The Balanced Scorecard (BSC) is a strategic management tool that provides a comprehensive framework for tracking and improving business performance. Developed to ensure that organizations focus not only on financial outcomes but also on key drivers of future performance, the Balanced Scorecard aligns daily operations with long-term strategic goals. It integrates four key perspectives: Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, and Learning & Growth. By measuring performance across these diverse areas, organizations can make more informed decisions, monitor progress, and align their resources effectively to achieve success.
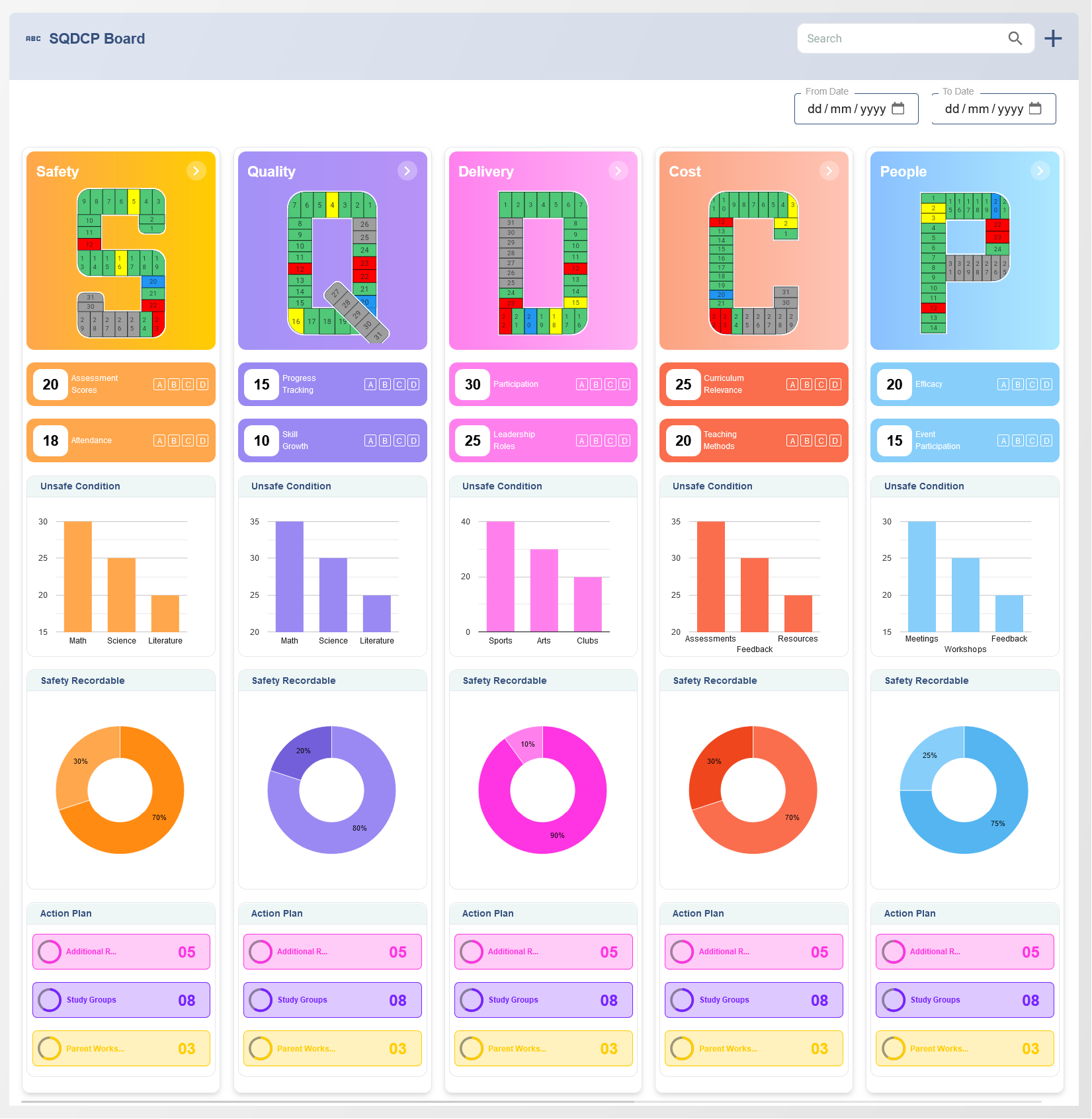
1. Understanding the Balanced Scorecard Framework
The Balanced Scorecard was created to overcome the limitations of traditional performance measurement systems that focused primarily on financial metrics. While financial outcomes such as profit and revenue are important, they often provide a retrospective view of an organization's success. The BSC expands the scope of measurement by incorporating leading indicators of future performance, which can be managed and improved in real-time. The four perspectives of the Balanced Scorecard are:
- Financial Perspective: Focuses on traditional financial metrics such as profitability, revenue growth, and cost management. This perspective helps organizations measure how well they are achieving their financial objectives and whether their strategies are delivering the desired economic returns.
