The SQDCP framework is a comprehensive approach used to monitor and improve supplier performance across five key dimensions: Safety, Quality, Delivery, Cost, and People. This framework is widely adopted in supply chain management to ensure that suppliers meet or exceed expectations, ultimately leading to improved product quality, efficient operations, and long-term partnerships. Implementing the SQDCP framework in supplier performance monitoring is essential for companies aiming to maintain competitive advantage, reduce risks, and optimize operational efficiency.
What is the SQDCP Framework?
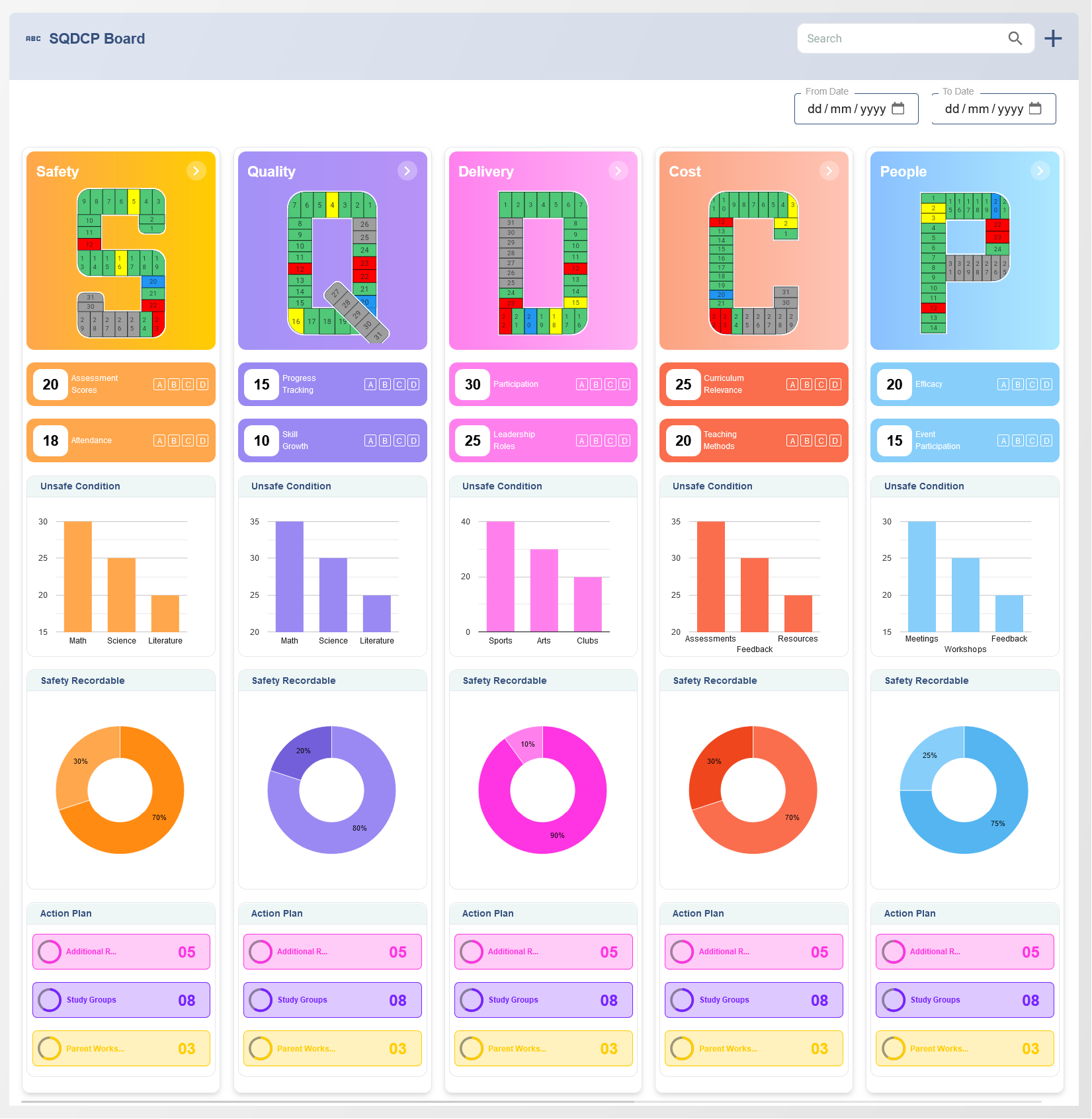
The SQDCP framework serves as a tool for organizations to evaluate their suppliers on several key metrics that directly impact business outcomes. Each component of SQDCP represents a specific area of supplier performance:
- Safety (S): Ensures that suppliers operate in a safe environment, minimizing hazards and complying with health and safety regulations.
