Integrating a Digital Balanced Scorecard (BSC) with Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems offers companies a strategic advantage. This integration provides seamless tracking of both operational and financial performance, aligning day-to-day manufacturing activities with long-term business objectives. Below is a comprehensive guide on how to effectively integrate these systems and the benefits this integration can bring to an organization.
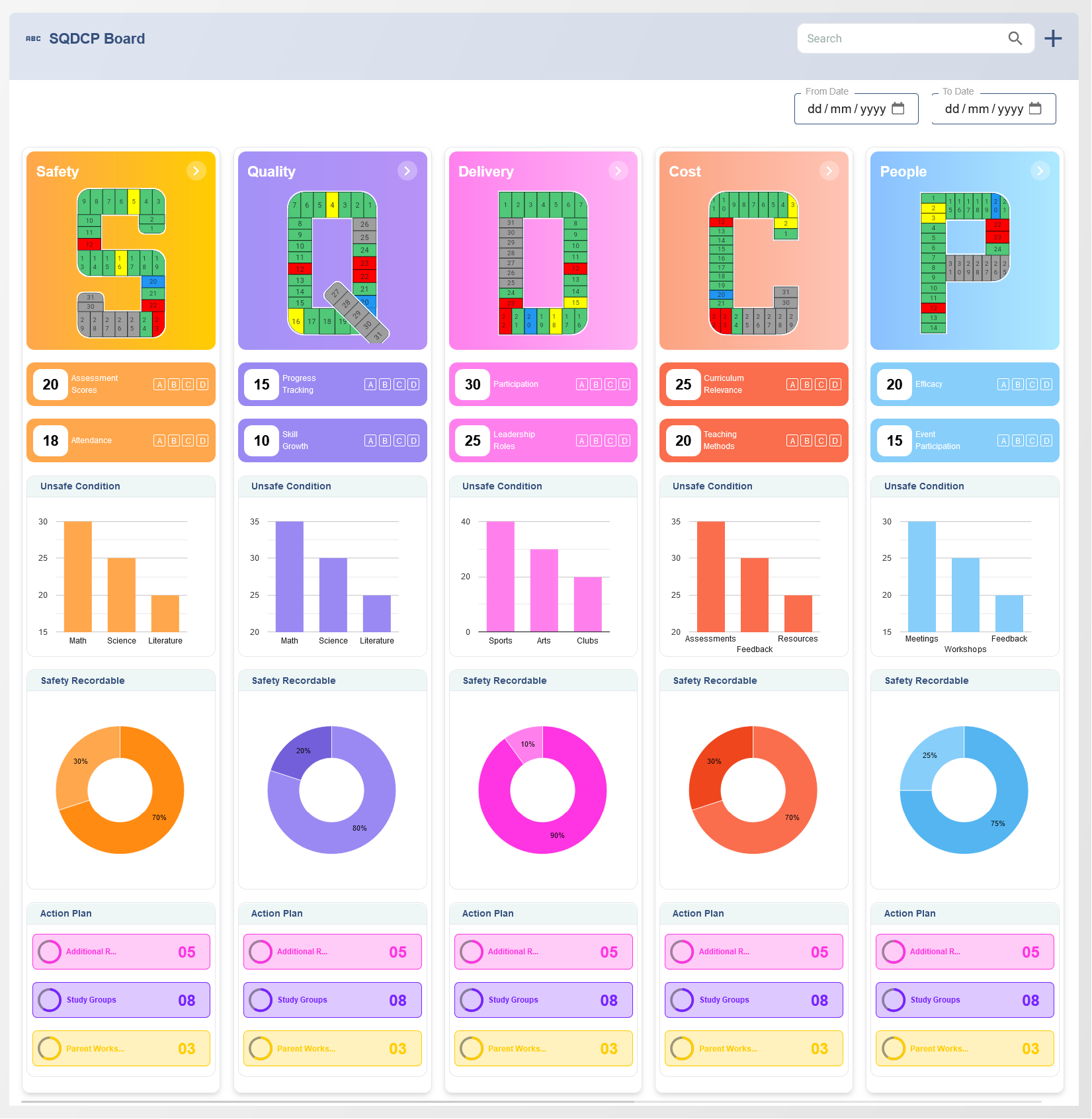
Understanding the Digital Balanced scorecard
The Digital Balanced Scorecard is a strategic management tool that helps organizations translate their vision and strategy into a set of performance measures. It typically measures performance across four key perspectives: Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, and Learning and Growth. These perspectives provide a balanced view of the organization's overall performance, enabling decision-makers to monitor critical aspects of operations, customer satisfaction, financial results, and innovation.
