Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) is a comprehensive approach to equipment maintenance that aims to achieve perfect production (i.e., no breakdowns, small stops or slow running, no defects, and no accidents). It involves all employees from top management to shop-floor workers and is designed to improve production efficiency by reducing downtime and enhancing the overall reliability and effectiveness of equipment.
Key Concepts of TPM:
Pillar of TPM:
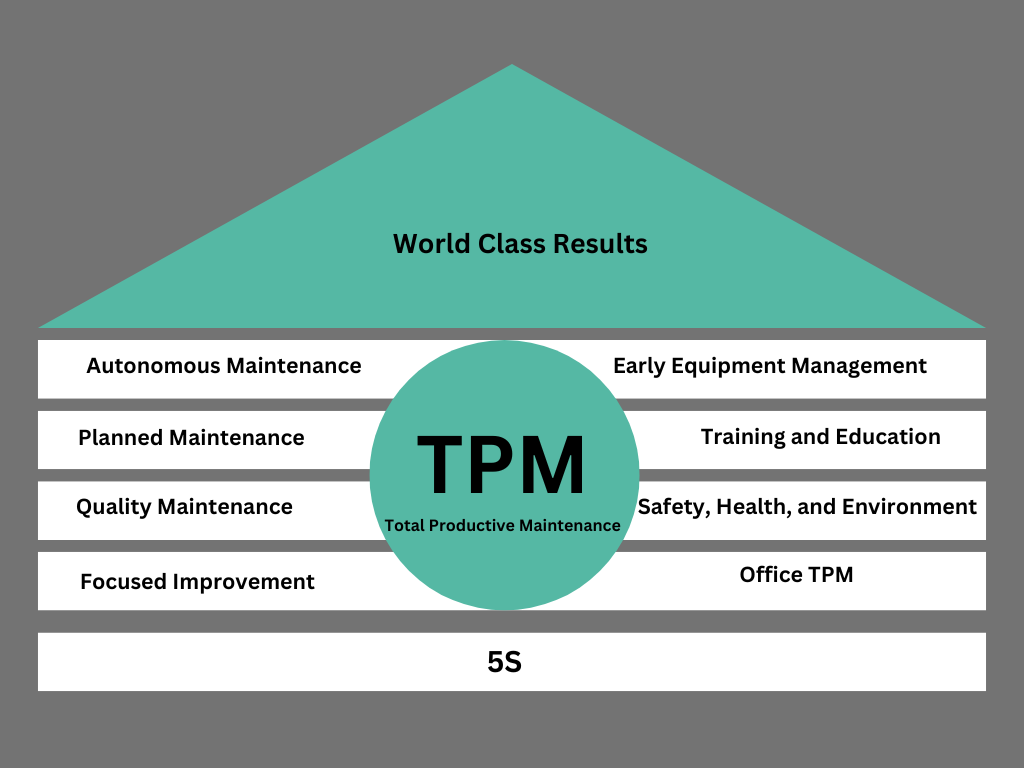
Autonomous Maintenance: Operators are trained to maintain their equipment daily to prevent deterioration.
Planned Maintenance: Maintenance tasks are scheduled based on equipment failure data and condition monitoring.
Quality Maintenance: Focuses on ensuring that equipment consistently produces defect-free products.
Focused Improvement: Continuous efforts are made to identify and eliminate losses in the production process.
Early Equipment Management: Incorporating maintenance prevention in the design of new equipment.
Training and Education: Ensuring that all employees are trained to understand and implement TPM principles.
Safety, Health, and Environment: Ensuring a safe working environment to avoid accidents and injuries.
Office TPM: Extending TPM principles to administrative functions to improve overall productivity.
Goals of TPM:
- Zero Accidents
- Zero Defects
- Zero Breakdowns
Key Metrics:
Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE): Measures the effectiveness of equipment and includes availability, performance, and quality rates.
Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF): Average time between equipment breakdowns.
Mean Time to Repair (MTTR): Average time taken to repair equipment after a failure.
Implementation Steps:
Initial Assessment: Evaluating the current state of maintenance practices and equipment.
Education and Training: Training employees at all levels on TPM concepts and practices.
Pilot Projects: Starting with pilot projects to demonstrate the benefits and refine the approach.
Full-Scale Implementation: Rolling out TPM practices across the entire organization.
Continuous Improvement: Ongoing efforts to refine and improve maintenance practices.
Benefits:
- Increased equipment reliability and lifespan.
- Reduced downtime and maintenance costs.
- Enhanced production quality and efficiency.
- Improved workplace safety.
- Greater employee involvement and morale.
By implementing TPM, organizations can achieve significant improvements in their manufacturing processes, leading to higher productivity, better product quality, and reduced operational costs.
Total Productive Maintenance
1. What is Total Productive Maintenance (TPM)?
Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) is a holistic approach to equipment maintenance that aims to maximize overall equipment effectiveness (OEE) by involving all employees in the maintenance process.

2. What are the main goals of TPM?
The main goals of TPM are to improve equipment reliability, reduce downtime, enhance productivity, and involve all employees in maintenance activities.
3. What are the key components of TPM?
Key components of TPM include Autonomous Maintenance, Planned Maintenance, Quality Maintenance, Focused Improvement, and Training and Education.
4. How does Autonomous Maintenance work in TPM?
Autonomous Maintenance empowers operators to perform routine maintenance tasks, such as cleaning and inspections, to prevent equipment issues and maintain performance.
5. What is Planned Maintenance in TPM?
Planned Maintenance involves scheduling and performing preventive and predictive maintenance activities based on equipment usage and condition to avoid unexpected breakdowns.