- Customer Perspective: Measures customer satisfaction, retention, and acquisition, as well as market share. This perspective emphasizes understanding customer needs and ensuring that the organization delivers value in a way that meets or exceeds customer expectations.
- Internal Processes Perspective: Examines the efficiency and effectiveness of internal business processes that create value for customers. By evaluating areas like innovation, production efficiency, and service delivery, organizations can identify opportunities for improvement that drive long-term success.
- Learning & Growth Perspective: Focuses on the development and alignment of organizational capabilities, including employee skills, knowledge, and infrastructure. This perspective ensures that employees are well-equipped to execute the organization’s strategy and that the company’s culture fosters innovation and continuous improvement.
By balancing these four perspectives, the Balanced Scorecard enables organizations to align their strategy with their operations, ensuring that performance is tracked holistically and proactively.
2. The Benefits of Using a Balanced Scorecard
Implementing the Balanced Scorecard offers several key benefits that help organizations optimize performance across multiple dimensions:
- Holistic View of Performance: The Balanced Scorecard enables organizations to track performance across four key areas, providing a more complete picture of overall business health. This balanced approach helps organizations identify potential risks and opportunities that might otherwise be overlooked if the focus were solely on financial results.
- Alignment with Strategy: By linking performance measures to strategic goals, the Balanced Scorecard ensures that every department and employee is aligned with the organization’s long-term objectives. This alignment fosters greater focus, clarity, and purpose at all levels of the organization.
- Improved Decision-Making: The Balanced Scorecard provides a comprehensive set of performance metrics that support better decision-making. Managers can use real-time data from multiple perspectives to evaluate performance and adjust strategies as needed, leading to more informed and timely decisions.
- Enhanced Communication and Collaboration: The Balanced Scorecard encourages open communication about goals, priorities, and performance. By sharing progress across all levels of the organization, employees understand how their work contributes to overall success, fostering collaboration and motivation.
- Focus on Long-Term Success: The Balanced Scorecard places equal emphasis on short-term results and long-term sustainability. By measuring customer satisfaction, internal processes, and employee growth, the BSC helps organizations build a foundation for long-term competitive advantage.
3. Developing and Implementing a Balanced Scorecard
Implementing the Balanced Scorecard involves several steps that ensure its success and relevance to the organization’s strategic goals. These steps typically include:
- Define Strategic Objectives: The first step in creating a Balanced Scorecard is to define the organization’s strategic objectives in each of the four perspectives. These objectives should align with the company’s vision and mission and provide a clear direction for the organization.
- Identify Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): For each strategic objective, identify specific KPIs that will measure progress. These KPIs should be quantifiable, actionable, and relevant to the strategic goals. For example, a financial KPI might be revenue growth, while a customer KPI might focus on customer satisfaction scores.
- Develop Action Plans: Once the KPIs are defined, develop detailed action plans for achieving the objectives. These action plans should outline the specific steps that need to be taken to improve performance and meet the goals set within each perspective.
- Monitor and Review Progress: The Balanced Scorecard requires regular monitoring and evaluation of performance. This can be done through monthly or quarterly reviews of the KPIs to assess progress, identify any performance gaps, and make adjustments as needed.
- Communicate Results: Share progress and results across the organization to ensure that everyone is aligned and understands the direction. Regularly communicating results helps employees understand the impact of their work and keeps them motivated to achieve the company’s strategic goals.
These steps ensure that the Balanced Scorecard is effectively integrated into the organization’s strategic planning and decision-making processes, supporting a culture of continuous improvement.
4. Key Performance Indicators in the Balanced Scorecard
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are the backbone of the Balanced Scorecard, providing measurable data to track performance and progress toward strategic objectives. The KPIs should be tailored to each of the four perspectives and aligned with the company’s overall strategy. Examples of KPIs include:
- Financial Perspective KPIs: Return on Investment (ROI), Gross Profit Margin, Revenue Growth, Cost Reduction, and Economic Value Added (EVA).
- Customer Perspective KPIs: Customer Satisfaction Index, Net Promoter Score (NPS), Customer Retention Rate, Market Share, and Customer Acquisition Cost.
