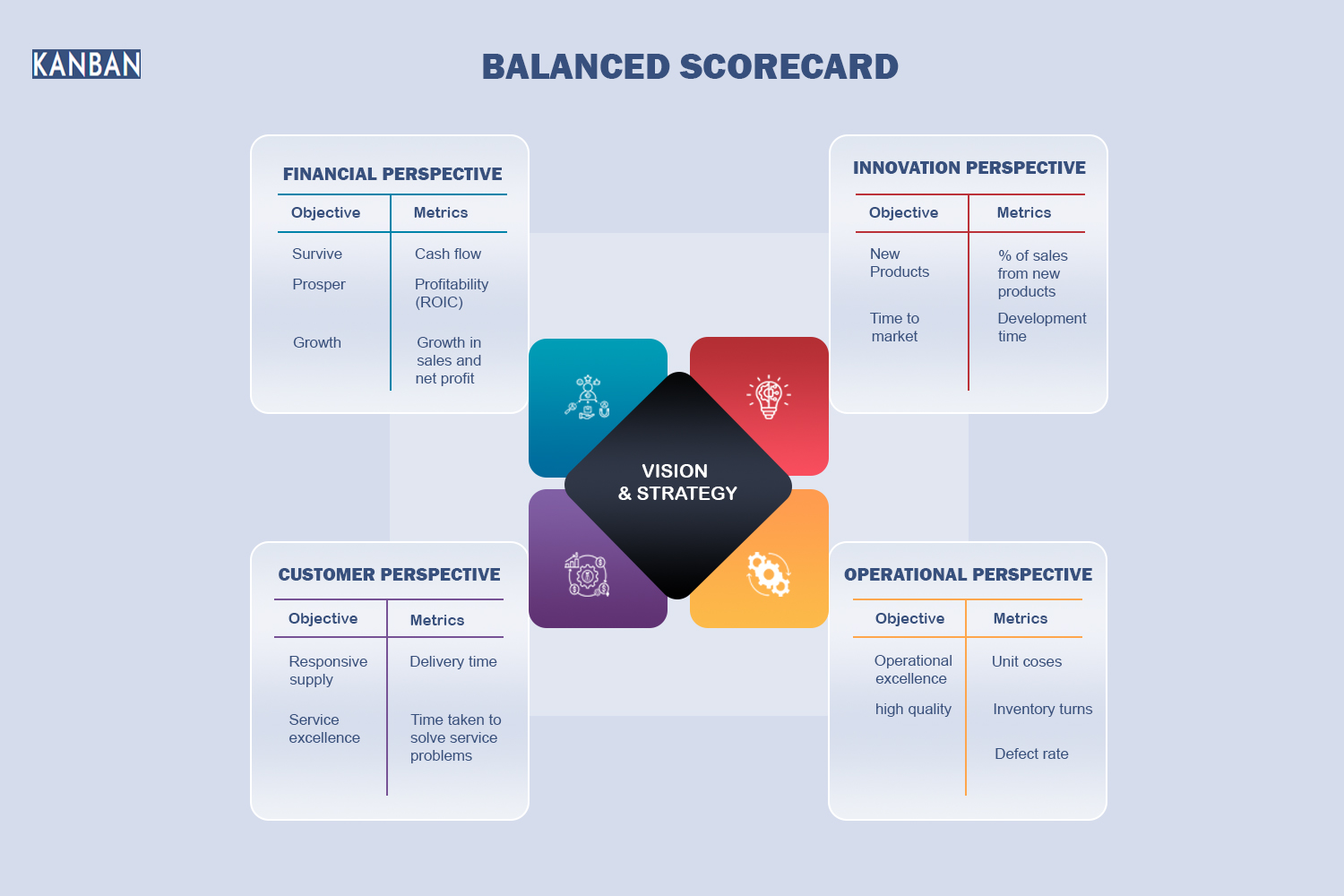
Four Perspectives of a Balanced Scorecard
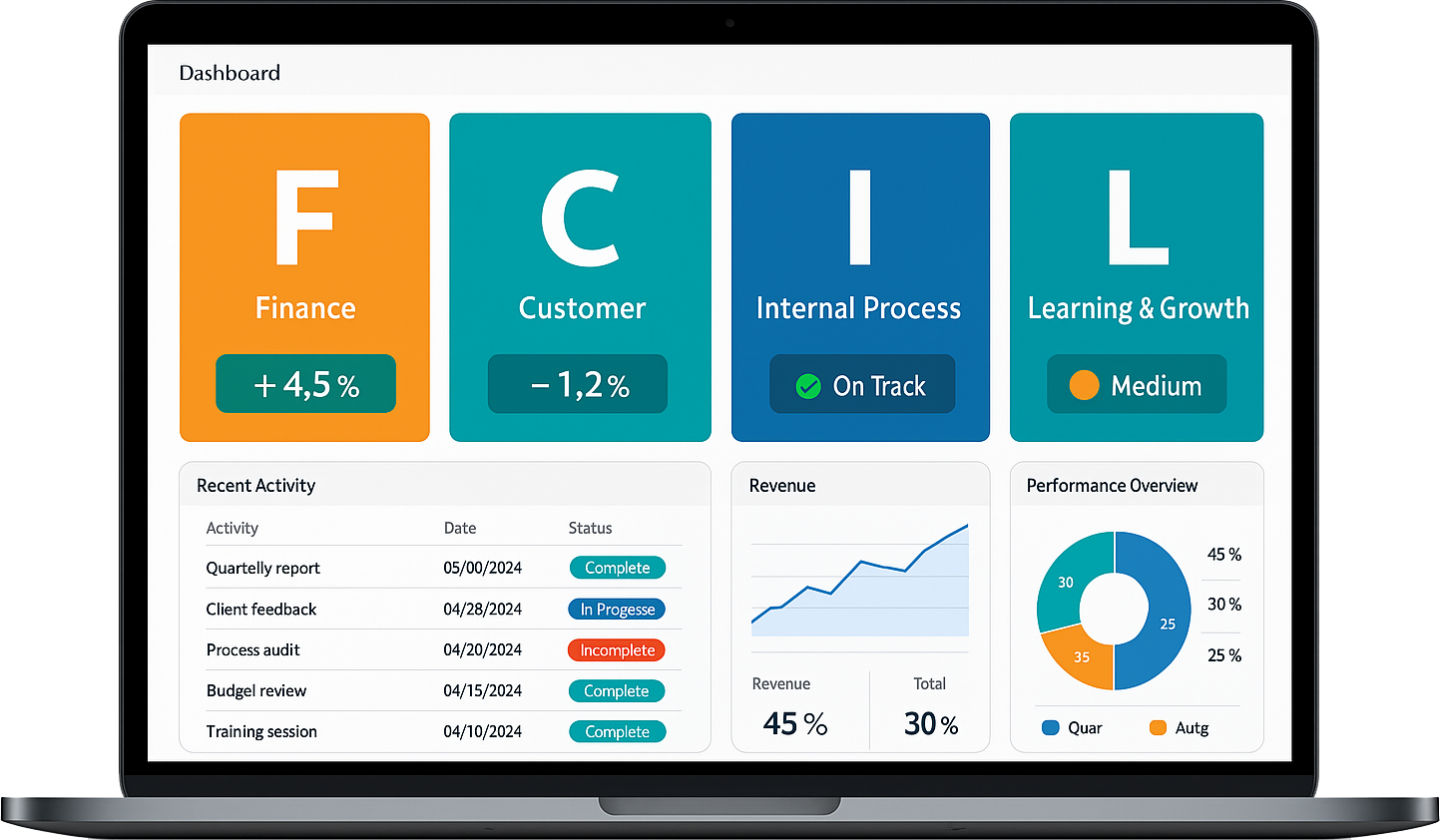
Financial Perspective:
Objective: Measures the financial performance of the organisation.
Key Metrics: Revenue growth, profitability, return on investment (ROI), and cost management.
Purpose: To ensure that the company’s financial health is improving and that it is delivering value to shareholders.
Customer Perspective:
Objective: Assesses customer satisfaction and market positioning.
Key Metrics: Customer satisfaction score (CSAT), net promoter score (NPS), market share, and customer retention rates.
Purpose: To ensure that the organisation is meeting customer needs and expectations, which is crucial for long-term success.
Internal Processes Perspective:
Objective: Evaluates the efficiency and quality of internal processes.
Key Metrics: Process cycle time, defect rates, cost per process, and efficiency ratios.
Purpose: To improve the internal operations that create value for customers and shareholders.
Learning and Growth Perspective:
Objective: Focuses on the development of organisational culture and employee capabilities.
Key Metrics: Employee satisfaction, training and development hours, innovation rates, and employee turnover.
Purpose: To ensure the organisation is continuously improving and innovating by investing in its people and infrastructure.
How Does the Balanced Scorecard Drive Business Improvement?
Aligning Strategic Objectives: The Balanced Scorecard(BSC) helps organisations translate their vision and strategy into specific, actionable objectives across different perspectives. This alignment ensures that all departments and employees are working towards common goals, fostering a unified direction.
Improving Communication: By providing a common language and framework for discussing strategy and performance, the Balanced Scorecard(BSC) enhances communication across the organisation. This improved communication helps ensure that everyone understands the strategic priorities and how their roles contribute to achieving them.
