The Balanced Scorecard (BSC) is a strategic performance management tool that enables organizations to translate their vision and strategy into actionable objectives. It provides a framework for aligning business activities with the strategic goals of the organization, tracking progress, and enhancing overall performance. By focusing on multiple dimensions of success, the Balanced Scorecard helps organizations achieve sustainable growth and operational excellence.
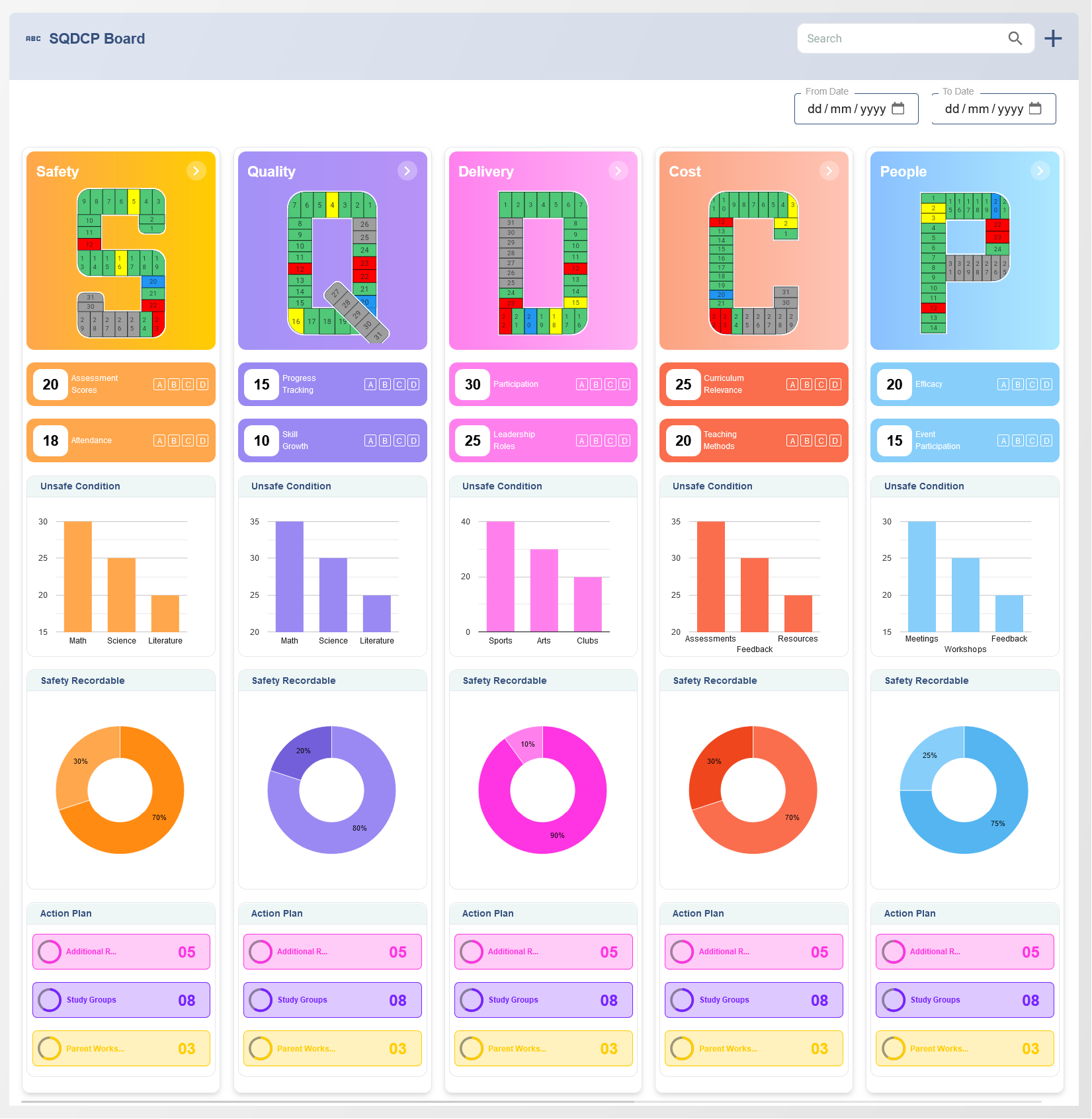
What is the Balanced Scorecard?
The Balanced Scorecard is a management tool designed to provide a comprehensive view of an organization's performance. Unlike traditional methods that focus solely on financial metrics, the Balanced Scorecard evaluates performance from four distinct perspectives:
- Financial Perspective: Measures financial performance, such as revenue growth, profitability, and cost management.
- Customer Perspective: Evaluates customer satisfaction, retention, and market share metrics.
- Internal Process Perspective: Assesses the efficiency and effectiveness of business processes.
- Learning and Growth Perspective: Focuses on organizational development, employee training, and innovation.
By integrating these perspectives, the Balanced Scorecard provides a holistic view of an organization's performance and strategic alignment.
Why Use a Balanced Scorecard?
The Balanced Scorecard offers several advantages that make it a vital tool for organizations aiming to achieve their strategic objectives:
- Strategic Alignment: Aligns daily operations with long-term goals to ensure consistency and focus.
- Improved Decision-Making: Provides actionable insights by linking performance metrics to strategic priorities.
- Enhanced Communication: Clearly communicates organizational goals and progress to stakeholders.
