What is a Balanced Scorecard (BSC)?
A Balanced Scorecard (BSC) is a strategic tool used to measure and improve business performance. It helps organisations align their activities with key goals by focusing on multiple areas, not just financial results.
Key Perspectives of a Balanced Scorecard
The BSC evaluates performance through four key perspectives:
- Financial: Tracks revenue, costs, and profitability.
- Customer: Measures customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Internal Processes: Assesses operational efficiency.
- Learning and Growth: Focuses on employee development and innovation.
By using a Balanced Scorecard, organisations can achieve long-term success through continuous improvement and strategic alignment.
What are the Four Perspectives of a Balanced Scorecard (BSC)?
The Balanced Scorecard (BSC) is a strategic tool that helps organisations measure performance from multiple angles. It provides a balanced view of success by focusing on four key perspectives. These perspectives ensure that businesses improve in all areas, not just financial performance.
Financial Perspective
This perspective focuses on financial performance and profitability. It includes key metrics such as revenue growth, cost management, and return on investment. Strong financial performance ensures the long-term success of an organisation.
Customer Perspective
The customer perspective measures how well a business meets customer needs. It includes factors like customer satisfaction, retention, and loyalty. A business that delivers value to customers will build strong relationships and maintain a competitive advantage.
Internal Processes Perspective
This area focuses on operational efficiency and process improvement. It evaluates how well an organisation’s internal processes support its goals. Improving workflow, reducing waste, and enhancing productivity are key to maintaining smooth operations.
Learning and Growth Perspective
This perspective focuses on employee development, skills, and innovation. It includes training programmes, employee engagement, and knowledge-sharing. A strong focus on learning helps businesses adapt to change and improve overall performance.
By balancing these four perspectives, organisations can create a well-rounded strategy that drives long-term success and continuous improvement.
Why is it Called a "Balanced" Scorecard?
The Balanced Scorecard (BSC) is called "balanced" because it provides a complete view of organisational performance. Instead of focusing only on financial outcomes, it includes other critical areas that drive long-term success. This approach ensures a well-rounded strategy that aligns business activities with overall goals.
How Does It Achieve Balance?
- Financial and Non-Financial Measures: It evaluates profits alongside customer satisfaction, internal processes, and employee growth.
- Short-Term and Long-Term Focus: It helps businesses achieve immediate goals while planning for sustainable success.
- Internal and External Performance: It assesses operational efficiency as well as customer relationships.
By balancing these perspectives, organisations can make informed decisions, improve efficiency, and enhance overall business performance.
What is a Strategy Map, and How Does it Relate to the BSC?
A strategy map is a visual representation of an organisation’s key objectives and how they connect across different areas. It helps businesses align their goals, improve communication, and ensure that all departments work towards a common strategy.
How a Strategy Map Works
A strategy map outlines objectives within four key areas, similar to the Balanced Scorecard (BSC):
- Financial: Goals related to revenue growth and cost efficiency.
- Customer: Objectives focused on customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Internal Processes: Strategies to improve workflow and productivity.
- Learning and Growth: Goals for employee development and innovation.
How It Relates to the Balanced Scorecard
A strategy map and the BSC work together to create a structured approach to performance management. The strategy map provides a clear framework for achieving objectives, while the BSC tracks progress using measurable indicators.
By using both tools, organisations can align their vision, improve efficiency, and drive long-term success.
How Can a Balanced Scorecard (BSC) Help an Organisation Improve Its Strategic Planning?
A Balanced Scorecard (BSC) helps organisations improve strategic planning by providing a clear structure for setting, tracking, and achieving goals. It ensures that all areas of the business align with the overall strategy, leading to better decision-making and long-term success.
Aligning Goals with Strategy
The BSC helps businesses define key objectives across different areas, including financial performance, customer satisfaction, internal processes, and employee growth. This alignment ensures that every department works towards the same vision.