What is MES and ERP?
Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) are software systems that control and monitor manufacturing processes in real-time. MES helps ensure efficient production by tracking and managing production schedules, quality control, inventory, and machine performance. It provides visibility into manufacturing operations, enabling quicker response times to issues and enhancing process optimization.
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems are integrated platforms that help organizations manage their core business functions such as finance, human resources, sales, procurement, and supply chain management. ERP systems centralize data and processes, allowing for better decision-making and resource allocation across departments.
Why Integrate BSC with MES and ERP?
Integrating the Digital Balanced Scorecard with MES and ERP systems helps to bridge the gap between strategic goals and operational execution. While MES handles the real-time operations of manufacturing, and ERP provides insight into enterprise-wide resource management, the Digital BSC aligns these activities with strategic performance goals. This integration helps organizations monitor the effectiveness of their operations and ensures that their daily tasks contribute to the achievement of long-term objectives.
Steps to Integrate Digital Balanced scorecard with MES and ERP
1. Define Strategic Objectives and KPIs
The first step in integrating BSC with MES and ERP is to clearly define strategic objectives. These objectives should align with your business vision and mission. Each objective should have associated Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) that measure the performance and progress toward the goal. For example, a manufacturing company might focus on reducing production costs, improving on-time delivery, and increasing product quality.
2. Align KPIs with Operational Data
Next, align the KPIs from the Digital BSC with the data captured by the MES and ERP systems. For example, MES can provide real-time production data, such as cycle times, yield rates, and machine downtime, while ERP can offer insights into inventory levels, order fulfillment, and financial performance. Integrating these systems ensures that the data flows seamlessly and is connected to the right KPIs. This helps decision-makers track whether the company is meeting its objectives and allows them to make data-driven decisions.
3. Real-Time Data Integration
One of the key advantages of integrating BSC with MES and ERP is the ability to monitor real-time data. MES systems provide real-time data on production performance, while ERP systems offer insights into financial and operational metrics. By integrating these systems with the Digital BSC, organizations can visualize performance in real-time across different levels of the company. For example, a manager can track if production is on schedule while also keeping an eye on the company’s financial health and customer satisfaction levels.
4. Automate Reporting
Integrating the BSC with MES and ERP enables automated reporting. The Digital BSC can pull data from MES and ERP systems to generate automated reports. These reports can be customized to track the performance metrics and KPIs that matter most to the organization. Managers and executives can receive regular updates on performance, which helps them to make informed decisions quickly and adjust strategies as necessary.
5. Performance Dashboards
A key feature of integrating BSC with MES and ERP is the creation of performance dashboards. Dashboards allow organizations to monitor the performance of key business processes in one central location. By consolidating data from both systems, the Digital BSC can provide a comprehensive view of organizational performance. Dashboards should be designed to provide quick access to relevant metrics, including operational efficiency, production quality, and financial health.
6. Continuous Improvement
Integrating the Digital BSC with MES and ERP fosters a culture of continuous improvement. With real-time data and performance reports, organizations can quickly identify areas for improvement and take corrective action. For example, if production efficiency drops, the system will flag this as a deviation from the desired goal. The BSC can then be used to guide efforts to improve production processes, ensuring that changes are aligned with the company's strategic objectives.
Benefits of Integrating BSC with MES and ERP
1. Better Alignment Between Strategy and Execution
Integration ensures that daily operations are aligned with the company's long-term strategic goals. This alignment improves decision-making, resource allocation, and overall organizational efficiency. Managers can focus on actions that directly contribute to achieving business objectives, whether improving customer satisfaction or reducing operational costs.
