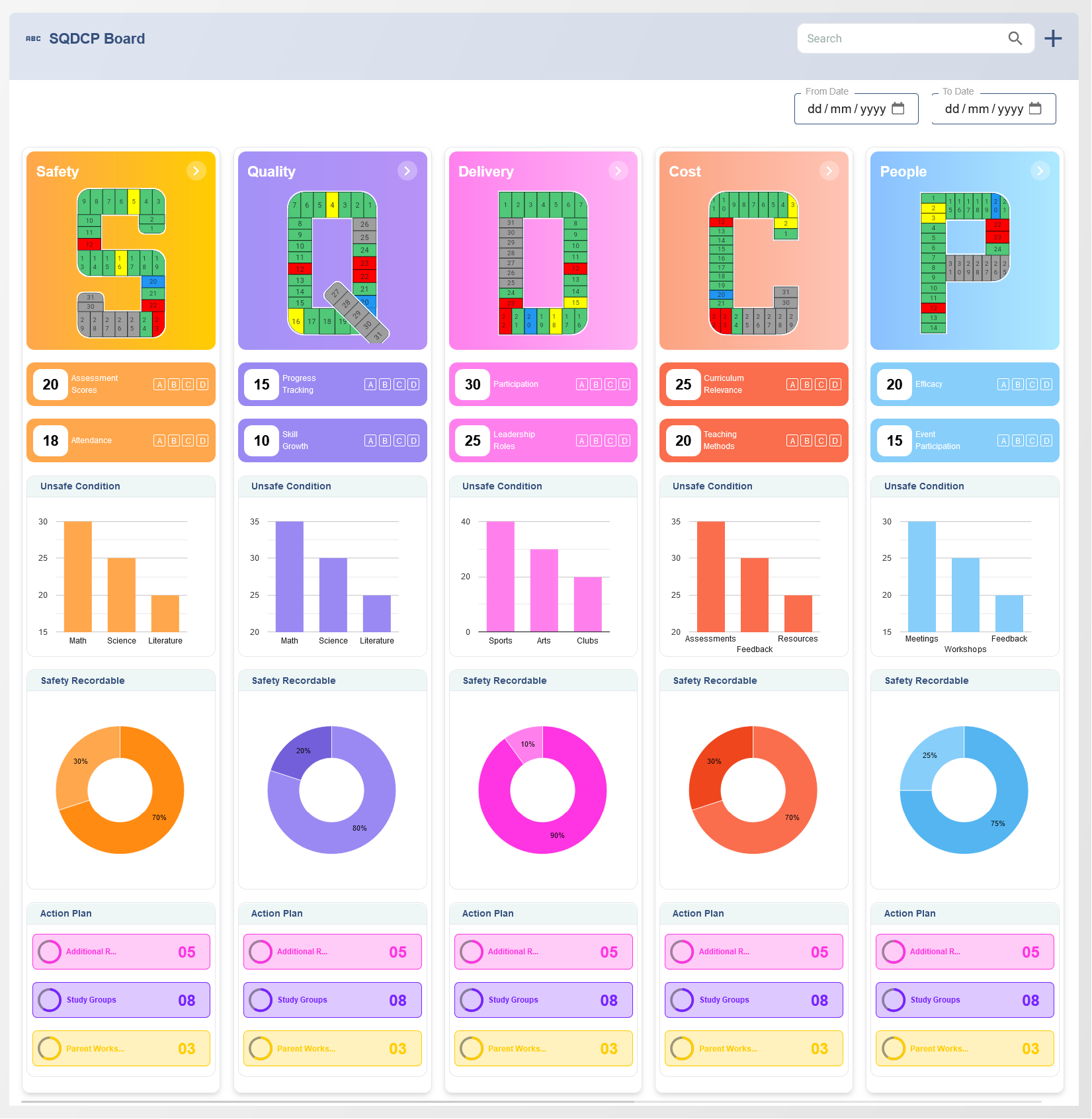
The Balanced Scorecard (BSC) is a strategic planning and management tool that helps organizations align their business activities with their vision and strategy. Developed in the early 1990s, the BSC provides a comprehensive framework that incorporates financial and non-financial measures to assess an organization's performance. It moves beyond traditional financial metrics by adding perspectives such as customer satisfaction, internal processes, and employee learning and growth.
The Four Perspectives of the Balanced scorecard
The core concept of the Balanced Scorecard is its four key perspectives. These perspectives are designed to give a holistic view of an organization’s performance. By focusing on both financial and non-financial aspects, the BSC enables organizations to achieve a balanced approach to performance management.