Tracking Performance
With measurable indicators, the BSC allows organisations to monitor progress in real time. It helps identify strengths, weaknesses, and areas needing improvement, making adjustments easier.
Enhancing Communication
A well-structured BSC improves internal communication by clearly outlining priorities and expectations. Teams can better understand their roles and how their work contributes to the organisation’s success.
By using a Balanced Scorecard, businesses can create a focused, data-driven strategy that enhances efficiency, drives growth, and ensures continuous improvement.
What are Key Performance Indicators (KPIs), and How Are They Used in a Balanced Scorecard (BSC)?
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are measurable values that help organisations track progress towards their goals. They provide clear insights into performance by measuring success in different areas, such as finance, customer satisfaction, operations, and employee development.
How KPIs Work
KPIs are selected based on business objectives and help organisations monitor efficiency, productivity, and overall success. They can be quantitative, like revenue growth, or qualitative, like customer feedback scores. Effective KPIs are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound.
Using KPIs in a Balanced Scorecard (BSC)
In a Balanced Scorecard, KPIs are assigned to different perspectives to track performance:
- Financial Perspective: Measures revenue, profit margins, and cost reductions.
- Customer Perspective: Tracks customer satisfaction, retention rates, and service quality.
- Internal Processes Perspective: Monitors production efficiency, error rates, and process improvements.
- Learning and Growth Perspective: Evaluates employee training, skill development, and innovation.
Why KPIs Matter in a BSC
KPIs help businesses assess performance, identify areas for improvement, and make data-driven decisions. They ensure that all activities align with strategic goals, leading to continuous improvement and long-term success.
How Does a Balanced Scorecard (BSC) Improve Communication and Alignment Within an Organisation?
A Balanced Scorecard (BSC) improves communication and alignment by providing a structured approach to strategy execution. It ensures that all departments understand business goals and work towards common objectives.
Creating a Clear Vision
The BSC translates strategic goals into specific, measurable objectives. By outlining priorities across financial, customer, internal process, and learning perspectives, it helps employees understand how their roles contribute to success.
Enhancing Communication
With clear goals and performance indicators, the BSC improves internal communication. Teams can track progress, discuss challenges, and make informed decisions based on data rather than assumptions.
Aligning Teams and Departments
The BSC links individual and departmental objectives to overall business strategy. This alignment ensures that all employees work towards shared goals, reducing misunderstandings and improving collaboration.
By using a Balanced Scorecard, organisations can improve focus, boost teamwork, and create a culture of transparency, leading to better decision-making and long-term success.
What Are the Benefits of Using a Digital Balanced Scorecard (BSC)?
A digital Balanced Scorecard (BSC) offers an efficient way to track and manage business performance. It improves accuracy, accessibility, and decision-making by providing real-time data and automated reporting.
Real-Time Data and Insights
A digital BSC provides instant updates on key performance indicators (KPIs). This allows organisations to monitor progress, identify trends, and make quick adjustments to improve performance.
Improved Accessibility
With cloud-based access, a digital BSC enables teams to view and update performance data from any location. This enhances collaboration and ensures that all departments stay aligned with business objectives.
Automated Tracking and Reporting
A digital system reduces manual work by automating data collection and reporting. This saves time, minimises errors, and ensures accurate performance tracking.
By using a digital Balanced Scorecard, organisations can streamline strategic planning, improve communication, and achieve better business outcomes.
How Can a Balanced Scorecard (BSC) Be Used in Different Industries?
A Balanced Scorecard (BSC) is a powerful tool that helps organisations in various industries measure performance, align strategies, and achieve long-term success. It provides a structured approach to tracking key objectives across financial, customer, internal processes, and learning perspectives.
Manufacturing
In the manufacturing industry, a BSC is used to monitor production efficiency, reduce waste, and improve quality. It helps track key performance indicators (KPIs) such as equipment utilisation, defect rates, and supply chain performance, ensuring smooth operations.
