In today’s fast-paced industrial landscape, manufacturers are constantly striving to improve productivity, efficiency, and profitability. One critical metric that has proven invaluable in assessing and enhancing the performance of manufacturing equipment is Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE). OEE is a powerful tool that provides a clear, data-driven measure of how well a manufacturing process is performing in terms of equipment utilization, quality, and availability.
OEE is commonly used in manufacturing industries to monitor and improve the performance of equipment by identifying areas for improvement and quantifying progress over time. By understanding and applying OEE, companies can minimize downtime, optimize their production processes, and ensure that their machinery is running at maximum potential.
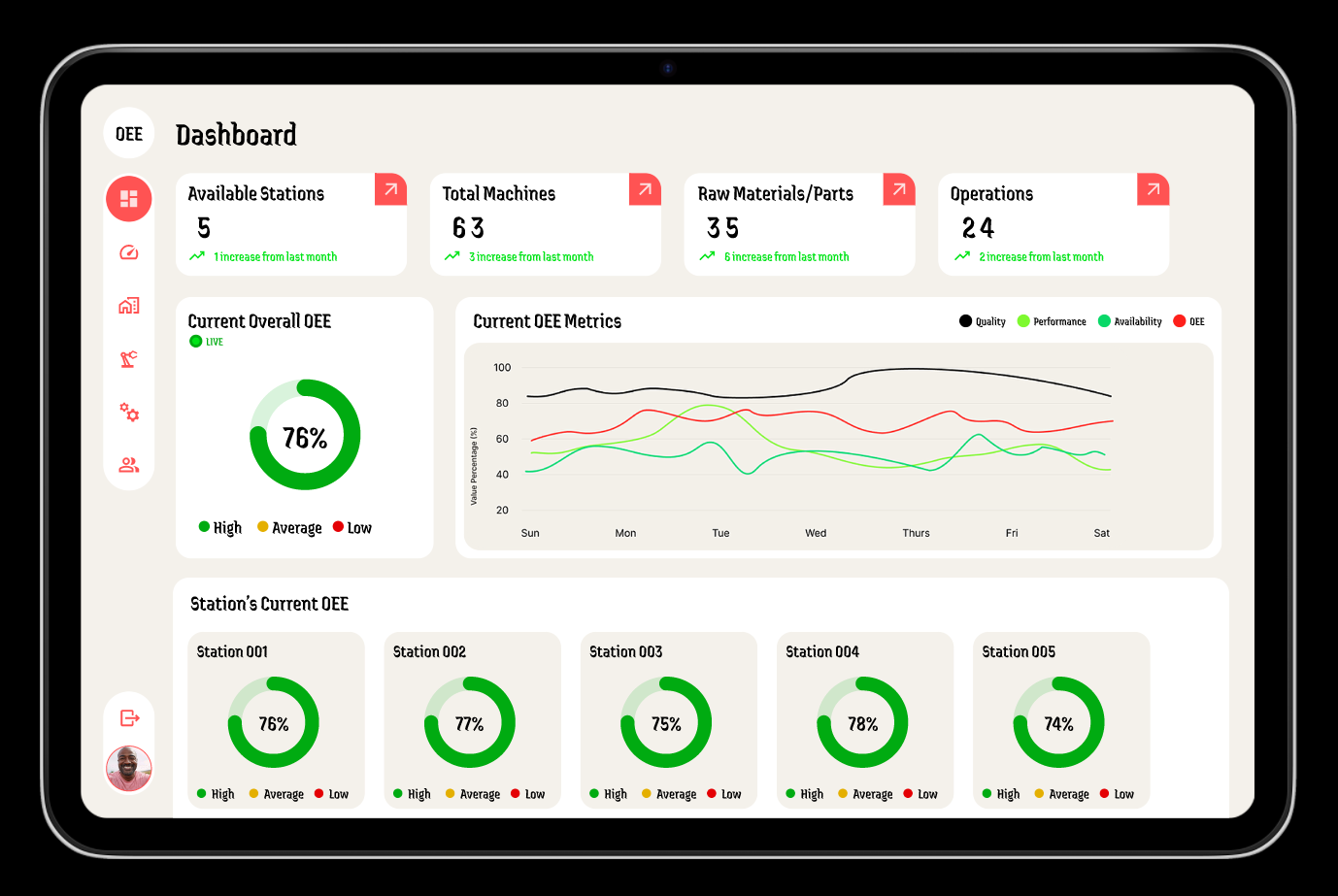
The Three Components of OEE
OEE is calculated based on three key factors: Availability, Performance, and Quality. Each of these factors targets a different aspect of equipment utilization and together provides a comprehensive view of equipment effectiveness.