6. How does TPM contribute to reducing equipment downtime?
TPM reduces equipment downtime by implementing preventive maintenance, improving equipment reliability, and involving operators in the maintenance process to address issues before they lead to failures.
7. What is the role of Focused Improvement in TPM?
Focused Improvement targets specific areas of the production process to eliminate losses and inefficiencies through team-based problem-solving and continuous improvement initiatives.
8. How is Quality Maintenance integrated into TPM?
Quality Maintenance ensures that equipment and processes are maintained to meet quality standards and prevent defects, thus contributing to overall product quality.
9. What types of training are involved in TPM?
TPM training includes operator training for autonomous maintenance, technical training for maintenance personnel, and education on TPM principles and practices for all employees.
10. What are the benefits of implementing TPM?
Benefits include increased equipment uptime, improved product quality, reduced maintenance costs, higher employee morale, and greater overall efficiency.
11. What are the challenges of implementing TPM?
Challenges include resistance to change, lack of employee engagement, insufficient training, and the need for a cultural shift towards collective responsibility for equipment maintenance.
12. How does TPM differ from traditional maintenance approaches?
TPM differs from traditional maintenance by involving all employees in maintenance activities, focusing on proactive measures rather than reactive repairs, and aiming to improve overall equipment effectiveness.
13. What is the role of leadership in TPM?
Leadership plays a crucial role in TPM by setting clear goals, providing resources, supporting training initiatives, and fostering a culture of continuous improvement and teamwork.
14. How can TPM be aligned with Lean Manufacturing?
TPM aligns with Lean Manufacturing by focusing on eliminating waste, improving processes, and enhancing overall equipment effectiveness, which complements Lean principles of efficiency and continuous improvement.
15. What metrics are used to measure TPM effectiveness?
Metrics include Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE), mean time between failures (MTBF), mean time to repair (MTTR), and maintenance cost as a percentage of production value.
16. How does TPM impact employee involvement?
TPM enhances employee involvement by encouraging operators to participate in maintenance activities, contribute to problem-solving, and take ownership of equipment performance.
17. What is the role of preventive maintenance in TPM?
Preventive maintenance is a proactive approach that involves regular inspections, servicing, and repairs to prevent equipment failures and extend its operational life.
18. How do you develop a TPM implementation plan?
A TPM implementation plan involves setting clear objectives, assessing current practices, engaging stakeholders, providing training, and establishing a system for monitoring and continuous improvement.
19. What is the importance of documentation in TPM?
Documentation is important for tracking maintenance activities, recording equipment performance, standardizing procedures, and providing a reference for continuous improvement efforts.
20. How can TPM be sustained over the long term?
TPM can be sustained through ongoing training, regular audits, continuous improvement initiatives, and maintaining a strong commitment from all levels of the organization.
21. What is the role of TPM in safety?
TPM contributes to safety by ensuring equipment is well-maintained, reducing the risk of accidents caused by equipment failures, and promoting a culture of safety awareness among employees.
22. How does TPM affect maintenance costs?
TPM can reduce maintenance costs by decreasing the frequency of unplanned repairs, extending equipment life, and improving overall efficiency through proactive maintenance practices.
23. What is the relationship between TPM and Total Quality Management (TQM)?
TPM and TQM are complementary practices; TPM focuses on equipment reliability and effectiveness, while TQM focuses on overall quality improvements, both aiming to enhance organizational performance.
24. How can TPM be applied to new equipment?
TPM can be applied to new equipment by incorporating it into the maintenance strategy from the start, including operator training, setting maintenance schedules, and establishing performance benchmarks.
25. What are the typical steps in a TPM implementation process?
Typical steps include assessing current maintenance practices, setting TPM goals, developing a detailed plan, training employees, implementing TPM practices, and monitoring progress.
26. How does TPM support continuous improvement?
TPM supports continuous improvement by fostering a culture of regular evaluation, problem-solving, and process optimization, leading to ongoing enhancements in equipment performance and overall productivity.
27. What role does technology play in TPM?
Technology plays a role in TPM by providing tools for data collection, monitoring equipment performance, and implementing predictive maintenance strategies, enhancing the effectiveness of TPM practices.
28. How can TPM be adapted for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs)?
TPM can be adapted for SMEs by scaling practices to fit available resources, focusing on key equipment, and prioritizing high-impact areas to achieve improvements without overwhelming the organization.
29. What is the significance of maintenance teams in TPM?
Maintenance teams are crucial in TPM for executing maintenance tasks, providing expertise, supporting operators, and contributing to continuous improvement efforts.
30. How can TPM be integrated with existing maintenance practices?
TPM can be integrated with existing practices by aligning TPM principles with current maintenance activities, updating procedures, and involving all stakeholders in the transition process.
31. What are the common pitfalls in TPM implementation?
Common pitfalls include lack of management support, insufficient training, inadequate resources, and failure to involve all employees in the maintenance process.
32. How does TPM impact equipment life cycle management?
TPM positively impacts equipment life cycle management by extending equipment life through regular maintenance, reducing the need for premature replacements, and improving overall asset utilization.
33. What are some examples of TPM tools and techniques?
Examples include failure mode and effects analysis (FMEA), root cause analysis, 5S, and standard operating procedures (SOPs) for maintenance tasks.
34. How does TPM impact customer satisfaction?
TPM can improve customer satisfaction by ensuring consistent product quality, reducing production downtime, and enhancing on-time delivery through reliable equipment performance.
35. What is the role of cross-functional teams in TPM?
Cross-functional teams in TPM bring together diverse expertise to address maintenance issues, develop improvement initiatives, and ensure alignment with overall organizational goals.