Healthcare
Hospitals and healthcare providers use a BSC to enhance patient care, manage resources, and track treatment success rates. It ensures compliance with safety standards, monitors staff performance, and helps improve patient satisfaction.
Retail
Retail businesses use a BSC to measure sales performance, customer engagement, and inventory management. By tracking customer satisfaction, supply chain efficiency, and financial performance, retailers can enhance their competitive edge.
Education
In the education sector, a BSC is used to track student performance, faculty effectiveness, and institutional growth. It helps improve curriculum development, resource allocation, and overall learning outcomes.
Finance
Financial institutions use a BSC to monitor risk management, customer satisfaction, and operational efficiency. It helps banks and financial service providers make data-driven decisions and improve customer relationships.
By adapting the Balanced Scorecard to industry-specific needs, organisations can improve efficiency, enhance decision-making, and drive long-term growth.
What Are the Challenges of Implementing a Balanced Scorecard (BSC)?
Implementing a Balanced Scorecard (BSC) can help organisations improve performance, but it also comes with challenges. These difficulties can affect the successful adoption and effectiveness of the system.
Resistance to Change
One of the biggest challenges is resistance from employees and management. Adopting a BSC requires a shift in mindset, and some individuals may be reluctant to accept new processes or additional performance tracking.
Defining the Right Metrics
Choosing the right key performance indicators (KPIs) is essential for a successful BSC. If the selected metrics do not align with business goals, it can lead to poor decision-making and ineffective performance tracking.
Data Collection and Accuracy
A BSC relies on accurate and up-to-date data. If data collection processes are inefficient or prone to errors, the insights gained from the scorecard may not reflect the true performance of the organisation.
Ongoing Monitoring and Updates
For a BSC to remain effective, it requires regular updates and reviews. Without continuous monitoring, the scorecard can become outdated, leading to poor strategic decisions.
Despite these challenges, organisations that plan carefully and engage their teams effectively can successfully implement a Balanced Scorecard and improve overall performance.
How Do You Develop a Balanced Scorecard (BSC)?
Developing a Balanced Scorecard (BSC) helps organisations align their strategy with performance measurements. A well-structured BSC improves decision-making, tracks progress, and enhances overall business efficiency.
Define Organisational Vision and Strategy
The first step is to clearly define the organisation’s vision, mission, and strategic goals. This ensures that every element of the BSC aligns with long-term objectives.
Identify Key Performance Areas
A BSC focuses on four main perspectives: financial, customer, internal processes, and learning and growth. Identifying key areas in each category helps measure success effectively.
Set Measurable Objectives
Each performance area should have specific and measurable objectives. For example, financial goals may include revenue growth, while customer objectives may focus on satisfaction and retention rates.
Choose Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
KPIs help track progress towards strategic goals. These should be relevant, achievable, and provide valuable insights into business performance.
Establish Targets and Initiatives
Setting targets ensures that employees have clear performance expectations. Developing initiatives, such as training programs or process improvements, supports goal achievement.
Implement and Monitor
Once the BSC is developed, it must be implemented across the organisation. Regular monitoring and updates ensure the system remains relevant and continues to support business success.
By following these steps, businesses can create a Balanced Scorecard that drives performance, improves decision-making, and supports long-term growth.
What Is the Financial Perspective in a Balanced Scorecard (BSC)?
The financial perspective in a Balanced Scorecard (BSC) focuses on measuring an organisation’s financial performance and profitability. It helps businesses track financial health and ensures that strategic goals align with revenue growth and cost management.
Key Financial Metrics
Organisations use key performance indicators (KPIs) to assess financial success. Common metrics include revenue growth, profit margins, cost reduction, and return on investment. These indicators help businesses understand how well they are performing financially.
Improving Financial Performance
To enhance financial results, companies focus on increasing sales, reducing operational costs, and improving cash flow. Effective budgeting and resource management also contribute to long-term financial stability.
Aligning with Business Strategy
The financial perspective is linked to other areas of the BSC, such as customer satisfaction and internal processes. A strong financial foundation supports business expansion and sustainability.