- Internal Processes Perspective KPIs: Cycle Time, Defect Rate, Process Efficiency, On-Time Delivery, and Product Innovation Rate.
- Learning & Growth Perspective KPIs: Employee Satisfaction, Training Hours per Employee, Employee Turnover Rate, Leadership Development, and Innovation Capability.
Each of these KPIs helps organizations measure progress and identify areas for improvement. Regularly tracking and evaluating these indicators allows businesses to adjust their strategies in real-time, ensuring long-term success.
5. Challenges and Considerations in Using the Balanced Scorecard
While the Balanced Scorecard is a powerful tool, organizations may encounter several challenges during its implementation:
- Data Collection and Analysis: Gathering accurate data for all KPIs can be time-consuming and resource-intensive. Organizations need robust data collection systems in place to ensure that information is reliable and up-to-date.
- Overcomplicating the Scorecard: Some organizations may attempt to track too many metrics, making the Balanced Scorecard overly complex and difficult to manage. It’s important to keep the focus on a manageable set of KPIs that align with strategic objectives.
- Resistance to Change: Employees may resist changes in performance measurement systems. Effective communication and employee involvement in the process are critical for overcoming this resistance and ensuring successful implementation.
The Balanced Scorecard: Measures that Drive Performance
What is the Balanced Scorecard?
The Balanced Scorecard is a strategic planning and management tool that organizations use to track and improve performance across four key perspectives: financial, customer, internal business processes, and learning and growth.
How does the Balanced Scorecard measure performance?
The Balanced Scorecard measures performance by using a set of key performance indicators (KPIs) aligned with strategic objectives across the four perspectives, providing a balanced view of the organization's health and progress.
What are the four perspectives of the Balanced Scorecard?
The four perspectives of the Balanced Scorecard are: 1) Financial, 2) Customer, 3) Internal Business Processes, and 4) Learning and Growth. These perspectives ensure a comprehensive approach to measuring organizational success.
How do you define strategic objectives in a Balanced Scorecard?
Strategic objectives in a Balanced Scorecard are specific, measurable goals that align with the organization's overall strategy. These objectives are set within each of the four perspectives to drive long-term performance and success.
Why is financial performance included in the Balanced Scorecard?
Financial performance is included in the Balanced Scorecard to ensure that the organization's strategic initiatives are contributing to its bottom line and long-term financial health.
What role does customer perspective play in the Balanced Scorecard?
The customer perspective in the Balanced Scorecard focuses on customer satisfaction, retention, and acquisition. It helps organizations ensure that their strategies align with customer needs and expectations, driving business success.
How does the internal business process perspective contribute to the Balanced Scorecard?
The internal business process perspective focuses on improving internal operations and processes. It helps organizations streamline their operations to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and deliver better products and services to customers.
How does the learning and growth perspective fit into the Balanced Scorecard?
The learning and growth perspective emphasizes employee development, skills, and organizational culture. It ensures that the workforce is capable and motivated to support the company’s strategic objectives.
Can the Balanced Scorecard be applied to small businesses?
Yes, the Balanced Scorecard can be applied to small businesses by adapting the four perspectives to the company’s specific goals and resources. It helps small businesses align their strategies and track progress effectively.
How do you set targets and goals in a Balanced Scorecard?
Targets and goals in the Balanced Scorecard are set based on strategic objectives within each perspective. These goals should be SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound) to ensure effective tracking and performance measurement.
How do organizations track performance using the Balanced Scorecard?
Organizations track performance using the Balanced Scorecard by regularly measuring KPIs aligned with each perspective. This helps them assess progress, identify areas of improvement, and adjust strategies as needed.
What is the role of key performance indicators (KPIs) in the Balanced Scorecard?
KPIs are used in the Balanced Scorecard to measure the success of strategic objectives. These indicators provide quantifiable data that helps organizations track performance and make informed decisions based on real-time insights.
What are the benefits of using the Balanced Scorecard?
The Balanced Scorecard provides a holistic view of an organization’s performance, aligning objectives with strategy, improving decision-making, tracking progress, and fostering communication and accountability across the organization.
How does the Balanced Scorecard align with an organization’s strategy?
The Balanced Scorecard aligns with an organization’s strategy by ensuring that strategic objectives are clearly defined and tracked across all perspectives. It helps focus the organization’s efforts on achieving long-term goals and sustaining growth.
How often should the Balanced Scorecard be reviewed and updated?
The Balanced Scorecard should be reviewed regularly (quarterly or annually) to ensure that the strategic objectives and KPIs remain relevant and aligned with the organization’s evolving goals and market conditions.