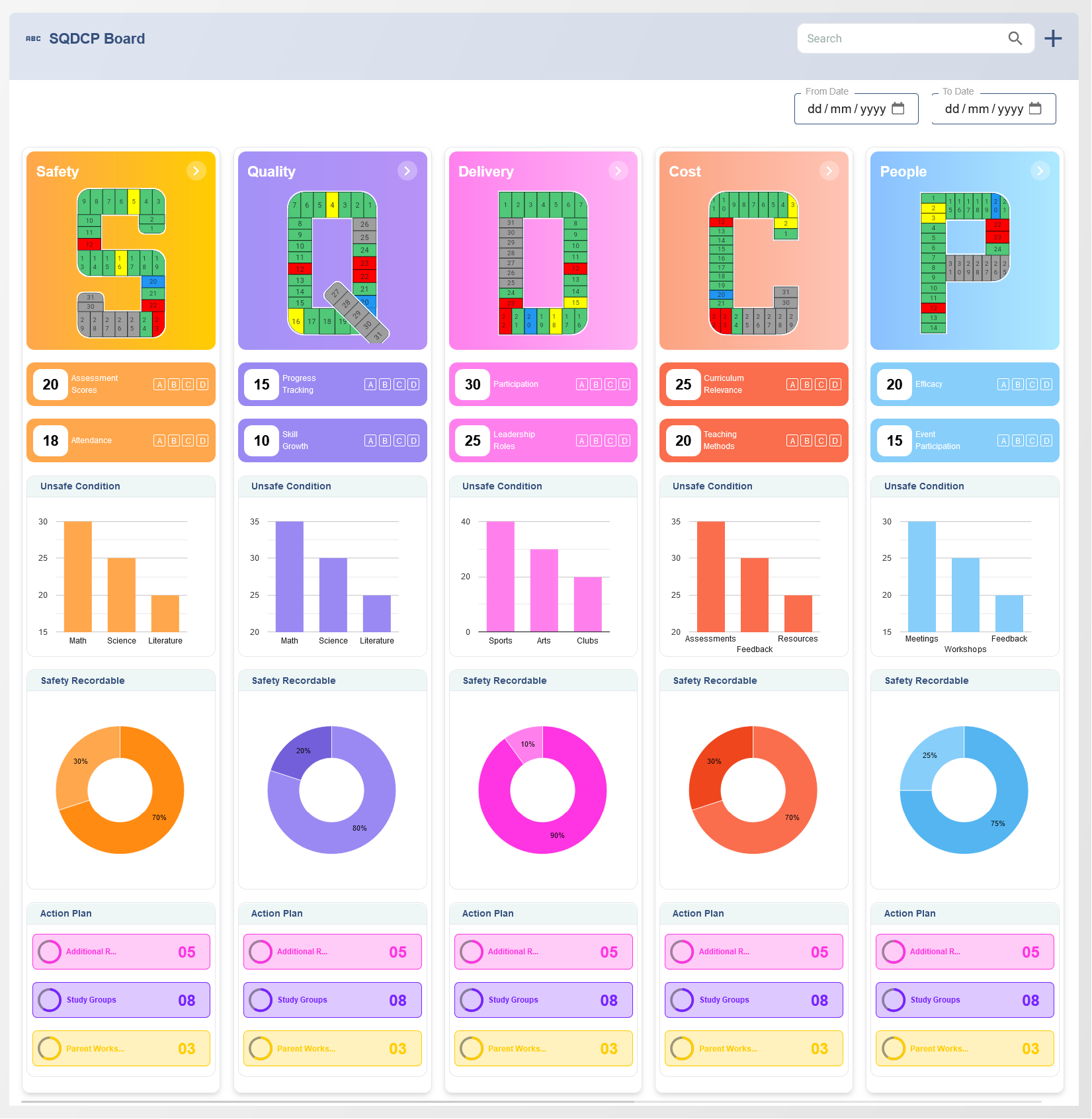
The strategy map is a vital component of the balanced scorecard framework, serving as a visual representation of an organization's strategic objectives and their interconnections. It bridges the gap between strategic goals and operational activities, aligning all organizational efforts toward achieving the desired outcomes.
What is a Strategy Map?
A strategy map is a one-page diagram that outlines the cause-and-effect relationships among the key objectives of an organization across four balanced scorecard perspectives: financial, customer, internal processes, and learning and growth. It provides clarity on how value is created, allowing organizations to prioritize efforts and resources effectively.
Components of a Strategy Map
- Financial Perspective: Focuses on financial objectives such as revenue growth, cost management, and profitability. This perspective answers the question: "How do we deliver value to our shareholders?"
- Customer Perspective: Emphasizes customer satisfaction, retention, and acquisition. It addresses the question: "How do we create value for our customers?"
- Internal Processes Perspective: Concentrates on optimizing business processes that drive value. It asks: "What internal processes must we excel at to meet customer and financial expectations?"