By monitoring financial performance through a Balanced Scorecard, organisations can make informed decisions, improve profitability, and achieve long-term success.
What Is the Customer Perspective in a Balanced Scorecard (BSC)?
The customer perspective in a Balanced Scorecard (BSC) focuses on understanding customer needs and measuring satisfaction. It helps organisations improve their products, services, and overall customer experience to drive business growth.
Key Customer Metrics
Businesses track key performance indicators (KPIs) such as customer satisfaction, retention rates, service response times, and market share. These metrics help evaluate how well a company is meeting customer expectations.
Improving Customer Experience
To enhance customer satisfaction, organisations focus on quality, reliability, and service efficiency. Clear communication, personalised experiences, and quick issue resolution also contribute to a positive customer journey.
Aligning with Business Goals
The customer perspective is directly linked to financial success and internal processes. Satisfied customers are more likely to remain loyal and recommend a business, leading to higher revenue and long-term growth.
By monitoring the customer perspective in a Balanced Scorecard, organisations can strengthen relationships, increase market competitiveness, and achieve sustainable success.
What Is the Internal Process Perspective in a Balanced Scorecard (BSC)?
The internal process perspective in a Balanced Scorecard (BSC) focuses on improving business operations to enhance efficiency, quality, and performance. It helps organisations identify key processes that contribute to customer satisfaction and financial success.
Key Process Metrics
Businesses track key performance indicators (KPIs) such as production efficiency, cycle time, cost reduction, and quality control. These metrics help evaluate how well internal processes support business goals.
Enhancing Operational Efficiency
To improve internal processes, organisations focus on streamlining workflows, reducing waste, and implementing automation. Regular process reviews and continuous improvements help maintain efficiency and productivity.
Linking to Overall Strategy
Strong internal processes lead to better product quality, faster service delivery, and increased customer satisfaction. This, in turn, supports financial growth and long-term business success.
By monitoring and refining internal processes through a Balanced Scorecard, organisations can optimise operations, reduce costs, and improve overall performance.
What Is the Learning and Growth Perspective in a Balanced Scorecard (BSC)?
The learning and growth perspective in a Balanced Scorecard (BSC) focuses on improving employee skills, innovation, and overall organisational development. It ensures that businesses invest in their workforce and technology to achieve long-term success.
Key Performance Metrics
Businesses track key performance indicators (KPIs) such as employee training, staff retention, skill development, and innovation rates. These metrics help measure the organisation’s ability to adapt and grow in a competitive market.
Enhancing Employee Development
To improve learning and growth, organisations focus on continuous training, leadership development, and knowledge sharing. Creating a positive work environment encourages employee engagement and productivity.
Linking to Business Success
When employees are skilled and motivated, they contribute to better internal processes, improved customer service, and increased financial performance. A strong learning culture helps businesses remain competitive and innovative.
By focusing on learning and growth in a Balanced Scorecard, organisations can build a knowledgeable workforce, drive innovation, and ensure long-term stability.
How Does a Balanced Scorecard (BSC) Relate to Continuous Improvement?
A Balanced Scorecard (BSC) supports continuous improvement by providing a structured approach to measuring and enhancing performance. It helps organisations identify weaknesses, track progress, and implement changes for long-term success.
Monitoring Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
The BSC uses key performance indicators (KPIs) across financial, customer, internal processes, and learning perspectives. By tracking these metrics, businesses can assess efficiency, customer satisfaction, and overall growth.
Identifying Areas for Improvement
With regular performance reviews, organisations can spot inefficiencies and bottlenecks. The BSC highlights areas needing improvement, ensuring that corrective actions are taken to optimise processes.
Aligning Strategy with Improvement Goals
Continuous improvement requires alignment between business strategy and daily operations. The BSC ensures that improvement efforts support long-term objectives, leading to sustained growth and competitiveness.