1. Availability
Availability measures the percentage of scheduled time that the equipment is ready for production. It accounts for any downtime that occurs during the production process, whether it’s planned (such as maintenance or changeovers) or unplanned (such as equipment failures or breakdowns). Essentially, availability is the ratio of actual operating time to planned production time.
Formula for Availability:
Availability = (Operating Time / Planned Production Time)
Improving Availability:
To enhance availability, manufacturers can focus on reducing both planned and unplanned downtime. This may include scheduling preventive maintenance during non-operational hours, improving equipment reliability, and streamlining changeovers or setups.
2. Performance
Performance takes into account the speed at which the equipment operates compared to its maximum designed speed. It measures how efficiently the machine produces goods when it is running, without considering downtime. Performance losses can occur due to slow cycles, idling, or short stops that reduce the overall speed of the equipment.
Formula for Performance:
Performance = (Ideal Cycle Time × Total Count) / Operating Time
Improving Performance:
Improving performance typically involves identifying and eliminating inefficiencies such as bottlenecks, suboptimal machine settings, or operator errors. By ensuring that machines are running at their ideal speeds, manufacturers can significantly boost production rates without the need for additional resources.
3. Quality
Quality measures the percentage of products that meet quality standards out of the total products produced. It considers any defects, rework, or scrap that occurs during the production process. Poor quality can result in wasted materials, rework, and increased production costs, all of which negatively affect overall equipment effectiveness.
Formula for Quality:
Quality = Good Count / Total Count
Improving Quality:
To improve the quality component of OEE, manufacturers should focus on minimizing defects and scrap. This may involve enhancing the precision of the equipment, providing operator training, and implementing quality control measures throughout the production process.
Calculating OEE
Once the values for availability, performance, and quality have been determined, calculating the OEE becomes straightforward. OEE is the product of the three factors, represented as a percentage.
Formula for OEE:
OEE = Availability × Performance × Quality

The Importance of OEE
OEE is an essential tool for manufacturers because it provides a clear, actionable insight into how well their equipment is performing. By breaking down equipment effectiveness into availability, performance, and quality, it becomes easier to pinpoint specific issues and develop targeted strategies for improvement.
1. Identifying Bottlenecks
OEE helps identify bottlenecks in the production process. If a machine is consistently underperforming or experiencing frequent breakdowns, OEE data can highlight these issues, allowing managers to focus their efforts on resolving the root cause of the problem.
2. Reducing Downtime
OEE allows manufacturers to monitor and minimize downtime by providing real-time data on machine availability. This data can then be used to develop more effective maintenance schedules, reduce changeover times, and ensure that equipment is operational when needed.
3. Improving Quality Control
OEE also plays a crucial role in improving product quality. By monitoring the quality component of OEE, manufacturers can detect defects early in the production process and take corrective action before they lead to costly rework or scrap.
4. Benchmarking and Continuous Improvement
OEE provides a quantifiable metric that can be used for benchmarking performance over time. By tracking OEE data, manufacturers can set performance targets, measure progress, and identify opportunities for continuous improvement.
Best Practices for Maximizing OEE
To maximize the effectiveness of OEE and improve overall equipment performance, manufacturers should adopt the following best practices:
- Regular Equipment Maintenance: Scheduled preventive maintenance is crucial for ensuring that machines are always operating at their best.
- Operator Training: Well-trained operators are essential for maintaining high levels of equipment performance and quality.