Enhancing Decision-Making: The Balanced Scorecard(BSC) offers a balanced view of organisational performance by integrating financial and non-financial measures. This holistic perspective enables better-informed decisions, as leaders can see the impact of their choices on various aspects of the business.
Tracking Progress: The Balanced Scorecard(BSC) provides a mechanism for regularly monitoring and reviewing performance against strategic targets. This tracking allows organisations to identify areas where they are on track and where they need to make adjustments, ensuring that they stay aligned with their strategic objectives.
Encouraging Continuous Improvement: By identifying areas for improvement across various business functions, the Balanced Scorecard(BSC) fosters a culture of continuous improvement. Organisations can use the insights gained from the BSC to implement changes and measure the impact of those changes, driving ongoing enhancement of processes, customer satisfaction, and financial performance.

How to Implement a Balanced Scorecard?
Define Vision and Strategy: Clarify your organisation's mission, vision, and strategic objectives.
Identify Perspectives: Determine key performance perspectives: Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, Learning and Growth.
Select KPIs: Choose relevant Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for each perspective.
Set Targets: Define measurable targets for each KPI.
Develop Initiatives: Create action plans to achieve the targets.
Communicate and Train: Ensure all employees understand the Balanced Scorecard(BSC) and their role in it.
Monitor and Review: Regularly track progress, review performance, and adjust strategies as needed.
What is the Balanced Scorecard?
1. What is the Balanced Scorecard?
The Balanced Scorecard is a strategic management tool that organisations use to track performance by monitoring key business objectives across four perspectives: Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, and Learning and Growth.
2. What are the four perspectives of the Balanced Scorecard?
The four perspectives of the Balanced Scorecard are Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, and Learning and Growth. These perspectives provide a comprehensive view of organisational performance from different angles.
3. How does the Balanced Scorecard help organisations?
The Balanced Scorecard helps organisations align their strategic goals with daily operations by translating high-level objectives into measurable outcomes and tracking performance in critical areas of the business.
4. How is the Balanced Scorecard different from traditional performance management systems?
Unlike traditional systems that focus primarily on financial metrics, the Balanced Scorecard includes non-financial measures like customer satisfaction, internal processes, and learning and growth to provide a more holistic view of performance.
5. How can organisations implement the Balanced Scorecard?
Organisations can implement the Balanced Scorecard by defining strategic objectives, identifying key performance indicators (KPIs), setting targets, aligning initiatives, and regularly reviewing progress to ensure strategic alignment.
6. Can the Balanced Scorecard be customised?
Yes, the Balanced Scorecard is highly customisable. Organisations can tailor it to their specific needs by adjusting perspectives, metrics, and objectives to fit their strategy and industry.
7. What are Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) in the Balanced Scorecard?
KPIs are measurable metrics that track the performance of an organisation against its strategic goals. Examples include revenue growth (Financial), customer retention (Customer), and employee training (Learning and Growth).
8. Who uses the Balanced Scorecard?
The Balanced Scorecard is used by a wide range of organisations, from large corporations to small businesses, as well as non-profits and government agencies. It is typically employed by senior leaders and managers to track organisational performance.
9. How often should the Balanced Scorecard be updated?
The Balanced Scorecard should be updated quarterly or annually to reflect changes in strategic objectives, market conditions, or new performance data.
10. What are the benefits of using a Balanced Scorecard?
The Balanced Scorecard provides a comprehensive view of performance, improves strategic alignment, fosters better decision-making, and enhances accountability within the organisation.
11. Can small businesses use the Balanced Scorecard?
Yes, small businesses can effectively use the Balanced Scorecard to align their operations with strategic goals and improve overall performance, making it a flexible tool for organisations of any size.
12. What role does leadership play in the success of the Balanced Scorecard?
Leadership plays a crucial role in the success of the Balanced Scorecard by setting clear objectives, promoting alignment across departments, and fostering a culture of accountability and performance monitoring.
13. How does the Balanced Scorecard drive continuous improvement?
The Balanced Scorecard drives continuous improvement by regularly monitoring performance data, identifying areas for improvement, and adjusting strategies to enhance operational efficiency and outcomes.
14. What are common challenges in implementing the Balanced Scorecard?
Common challenges include defining clear objectives, selecting the right KPIs, ensuring alignment across departments, and overcoming resistance to change within the organisation.
15. What is a strategy map in the Balanced Scorecard framework?
A strategy map is a visual tool that shows the cause-and-effect relationships between the organisation's objectives across the four Balanced Scorecard perspectives, helping stakeholders understand how different goals are interconnected.