Encouraging a Culture of Innovation
By promoting learning and development, the BSC helps businesses foster innovation. Employees are encouraged to find better ways to work, improving overall efficiency and service quality.
Using a Balanced Scorecard for continuous improvement allows organisations to refine their strategies, enhance performance, and remain competitive in a changing market.
How Can a Balanced Scorecard (BSC) Be Used to Track Progress Toward Strategic Goals?
A Balanced Scorecard (BSC) is an effective tool for tracking progress toward strategic goals by measuring performance across key business areas. It ensures that every part of the organisation contributes to overall success.
Defining Strategic Objectives
The BSC helps businesses set clear strategic objectives linked to financial performance, customer satisfaction, internal processes, and learning. These objectives provide a roadmap for long-term growth.
Measuring Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
By tracking key performance indicators (KPIs), businesses can monitor progress toward their goals. KPIs may include revenue growth, customer retention, operational efficiency, and employee training metrics.
Aligning Departments and Teams
The BSC ensures that all departments work towards common goals. By linking strategic objectives to daily activities, organisations create a unified approach to achieving success.
Reviewing and Adjusting Strategies
Regular performance reviews using the BSC help businesses identify areas needing improvement. Adjustments can be made to strategies based on real-time data, ensuring continuous progress.
By using a Balanced Scorecard to track strategic goals, organisations can stay focused, measure success, and make informed decisions for long-term growth.
How Does a Balanced Scorecard (BSC) Aid in Decision Making?
A Balanced Scorecard (BSC) helps organisations make better decisions by providing a clear framework for measuring performance across key areas. It ensures that decisions align with long-term goals and business strategy.
Providing a Clear Overview of Performance
The BSC tracks performance across financial, customer, internal process, and learning perspectives. This gives decision-makers a complete view of the organisation’s strengths and areas that need improvement.
Using Data to Support Decisions
With key performance indicators (KPIs), businesses can rely on data rather than assumptions. The BSC helps managers analyse trends, compare results, and make informed choices that improve efficiency and growth.
Aligning Actions with Strategy
Every decision should support the overall business strategy. The BSC ensures that short-term actions contribute to long-term goals, keeping the organisation focused and on track.
Identifying and Addressing Challenges
By regularly reviewing performance data, businesses can spot challenges early. The BSC helps leaders take proactive steps to address risks, streamline processes, and optimise resources.
Using a Balanced Scorecard for decision-making helps organisations stay competitive, improve performance, and achieve sustainable growth.
How Does the Balanced Scorecard Relate to Industry 4.0?
Industry 4.0 focuses on digital transformation, automation, and data-driven decision-making. The Balanced Scorecard (BSC) helps businesses adapt to these changes by aligning performance measurement with technological advancements.
Integrating Digital Technologies
The BSC supports Industry 4.0 by tracking the impact of digital tools on business operations. It measures how automation, smart systems, and data analytics improve efficiency, productivity, and customer satisfaction.
Enhancing Decision-Making with Data
Industry 4.0 relies on real-time data for decision-making. The BSC ensures that businesses use accurate and relevant metrics to evaluate financial growth, process efficiency, and innovation.
Supporting Workforce Development
As businesses adopt new technologies, employee skills must evolve. The BSC helps track training, learning, and workforce development to ensure teams can adapt to Industry 4.0 changes.
Aligning Strategy with Digital Transformation
Businesses must integrate technology into their long-term strategy. The BSC provides a structured approach to monitoring progress, ensuring digital transformation aligns with business goals.
The Balanced Scorecard helps organisations transition into Industry 4.0 by providing a clear framework for measuring success, adapting to innovation, and maintaining a competitive edge.
What is the Role of Hoshin Kanri X Matrix in Relation to a Balanced Scorecard (BSC)?
The Hoshin Kanri X Matrix is a strategic planning tool that aligns organisational goals with specific actions. When combined with a Balanced Scorecard (BSC), it ensures a structured approach to achieving long-term objectives while tracking performance across key areas.