- Implementing Lean Manufacturing Principles: Lean manufacturing principles, such as reducing waste and optimizing workflows, complement OEE by focusing on efficiency and continuous improvement.
- Real-Time Monitoring and Data Analysis: Using real-time data collection and analysis tools can help manufacturers monitor OEE in real-time and take corrective action immediately.
Overall Equipment Effectiveness(OEE)
1. What is Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE)?
Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) is a performance metric that measures the efficiency of equipment in a manufacturing process. It combines three components—Availability, Performance, and Quality—into a single percentage, helping manufacturers understand how well their equipment is being utilized.

2. Why is OEE important for manufacturers?
OEE is crucial for manufacturers because it provides clear insights into equipment performance. By monitoring OEE, companies can identify bottlenecks, reduce downtime, improve product quality, and enhance overall productivity. It helps companies focus on areas needing improvement for efficient operations.
3. What are the components of OEE?
OEE is made up of three components:
- Availability: The proportion of scheduled time that the equipment is available for operation.
- Performance: How fast the equipment operates compared to its designed speed.
- Quality: The percentage of good products produced out of the total output.
4. How is OEE calculated?
OEE is calculated by multiplying the three components—Availability, Performance, and Quality. The formula is:
OEE = Availability × Performance × Quality.
For example, if Availability is 90%, Performance is 85%, and Quality is 95%, then OEE would be 0.90 × 0.85 × 0.95 = 72.675%.
5. What is considered a good OEE score?
An OEE score of 85% or above is considered world-class in most industries. However, scores can vary by industry and equipment type. Anything above 60% is considered an opportunity for improvement, but 85% and above indicates that the equipment is operating near its full potential.
6. What causes low OEE?
Low OEE can be caused by various factors such as frequent equipment downtime (both planned and unplanned), slow equipment speeds, production bottlenecks, or high defect rates. These factors contribute to inefficiency in Availability, Performance, and Quality.
7. How can Availability be improved?
Availability can be improved by reducing unplanned downtime through preventive maintenance, minimizing setup or changeover times, and ensuring that machines are reliable and well-maintained to avoid breakdowns during production hours.
8. What strategies can improve Performance?
Improving Performance involves identifying and eliminating inefficiencies such as slow cycles or machine idling. Ensuring that machines are running at their optimal speed, providing proper operator training, and reducing idle times can lead to better performance.
9. How can Quality be enhanced in OEE?
Quality can be improved by reducing defects and rework. Manufacturers can enhance Quality by implementing stricter quality control measures, training operators to ensure accurate production, and improving equipment precision to minimize variability and waste.
10. How does OEE help in continuous improvement?
OEE provides a measurable metric that helps manufacturers track their progress over time. By identifying specific areas of inefficiency in Availability, Performance, or Quality, manufacturers can set improvement goals and monitor how changes impact overall efficiency.
11. What is the difference between planned and unplanned downtime in OEE?
Planned downtime refers to scheduled activities such as maintenance, cleaning, or changeovers, while unplanned downtime is unexpected and occurs due to equipment failures, breakdowns, or errors. Unplanned downtime usually has a more significant negative impact on OEE.
12. How can OEE data be collected?
OEE data can be collected manually by operators or automatically using sensors, production monitoring systems, or OEE software tools. Automated systems provide real-time data, which allows for more accurate tracking and immediate adjustments.
13. How does OEE relate to lean manufacturing?
OEE aligns with lean manufacturing by focusing on eliminating waste, maximizing productivity, and optimizing the use of resources. Both OEE and lean methodologies aim to enhance efficiency and continuous improvement by reducing downtime and improving quality.
14. Can OEE be applied to non-manufacturing industries?
Yes, OEE principles can be applied to industries beyond manufacturing, such as healthcare, logistics, or services. Any industry that relies on equipment or processes to deliver products or services can benefit from OEE to measure and improve operational efficiency.
15. What are the common challenges in improving OEE?
Challenges in improving OEE include difficulties in data collection, resistance to change from staff, lack of resources for proper maintenance or process upgrades, and trouble in identifying root causes of inefficiencies in Availability, Performance, or Quality.