- Learning and Growth Perspective: Focuses on employee skills, organizational culture, and technology. It explores: "How do we sustain our ability to innovate and improve?"
Benefits of Using a Strategy Map
Strategy maps offer several advantages, including:
- Alignment: Ensures all organizational efforts are directed toward common goals by aligning departmental activities with strategic objectives.
- Clarity: Provides a clear and concise view of the organization's strategy, making it easier for employees at all levels to understand their roles.
- Focus: Helps prioritize initiatives by highlighting critical objectives and their dependencies.
- Communication: Acts as a tool for communicating strategy to stakeholders, fostering transparency and engagement.
- Decision-Making: Supports informed decision-making by visualizing the impact of various objectives on overall performance.
How to Create a Strategy Map
- Define the Vision and Mission: Start by articulating the organization's vision and mission, which form the foundation of the strategy map.
- Identify Strategic Objectives: Determine the key objectives for each perspective of the balanced scorecard. Ensure these objectives are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
- Establish Cause-and-Effect Relationships: Connect the objectives across perspectives to demonstrate how they influence one another. For example, improved employee training (learning and growth) leads to better process efficiency (internal processes), enhancing customer satisfaction (customer) and driving revenue growth (financial).
- Design the Map: Use a simple and visually appealing layout to depict the objectives and their relationships. Typically, the financial perspective is at the top, followed by customer, internal processes, and learning and growth perspectives.
- Validate and Refine: Review the strategy map with key stakeholders to ensure accuracy and completeness. Refine it based on feedback.
Examples of Objectives in Each Perspective
- Financial: Increase revenue, reduce operational costs, improve profit margins.
- Customer: Enhance customer satisfaction, increase market share, improve product quality.
- Internal Processes: Streamline production, reduce cycle time, enhance supply chain efficiency.
- Learning and Growth: Develop employee skills, foster a culture of innovation, implement advanced technology.
Challenges in Implementing Strategy Maps
While strategy maps are powerful tools, organizations may encounter challenges such as:
- Lack of Clarity: Poorly defined objectives can lead to confusion and misalignment.
- Resistance to Change: Employees may resist adopting new processes or strategies.
- Overcomplexity: Including too many objectives can make the strategy map cumbersome and difficult to use.
- Insufficient Communication: Failure to communicate the strategy effectively can hinder implementation.
Best Practices for Effective Strategy Maps
- Keep it Simple: Focus on the most critical objectives to maintain clarity and usability.
- Engage Stakeholders: Involve key stakeholders in the development process to ensure buy-in and alignment.
- Use Data: Base objectives and relationships on accurate data and analysis.
- Regularly Review: Update the strategy map periodically to reflect changes in the business environment or organizational priorities.
Strategy map in Balanced scorecard
What is a strategy map in the Balanced Scorecard?
A strategy map is a visual representation that outlines an organization’s objectives and their relationships across key perspectives of the Balanced Scorecard.
How does a strategy map align with the Balanced Scorecard?
It aligns objectives and actions across the four perspectives of the Balanced Scorecard: financial, customer, internal processes, and learning and growth.
What are the key components of a strategy map?
Key components include objectives, cause-and-effect relationships, performance measures, and alignment with organizational strategy.
How does a strategy map help organizations achieve their goals?
By clearly linking objectives across perspectives, a strategy map helps organizations align resources and actions to achieve their strategic goals.
What perspectives are included in a strategy map?
Perspectives include financial, customer, internal processes, and learning and growth, each representing a critical area of performance.
How is a strategy map used for decision-making?
It provides a clear framework for identifying priorities and assessing the impact of decisions on strategic objectives.
Can a strategy map be customized for specific industries?
Yes, organizations can tailor strategy maps to reflect industry-specific goals, metrics, and challenges.
How do you create a strategy map for the Balanced Scorecard?
Begin by defining objectives for each perspective, then map out cause-and-effect relationships that connect these objectives.
What role do objectives play in a strategy map?
Objectives represent the goals an organization aims to achieve and form the basis for the cause-and-effect relationships in the strategy map.
How does a strategy map improve organizational communication?
It provides a clear visual framework that communicates strategic priorities and their alignment to all stakeholders.
What are the benefits of using a strategy map?
Benefits include improved alignment of goals, better resource allocation, enhanced communication, and focused performance tracking.
How does a strategy map align with organizational vision and mission?
It translates the vision and mission into actionable objectives, ensuring alignment across all levels of the organization.
What is the relationship between KPIs and a strategy map?
KPIs measure the progress of objectives outlined in the strategy map, enabling tracking and performance assessment.
How does a strategy map facilitate performance tracking?
By defining clear objectives and metrics, a strategy map provides a structured approach for monitoring performance across key areas.
Can a strategy map evolve over time?
Yes, as organizational goals and market conditions change, a strategy map can be updated to reflect new priorities and strategies.