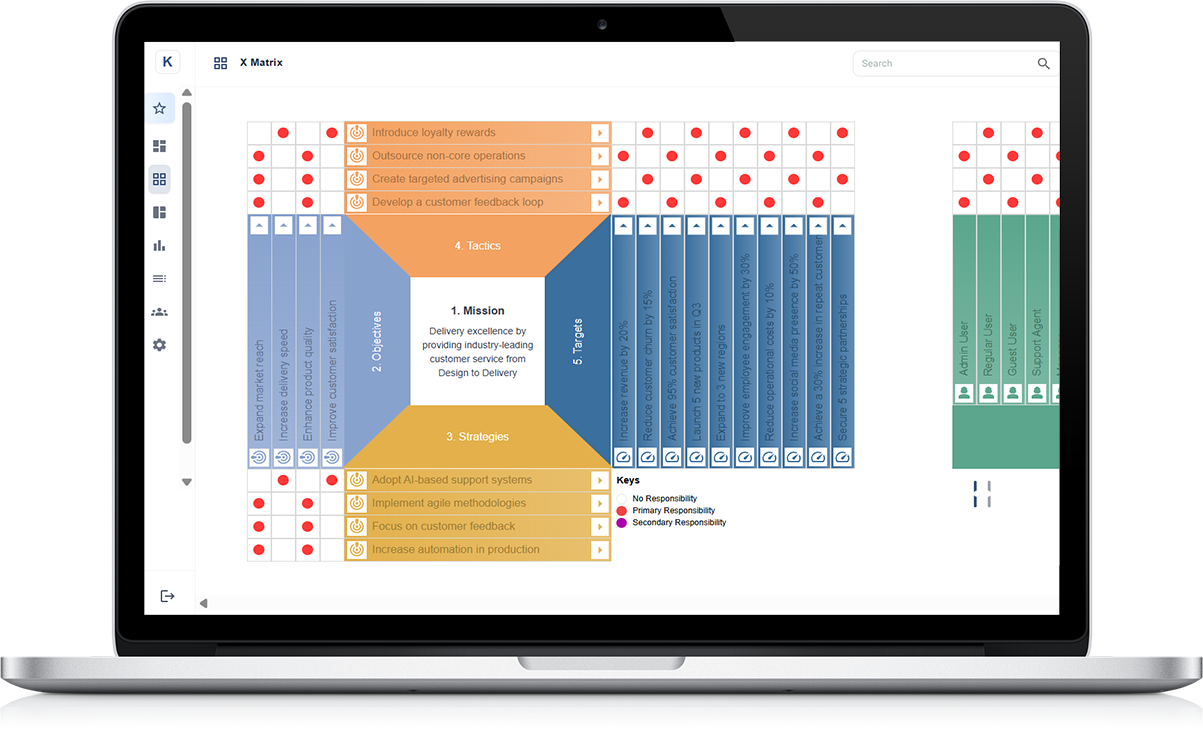
Aligning Strategy with Execution
The X Matrix helps businesses break down high-level goals into actionable steps. The BSC measures performance across different perspectives, ensuring that these strategic actions contribute to financial growth, customer satisfaction, process efficiency, and learning.
Ensuring Cross-Departmental Collaboration
The X Matrix visually connects objectives, measures, and responsibilities across teams. The BSC complements this by providing performance metrics to track progress, ensuring all departments work towards shared goals.
Improving Decision-Making
By integrating the X Matrix with the BSC, organisations can make data-driven decisions. The X Matrix outlines key initiatives, while the BSC evaluates their effectiveness using measurable indicators.
Enhancing Continuous Improvement
The X Matrix follows a structured review cycle, ensuring businesses regularly assess progress. The BSC supports this by identifying areas for improvement through performance tracking.
By using the Hoshin Kanri X Matrix alongside a Balanced Scorecard, organisations can effectively align strategy, execution, and performance measurement, leading to long-term success.