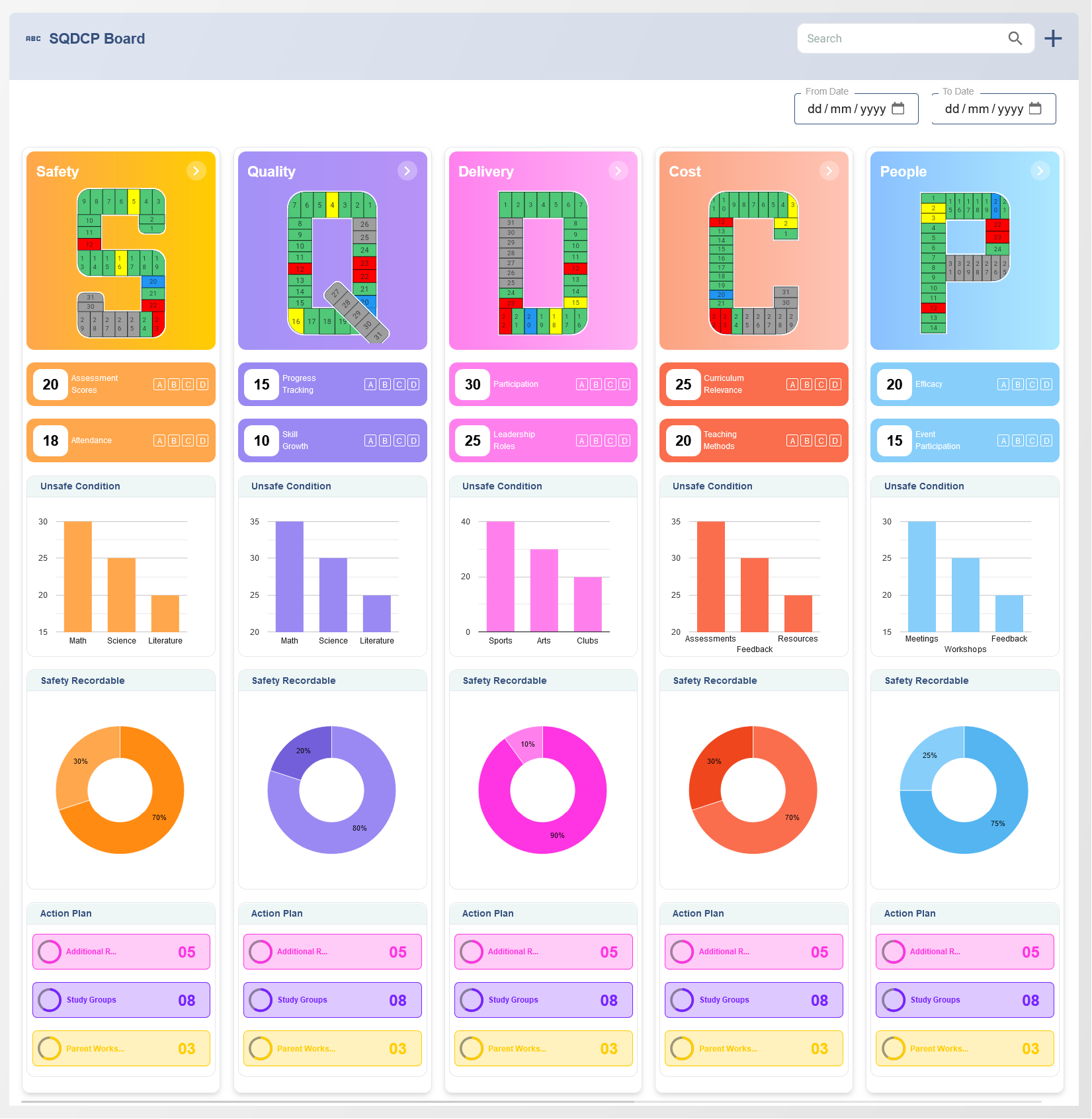
The Balanced Scorecard (BSC) is a strategic management tool that helps organizations translate their vision and strategy into actionable objectives. Developed by Dr. Robert Kaplan and Dr. David Norton in the early 1990s, the BSC is designed to provide a comprehensive view of an organization's performance by measuring key areas. These areas are typically divided into four categories: financial performance, customer satisfaction, internal business processes, and learning and growth. By focusing on these four perspectives, organizations can ensure they balance short-term financial goals with long-term strategic objectives.
1. Holistic View of Organizational Performance
One of the primary benefits of the Balanced Scorecard is its ability to provide a holistic view of organizational performance. Traditionally, performance management systems focused primarily on financial metrics such as revenue and profit margins. However, the BSC expands beyond these financial measures to incorporate non-financial perspectives. This broad approach ensures that all critical factors contributing to the success of the business are measured and managed.