- Quality (Q): Focuses on the consistency and reliability of the products or services provided by the supplier, ensuring they meet agreed-upon standards.
- Delivery (D): Measures the supplier's ability to meet delivery deadlines and respond to changes in demand, ensuring timely shipments and order fulfillment.
- Cost (C): Evaluates the cost-effectiveness of the supplier, ensuring that pricing is competitive and transparent without sacrificing quality.
- People (P): Assesses the supplier’s workforce capabilities, including training, communication, and collaboration with the purchasing organization.
Why Implement SQDCP in Supplier Performance Monitoring?
Implementing the SQDCP framework in supplier performance monitoring offers several benefits:
- Holistic Supplier Evaluation: The SQDCP framework provides a well-rounded assessment of supplier performance, covering all critical aspects that affect the supply chain.
- Improved Risk Management: Monitoring these five key dimensions helps identify potential risks, such as quality issues or delivery delays, allowing businesses to mitigate disruptions.
- Enhanced Supplier Collaboration: By focusing on performance metrics, the framework fosters better communication and collaboration between suppliers and organizations.
- Continuous Improvement: SQDCP encourages suppliers to improve over time in each of the five areas, driving operational excellence and long-term relationships.
Steps to Implement SQDCP in Supplier Performance Monitoring
Implementing the SQDCP framework requires a structured approach. The following steps outline how organizations can integrate SQDCP into their supplier performance monitoring processes:
1. Define Performance Metrics
The first step in implementing SQDCP is to clearly define the performance metrics for each of the five dimensions. Each organization should tailor these metrics to suit their specific needs, ensuring they align with organizational goals. For instance:
- Safety: Frequency of workplace accidents, compliance with safety standards, and proactive safety measures.
- Quality: Defect rates, product returns, customer complaints, and adherence to product specifications.
- Delivery: On-time delivery rates, lead times, and flexibility in handling changes in demand.
- Cost: Pricing competitiveness, cost reduction initiatives, and value for money.
- People: Employee training levels, turnover rates, and communication effectiveness between the supplier and the organization.
2. Establish Data Collection Systems
For effective monitoring, organizations need robust data collection systems. These systems should gather real-time information about each of the five SQDCP areas. This may involve using enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, quality management tools, or direct data inputs from suppliers. Consistent, accurate data is essential for evaluating supplier performance and identifying areas for improvement.
3. Monitor and Evaluate Supplier Performance
Once the performance metrics and data collection systems are in place, organizations can begin monitoring and evaluating supplier performance. Performance should be tracked over time, with regular reviews conducted to assess whether suppliers are meeting or exceeding the agreed-upon standards. It's important to consider both quantitative data (e.g., defect rates, delivery times) and qualitative feedback (e.g., communication effectiveness, employee engagement).
4. Provide Feedback to Suppliers
Constructive feedback is a crucial element of the SQDCP framework. After evaluating performance, organizations should provide feedback to suppliers in a timely and clear manner. This feedback should highlight both areas of strength and opportunities for improvement. By fostering a transparent and collaborative relationship, organizations can work with suppliers to resolve issues and improve performance.
5. Develop Action Plans for Improvement
If performance gaps are identified in any of the SQDCP areas, action plans should be developed to address them. These plans should include specific goals, timelines, and resources needed for improvement. For instance, if a supplier is struggling with on-time delivery, an action plan could involve adjusting inventory levels, improving logistics processes, or enhancing communication between the supplier and the organization.
6. Measure Results and Continuously Improve
After implementing action plans, organizations must continue to measure supplier performance to ensure improvements are being achieved. Regular performance reviews, supplier audits, and ongoing data analysis are essential for monitoring progress. The SQDCP framework should be seen as a continuous cycle of improvement, with organizations and suppliers working together to enhance performance over time.
Challenges in Implementing the SQDCP Framework
While the SQDCP framework offers numerous benefits, there are challenges that organizations may face when implementing it:
- Data Availability: Collecting accurate and timely data for all five SQDCP dimensions can be challenging, especially for organizations that rely on manual systems or inconsistent reporting practices.
- Supplier Resistance: Suppliers may initially resist the implementation of performance monitoring frameworks, especially if they feel the process is overly burdensome or if the criteria are too strict.
- Resource Allocation: Developing and maintaining systems for monitoring SQDCP performance requires significant investment in both time and resources, including training staff and implementing new software tools.
SQDCP framework for supplier performance monitoring
What is the SQDCP framework for supplier performance monitoring?
The SQDCP framework for supplier performance monitoring is a structured approach that focuses on Supplier Quality (SQ), Development (D), Capability (C), and Performance (P). This framework helps businesses monitor and improve their suppliers’ ability to meet quality standards, address development needs, enhance capabilities, and track overall performance to ensure consistent delivery of high-quality products.