- Financial Perspective: This perspective focuses on traditional financial performance measures, such as profitability, revenue growth, and cost reduction. It answers the question: "How do we look to our shareholders?" By tracking financial metrics, organizations can measure their ability to deliver value to shareholders and stakeholders.
- Customer Perspective: The customer perspective emphasizes customer satisfaction, loyalty, and market share. It answers the question: "How do customers perceive us?" Key metrics may include customer retention rates, customer satisfaction scores, and the organization's ability to meet customer needs. By understanding customer expectations, organizations can ensure they remain competitive in the market.
- Internal Process Perspective: This perspective examines internal business processes to ensure that they are efficient and effective. It answers the question: "What must we excel at?" Organizations need to identify and improve key processes that directly impact their value proposition to customers and shareholders. Metrics might include operational efficiency, product quality, and innovation.
- Learning and Growth Perspective: This perspective focuses on employee development, organizational culture, and innovation. It answers the question: "How can we continue to improve and create value?" By investing in employee skills, knowledge, and leadership, organizations can ensure sustainable growth and adaptability to changing environments.
The Importance of a Balanced Approach
One of the key benefits of the Balanced Scorecard is its ability to integrate different performance metrics into a unified system. Traditional management tools often emphasize financial outcomes, but the BSC includes other critical dimensions of performance that contribute to long-term success. By balancing financial and non-financial indicators, organizations can avoid a narrow focus on short-term financial results and ensure they are addressing the underlying drivers of success.
The Balanced Scorecard is particularly effective in helping organizations translate their strategic objectives into actionable goals. For example, a company might have a strategic objective to improve customer satisfaction, which could be reflected in the customer perspective. The BSC allows the company to define specific goals (e.g., improving customer satisfaction scores) and identify the internal processes and employee skills necessary to achieve that goal.
How the Balanced Scorecard Drives Strategy Execution
The Balanced Scorecard is not just a tool for measuring performance; it is also a framework for executing strategy. It connects an organization’s long-term strategy with daily operations. By setting specific targets and tracking progress across all four perspectives, the BSC ensures that everyone in the organization is aligned with the overall strategy.
For example, an organization may set strategic objectives to expand into new markets. This could impact the financial perspective (e.g., revenue growth) as well as the customer perspective (e.g., gaining market share). To support this objective, the internal process perspective might include optimizing supply chain operations to handle increased demand, while the learning and growth perspective may focus on developing the sales team’s skills in international markets.
Steps in Implementing the Balanced scorecard
Implementing a Balanced Scorecard involves several key steps, including defining strategic objectives, identifying performance measures, setting targets, and developing action plans to achieve those targets.
- Step 1: Define Strategic Objectives: The first step is to define the organization's high-level strategic objectives. These should be aligned with the company’s mission and vision. Strategic objectives should be clear, measurable, and achievable.
- Step 2: Develop Performance Measures: Once strategic objectives are defined, the next step is to develop performance measures for each of the four perspectives. These measures should reflect both leading indicators (which predict future success) and lagging indicators (which measure past performance).
- Step 3: Set Targets: Targets should be set for each of the performance measures. These targets represent the desired levels of performance and should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
- Step 4: Align the Organization: It is essential to ensure that all departments and individuals are aligned with the strategic objectives. This can be done by communicating the Balanced Scorecard throughout the organization and ensuring that each team understands how their work contributes to the overall strategy.
- Step 5: Monitor and Review Performance: Regularly monitoring performance and reviewing progress toward strategic goals is crucial. The Balanced Scorecard provides a framework for ongoing assessment and allows organizations to make adjustments as needed to stay on track.
Benefits of the Balanced scorecard
There are numerous benefits to adopting the Balanced Scorecard framework. Some of the key advantages include:
- Strategic Alignment: The Balanced Scorecard helps ensure that all activities within an organization are aligned with its strategic objectives. This creates a clear connection between daily operations and long-term goals.
- Holistic View of Performance: By considering financial and non-financial metrics, the Balanced Scorecard provides a more complete picture of organizational performance. It enables leaders to address the full range of factors that drive success.
- Improved Communication: The Balanced Scorecard fosters better communication across the organization. By clearly defining goals and metrics, it ensures that everyone is working toward the same objectives.
- Enhanced Decision-Making: The Balanced Scorecard helps organizations make more informed decisions by providing real-time data on key performance indicators. This data can be used to identify opportunities for improvement and take corrective action when necessary.