- Performance Tracking: Monitors progress across multiple dimensions, enabling timely interventions and adjustments.
- Focus on Long-Term Value: Balances short-term financial goals with long-term strategic objectives.
Where is the Balanced Scorecard Applied?
The Balanced Scorecard is a versatile tool used across various industries and organizational levels. Common applications include:
- Corporate Strategy: Helps large organizations align diverse departments and business units with overarching strategic goals.
- Public Sector: Enables government agencies to improve service delivery and operational efficiency.
- Nonprofits: Assists in achieving mission-driven goals while ensuring financial sustainability.
- Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs): Provides a structured approach to growth and competitive advantage.
- Project Management: Tracks project performance and alignment with strategic objectives.
The adaptability of the Balanced Scorecard makes it valuable for organizations of all sizes and industries.
When to Use a Balanced Scorecard?
The Balanced Scorecard is most effective in scenarios where strategic clarity and performance alignment are essential. Common use cases include:
- Strategic Planning: During the development of long-term goals and objectives.
- Performance Reviews: When evaluating organizational, departmental, or individual performance.
- Change Management: To align organizational activities with new strategic directions.
- Continuous Improvement: As part of an ongoing effort to enhance processes and outcomes.
- Stakeholder Communication: To provide a transparent view of progress toward goals.
By integrating the Balanced Scorecard into routine operations, organizations can maintain focus on their strategic priorities.
How to Implement a Balanced Scorecard?
Implementing a Balanced Scorecard involves several key steps:
- Define the Vision and Strategy: Clearly articulate the organization’s mission, vision, and strategic goals.
- Identify Objectives for Each Perspective: Establish specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) objectives for the financial, customer, internal process, and learning and growth perspectives.
- Select Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Choose metrics that effectively measure progress toward each objective.
- Develop Initiatives: Create actionable plans to achieve the objectives and improve performance.
- Communicate the Balanced Scorecard: Ensure that all stakeholders understand the objectives, KPIs, and initiatives.
- Monitor and Review Progress: Regularly track performance and adjust strategies as needed.
Successful implementation requires strong leadership, clear communication, and a commitment to continuous improvement.
The Meaning of Balanced Scorecard: What, Why, Where, When and How
What is a Balanced Scorecard?
A Balanced Scorecard is a strategic planning and performance management tool that provides a comprehensive view of an organization's goals and progress across financial, customer, internal process, and learning and growth perspectives.
Why is a Balanced Scorecard important for organizations?
The Balanced Scorecard helps organizations align their activities with their vision and strategy, track performance, and ensure long-term success by focusing on both financial and non-financial objectives.
Where can a Balanced Scorecard be applied?
A Balanced Scorecard can be applied in any organization, including businesses, non-profits, and government entities, to manage strategy, improve performance, and achieve organizational goals.
When should a Balanced Scorecard be implemented?
The Balanced Scorecard can be implemented during any strategic planning process or when an organization seeks to improve performance tracking and align activities with its strategic goals.
How does the Balanced Scorecard work?
The Balanced Scorecard works by measuring performance in four key areas: financial performance, customer satisfaction, internal processes, and learning and growth. It helps organizations assess their strategies and make informed decisions to achieve long-term objectives.
What are the four main perspectives of a Balanced Scorecard?
The four perspectives are: 1) Financial - measures financial performance; 2) Customer - evaluates customer satisfaction and retention; 3) Internal Process - looks at efficiency and process improvements; 4) Learning & Growth - focuses on employee development and organizational learning.
How does a Balanced Scorecard improve decision-making?
The Balanced Scorecard improves decision-making by providing a clear framework to evaluate progress and performance from multiple perspectives, helping managers make more informed, data-driven decisions that align with organizational goals.
What role does the Balanced Scorecard play in strategy management?
The Balanced Scorecard helps manage strategy by translating high-level strategic objectives into measurable goals, ensuring that all activities and resources are aligned with the organization's vision and mission.
How is a Balanced Scorecard different from traditional performance metrics?
The Balanced Scorecard goes beyond financial metrics by incorporating non-financial metrics like customer satisfaction, internal processes, and employee development, providing a more holistic view of organizational performance.
Can the Balanced Scorecard be customized for specific industries?
Yes, the Balanced Scorecard can be tailored to specific industries by adjusting the metrics and goals to reflect the unique needs, challenges, and priorities of each sector.
How do you measure success with a Balanced Scorecard?
Success is measured through KPIs (Key Performance Indicators) that align with strategic goals in the four Balanced Scorecard perspectives. Regular monitoring of these indicators allows organizations to track progress toward their objectives.
What challenges might you face when implementing a Balanced Scorecard?
Challenges include resistance to change, difficulty in defining the right KPIs, ensuring alignment across departments, and the complexity of maintaining accurate data for reporting.
How does the Balanced Scorecard help align an organization's goals?
The Balanced Scorecard helps align goals by clearly linking performance metrics to strategic objectives, ensuring that all departments and employees work toward common organizational goals.
How frequently should the Balanced Scorecard be updated?
The Balanced Scorecard should be reviewed and updated regularly (quarterly or annually) to reflect changes in strategy, goals, and external factors that may impact the organization’s performance.
What are the key benefits of using a Balanced Scorecard?
Key benefits include enhanced strategic alignment, improved performance measurement, better decision-making, clearer communication of organizational goals, and increased accountability across all levels of the organization.