Why is the SQDCP framework important for supplier performance monitoring?
The SQDCP framework is important because it provides a comprehensive approach to managing supplier relationships. It helps businesses assess various aspects of supplier performance, from quality to capabilities, while identifying areas for improvement. This holistic approach ensures that suppliers consistently meet expectations and contribute to the overall success of the supply chain.
What are the main components of the SQDCP framework?
The main components of the SQDCP framework are:
- Supplier Quality (SQ): Ensuring that the supplier’s products meet the required quality standards.
- Development (D): Focusing on improving the supplier’s processes and systems to meet future needs.
- Capability (C): Assessing and improving the supplier’s capacity to meet increasing demand and quality requirements.
- Performance (P): Continuously monitoring and evaluating the supplier's performance based on defined metrics.
How can the SQDCP framework improve supplier performance?
The SQDCP framework improves supplier performance by systematically identifying areas where suppliers need improvement, offering them targeted development opportunities, and providing continuous monitoring of their quality, capabilities, and performance. This proactive approach helps suppliers meet or exceed performance expectations while contributing to long-term success.
What role does Supplier Quality (SQ) play in the SQDCP framework?
Supplier Quality (SQ) is the foundation of the SQDCP framework. It ensures that the supplier’s products meet predefined quality standards and specifications. By focusing on SQ, businesses can identify quality issues early, minimize defects, and improve the consistency of the products supplied by the vendor.
How does the Development (D) aspect of SQDCP impact supplier performance?
The Development (D) aspect of the SQDCP framework focuses on building the supplier’s capabilities and processes to meet evolving needs. This could involve training, process improvement, or equipment upgrades. By investing in supplier development, businesses ensure that their suppliers are continuously improving, which ultimately enhances overall supplier performance.
What is the significance of Capability (C) in the SQDCP framework?
Capability (C) in the SQDCP framework refers to the supplier’s ability to consistently meet quality standards, handle increasing production demands, and adapt to changes in the supply chain. Assessing and improving supplier capabilities ensures that they can scale operations efficiently and reliably, ultimately contributing to better overall performance.
How does Performance (P) monitoring work within the SQDCP framework?
Performance (P) monitoring within the SQDCP framework involves tracking and assessing the supplier’s ability to meet agreed-upon quality, delivery, and cost metrics over time. By monitoring these key performance indicators (KPIs), businesses can quickly identify underperforming suppliers and take corrective actions to maintain a high level of supplier performance.
How do you measure supplier performance in the SQDCP framework?
Supplier performance is measured using a combination of quantitative and qualitative metrics, such as product quality, on-time delivery, cost competitiveness, customer service, and responsiveness to issues. Regular audits, scorecards, and performance reviews are used to track these metrics and identify areas where improvement is needed.
What are common challenges in implementing the SQDCP framework for supplier performance monitoring?
Common challenges in implementing the SQDCP framework include resistance from suppliers, lack of clear communication about performance expectations, difficulty in aligning KPIs with business goals, and the complexity of tracking performance across multiple suppliers. Overcoming these challenges requires strong collaboration, clear guidelines, and an effective supplier engagement strategy.
How do you evaluate Supplier Quality (SQ) in the SQDCP framework?
Supplier Quality (SQ) is evaluated through inspections, product testing, and audits to ensure that the supplier’s output meets the required quality standards. Performance data, such as defect rates and customer feedback, is used to monitor supplier quality over time and identify any quality issues that need to be addressed.
How can the SQDCP framework help reduce risks in the supply chain?
The SQDCP framework helps reduce supply chain risks by proactively identifying potential quality, capability, and performance issues before they impact production or customer satisfaction. By continuously monitoring and developing suppliers, businesses can ensure that their suppliers are equipped to handle changing demands, reducing the likelihood of disruptions or quality failures.
What metrics are typically used to assess supplier performance in the SQDCP framework?
Common metrics used to assess supplier performance in the SQDCP framework include product defect rates, delivery timeliness, cost efficiency, lead times, customer satisfaction scores, and compliance with contractual agreements. These metrics are tracked through scorecards, audits, and regular performance reviews.
How can the SQDCP framework drive continuous improvement with suppliers?
The SQDCP framework drives continuous improvement by focusing on regular performance monitoring, identifying areas for improvement, and working with suppliers to implement development actions. This ongoing collaboration fosters a culture of innovation, ensuring that suppliers consistently improve their capabilities and performance over time.
What are the benefits of using the SQDCP framework for supplier performance monitoring?
The benefits of using the SQDCP framework for supplier performance monitoring include better alignment between suppliers and business goals, improved quality and consistency in products, proactive identification and resolution of issues, and stronger supplier relationships. Ultimately, this framework leads to improved supply chain performance and reduced risks.