By assessing performance across financial, customer, internal processes, and learning and growth perspectives, organizations can make better decisions, spot potential issues, and adapt to changes in the marketplace. This allows them to manage both day-to-day operations and long-term goals more effectively, ensuring alignment with overall strategy.
2. Improved Strategic Alignment
The Balanced Scorecard provides a framework for aligning an organization's activities with its strategic objectives. It helps management link various departments, units, or teams with the broader goals of the organization. This alignment ensures that all efforts across the organization are contributing toward the same strategic objectives, increasing efficiency and effectiveness.
With the BSC, employees can clearly see how their individual or team objectives fit into the larger picture, allowing them to understand their role in the organization's success. This clarity enhances motivation and fosters a sense of purpose, leading to improved performance and higher levels of employee engagement.
3. Enhanced Decision-Making
The Balanced Scorecard encourages data-driven decision-making by providing a wealth of performance data from multiple perspectives. With access to key performance indicators (KPIs) across different areas of the organization, leaders are empowered to make informed decisions based on accurate, real-time information. Instead of relying solely on financial results, the BSC enables managers to consider a broader range of factors that influence organizational success, such as customer satisfaction, process efficiency, and employee development.
By measuring both leading and lagging indicators, organizations are better equipped to identify potential issues before they become significant problems. For example, monitoring customer satisfaction levels can provide early warnings about potential churn, while assessing internal processes can highlight inefficiencies that may impact overall productivity. These insights allow management to take corrective actions proactively, rather than reacting to problems after they have already impacted performance.
4. Continuous Improvement
Continuous improvement is a central theme of the Balanced Scorecard. By regularly tracking performance across the four perspectives, organizations can identify areas where they are excelling and where they need to improve. This focus on ongoing performance evaluation encourages a culture of learning and growth within the organization.
For instance, the Learning and Growth perspective of the BSC emphasizes the development of employee skills and capabilities. By measuring this dimension, organizations can identify skills gaps and invest in training and development programs to address them. As employees grow and develop their skills, they can contribute more effectively to the organization's goals, leading to improved performance over time.
Similarly, the Internal Business Processes perspective focuses on optimizing processes to drive efficiency. By continuously reviewing and refining internal processes, organizations can reduce waste, eliminate bottlenecks, and improve overall productivity. This process-oriented approach helps organizations stay competitive and agile in a constantly changing business environment.
5. Better Communication and Collaboration
The Balanced Scorecard fosters better communication and collaboration across different departments or teams within an organization. Since the BSC aligns various functions around a shared vision and set of objectives, it encourages cross-functional collaboration to achieve strategic goals. Employees from different departments can work together to improve processes, resolve challenges, and contribute to achieving the organization's goals.
Furthermore, the BSC's structured approach to performance management provides a common language for discussing organizational objectives and results. Whether it's the leadership team, department managers, or frontline employees, everyone can speak the same language when discussing performance, making it easier to align efforts and share insights. This improves transparency, reduces misunderstandings, and fosters a more collaborative work environment.
6. Increased Accountability
The Balanced Scorecard enhances accountability by setting clear performance objectives and measuring progress toward them. With specific KPIs tied to organizational goals, employees and departments are held accountable for achieving the results that matter most. This accountability creates a strong sense of ownership, motivating employees to focus on the outcomes that directly contribute to the organization's success.
At the same time, the BSC helps organizations avoid the pitfall of focusing solely on financial metrics. By measuring performance across multiple dimensions, it encourages employees to take responsibility not only for financial results but also for customer satisfaction, operational efficiency, and personal development. This balanced approach ensures that all aspects of the organization's performance are considered and managed appropriately.
7. Alignment with Long-Term Goals
The Balanced Scorecard is an invaluable tool for ensuring that short-term actions align with long-term goals. Many organizations face the challenge of balancing immediate financial pressures with the need to invest in future growth. The BSC addresses this by emphasizing both leading indicators (such as employee skills and customer loyalty) and lagging indicators (such as financial performance and market share).
For example, an organization may prioritize customer satisfaction in the short term, knowing that satisfied customers are more likely to become repeat buyers and brand advocates. At the same time, the organization may invest in employee development and process optimization, ensuring that it remains competitive and efficient in the long term. This strategic alignment ensures that short-term actions are in harmony with the organization's overarching vision and objectives.
8. Greater Competitive Advantage
By integrating financial and non-financial metrics, the Balanced Scorecard provides a comprehensive view of an organization's competitive position. It helps organizations identify opportunities for differentiation and areas where they can outperform competitors. Whether through improving customer service, streamlining operations, or enhancing employee skills, the BSC enables organizations to build sustainable competitive advantages over time.