Introduction to the Balanced scorecard
What is the Balanced Scorecard?
The Balanced Scorecard is a strategic planning and management system used by organizations to align business activities with their vision and strategy. It helps measure performance from multiple perspectives, including financial, customer, internal processes, and learning and growth.
What are the main components of the Balanced Scorecard?
The main components of the Balanced Scorecard are the four key perspectives: financial, customer, internal processes, and learning and growth. These perspectives provide a comprehensive view of an organization's performance, balancing both short-term and long-term objectives.
Why is the Balanced Scorecard important for organizations?
The Balanced Scorecard is important because it provides a structured approach for organizations to translate strategy into action. It helps managers track performance across key areas, ensuring that objectives are met and resources are used effectively to achieve organizational goals.
How does the Balanced Scorecard help align business strategy with performance?
The Balanced Scorecard aligns business strategy with performance by establishing clear goals and measurable targets in key areas. It ensures that each perspective (financial, customer, internal processes, and learning and growth) supports the overall strategy, helping organizations focus on strategic objectives that drive success.
What are the four key perspectives in the Balanced Scorecard?
The four key perspectives in the Balanced Scorecard are:
- Financial: Measures the financial performance and how the organization creates value.
- Customer: Focuses on customer satisfaction, loyalty, and retention.
- Internal Processes: Evaluates the efficiency and effectiveness of internal processes.
- Learning and Growth: Assesses the organization's ability to innovate, improve, and develop its workforce.
How does the Balanced Scorecard contribute to strategic planning?
The Balanced Scorecard helps in strategic planning by translating an organization's vision and strategy into actionable objectives. It ensures that each department or unit aligns its goals with the organization's broader objectives, fostering a cohesive effort toward achieving long-term success.
How can the Balanced Scorecard improve decision-making in an organization?
The Balanced Scorecard improves decision-making by providing a balanced view of performance across multiple areas. It ensures that decisions are not based solely on financial outcomes but also consider customer satisfaction, internal processes, and long-term growth, leading to better-informed and strategic decisions.
What is the relationship between the Balanced Scorecard and business objectives?
The Balanced Scorecard helps connect business objectives with performance metrics by breaking down strategy into specific goals under each perspective. This alignment ensures that each area of the business contributes to the overall success of the organization and helps track progress toward achieving objectives.
Can the Balanced Scorecard be applied to both small and large organizations?
Yes, the Balanced Scorecard can be applied to both small and large organizations. It is a flexible tool that helps organizations of any size align their strategies, measure performance, and focus on key areas of improvement. The key is to adapt the framework to the organization's specific needs and goals.
How do you measure performance using the Balanced Scorecard?
Performance in the Balanced Scorecard is measured using a set of predefined metrics or Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) across the four perspectives. These KPIs are tied to the organization's strategic objectives and allow managers to track progress, identify areas of improvement, and make adjustments as needed.
What role does the Balanced Scorecard play in continuous improvement?
The Balanced Scorecard plays a key role in continuous improvement by enabling organizations to regularly review their performance across multiple areas. It encourages ongoing monitoring and adjustment of strategies, ensuring that the organization adapts and improves based on the results of each perspective.
How do you link financial and non-financial measures in the Balanced Scorecard?
The Balanced Scorecard links financial and non-financial measures by ensuring that both are considered in the strategic planning process. While financial metrics track financial performance, non-financial measures like customer satisfaction, internal efficiency, and employee development provide a more holistic view of organizational health and long-term success.
What challenges might organizations face when implementing the Balanced Scorecard?
Challenges organizations may face when implementing the Balanced Scorecard include resistance to change, lack of clear strategic objectives, insufficient data, and difficulty in aligning performance metrics with business goals. Proper training, clear communication, and alignment of the scorecard with organizational culture can help overcome these challenges.
How often should organizations update their Balanced Scorecard?
Organizations should review and update their Balanced Scorecard regularly, typically quarterly or annually, to ensure that it reflects the changing business environment and strategic priorities. Regular updates ensure that the scorecard remains relevant and aligned with the organization's evolving goals.
What are the benefits of using the Balanced Scorecard for performance management?
The benefits of using the Balanced Scorecard for performance management include improved strategic alignment, enhanced decision-making, clearer goals, better tracking of progress, and a balanced view of performance across key business areas. It helps organizations focus on long-term success while ensuring short-term objectives are met.