Furthermore, the BSC encourages a focus on customer needs and expectations. By understanding what drives customer satisfaction and loyalty, organizations can design better products, services, and experiences that resonate with their target market. This customer-centric approach helps organizations stay ahead of the competition and build long-lasting relationships with customers.
Key Benefits of the Balanced Scorecard (BSC) in Performance Management
What is the Balanced Scorecard (BSC)?
The Balanced Scorecard (BSC) is a strategic performance management tool that helps organizations translate their vision and strategy into a set of measurable objectives. It integrates both financial and non-financial performance indicators to provide a comprehensive view of organizational performance.
How does the Balanced Scorecard (BSC) improve performance management?
The BSC improves performance management by providing a balanced view of organizational performance through its four perspectives: financial, customer, internal processes, and learning & growth. It aligns operational activities with strategic goals, helping organizations focus on key drivers of success.
What are the key components of the Balanced Scorecard (BSC)?
The key components of the BSC include:
- Financial Perspective: Measures financial performance, such as profitability and cost management.
- Customer Perspective: Focuses on customer satisfaction and market share.
- Internal Process Perspective: Evaluates the efficiency and effectiveness of internal processes.
- Learning & Growth Perspective: Looks at employee development and organizational knowledge management.
Why is the Balanced Scorecard (BSC) considered a strategic management tool?
The BSC is considered a strategic management tool because it helps organizations link their strategic objectives with measurable goals. By focusing on both leading and lagging indicators, it enables organizations to track performance and make adjustments to stay on course toward long-term success.
How does the Balanced Scorecard (BSC) align business activities with strategy?
The BSC aligns business activities with strategy by translating high-level strategic goals into specific, measurable actions across different areas of the organization. It ensures that every department and employee works towards the same strategic objectives, fostering alignment and focus.
What are the four perspectives of the Balanced Scorecard (BSC)?
The four perspectives of the BSC are:
- Financial: Measures traditional financial outcomes like revenue and cost management.
- Customer: Evaluates customer satisfaction, loyalty, and market share.
- Internal Processes: Focuses on the efficiency and effectiveness of internal business processes.
- Learning & Growth: Concerned with the development of employee skills, knowledge, and innovation.
How does the Balanced Scorecard (BSC) help organizations track progress?
The BSC tracks progress by providing measurable metrics for each of its four perspectives. Organizations can monitor their performance across different areas in real-time, making it easier to identify areas of improvement and make data-driven decisions to stay aligned with their strategic objectives.
What are the benefits of using the Balanced Scorecard (BSC) for performance measurement?
The benefits of using the BSC for performance measurement include improved strategic alignment, better decision-making, enhanced performance visibility, and the ability to track both leading and lagging indicators. It fosters a holistic view of performance, reducing the risk of focusing on financial metrics alone.
How can the Balanced Scorecard (BSC) improve decision-making?
The BSC improves decision-making by providing a comprehensive framework for assessing performance across key areas. It helps managers identify where adjustments are needed, whether in financial performance, customer satisfaction, or internal processes, enabling more informed and strategic decisions.
How does the Balanced Scorecard (BSC) help with goal setting?
The BSC aids goal setting by breaking down strategic objectives into specific, measurable goals within each perspective. This makes it easier for teams to understand their role in achieving organizational success and provides a clear direction for performance improvement.
Can the Balanced Scorecard (BSC) be used to track non-financial metrics?
Yes, the BSC can be used to track non-financial metrics, such as customer satisfaction, employee engagement, and process efficiency. By focusing on both financial and non-financial indicators, the BSC offers a more comprehensive view of organizational performance.
How does the Balanced Scorecard (BSC) contribute to long-term strategic success?
The BSC contributes to long-term success by emphasizing continuous improvement across multiple dimensions of performance. By monitoring progress against strategic objectives, organizations can make adjustments and foster a culture of ongoing learning and growth.
How can the Balanced Scorecard (BSC) be adapted for different industries?
The BSC can be adapted for different industries by customizing the metrics and objectives within each perspective to reflect the unique challenges and goals of each sector. Whether in healthcare, manufacturing, or services, the BSC can be tailored to provide relevant insights and drive success.
What is the relationship between the Balanced Scorecard (BSC) and continuous improvement?
The BSC is closely linked to continuous improvement because it tracks performance across multiple dimensions and encourages ongoing learning. By providing actionable insights, the BSC helps organizations identify areas for improvement and take proactive steps toward better performance.
What challenges might organizations face when implementing the Balanced Scorecard (BSC)?
Some challenges organizations might face when implementing the BSC include selecting the right metrics, aligning the entire organization with strategic goals, ensuring proper data collection, and maintaining engagement across all levels. However, these challenges can be mitigated through proper training and communication.