2. Improved Visibility into Performance
Integrating BSC with MES and ERP systems provides comprehensive visibility into both financial and operational performance. Managers can track performance across departments and identify issues quickly. This visibility helps optimize processes and identify areas where improvements are needed.
3. Data-Driven Decision-Making
The integration allows companies to base their decisions on real-time, accurate data from MES and ERP systems. This reduces reliance on guesswork or outdated information, enabling more accurate forecasting and strategic decision-making.
4. Increased Operational Efficiency
Real-time monitoring of production performance and financial metrics helps identify inefficiencies quickly. By integrating the BSC with MES and ERP, businesses can streamline processes, reduce waste, and enhance productivity. This leads to cost savings and better resource utilization.
5. Faster Response to Market Changes
With integrated systems, companies can quickly respond to market changes. Whether it’s a change in customer demand or disruptions in the supply chain, having access to real-time performance data allows companies to adapt swiftly and maintain their competitive edge.
Integrate Digital Balanced scorecard to MES and ERP System
What is a Digital Balanced Scorecard?
A Digital Balanced Scorecard is a strategic management tool that provides a comprehensive view of an organization’s performance through key metrics across multiple perspectives, including financial, customer, internal processes, and learning & growth.
Why is integrating the Digital Balanced Scorecard with MES and ERP systems important?
Integration allows organizations to link real-time operational data from MES (Manufacturing Execution System) and ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) with strategic goals, providing a unified view of performance across both tactical and strategic levels.
How does integrating Digital Balanced Scorecard improve decision-making?
By integrating data from MES and ERP systems into the Balanced Scorecard, decision-makers gain access to real-time, accurate performance data, enabling more informed, timely decisions that align with both operational and strategic goals.
What are the benefits of integrating MES and ERP systems with a Digital Balanced Scorecard?
Benefits include improved decision-making, enhanced visibility of operational performance, better alignment of strategic goals with day-to-day activities, and the ability to monitor progress against key performance indicators (KPIs) in real time.
What are the key challenges in integrating Digital Balanced Scorecard with MES and ERP?
Challenges can include data synchronization, ensuring system compatibility, the complexity of aligning different data sets, and the need for ongoing maintenance and updates to the integration.
What metrics are included in a Digital Balanced Scorecard?
Metrics in a Digital Balanced Scorecard typically include financial performance indicators, customer satisfaction and loyalty metrics, process efficiency and quality measures, and employee development and innovation indicators.
How does a Digital Balanced Scorecard help track performance across various business functions?
It enables organizations to track and evaluate performance across key areas, such as finance, customer service, internal operations, and employee learning, ensuring that each function contributes to the organization’s overall goals.
What role does real-time data play in a Digital Balanced Scorecard integration?
Real-time data from MES and ERP systems provides up-to-date information that can be reflected in the Balanced Scorecard, enabling quick adjustments and ensuring that performance measures are always aligned with current conditions.
How does integration ensure better alignment between operational and strategic goals?
By integrating real-time operational data with strategic metrics, organizations can ensure that day-to-day activities and performance align with long-term objectives, facilitating goal alignment across different levels of the business.
How can organizations monitor and measure progress using Digital Balanced Scorecard integration?
Organizations can monitor and measure progress by continuously tracking KPIs and metrics from the MES and ERP systems, updating the Balanced Scorecard in real time, and identifying areas for improvement or corrective action.
Can integration help in reducing inefficiencies and operational costs?
Yes, by providing real-time insights into operations, integration helps organizations identify inefficiencies, improve process flows, and make data-driven decisions that reduce costs and optimize resources.
What tools and technologies are required for integrating Digital Balanced Scorecard with MES and ERP?
Integration may require middleware, APIs, data connectors, business intelligence tools, and compatible MES and ERP systems to ensure seamless data exchange and synchronization between the systems.
How do MES and ERP systems contribute to the effectiveness of the Digital Balanced Scorecard?
MES and ERP systems provide real-time, operational data that can be used to inform the KPIs in the Balanced Scorecard, ensuring that the scorecard reflects current performance and can drive timely actions.
How do KPIs and performance indicators in the Balanced Scorecard align with MES and ERP data?
KPIs and performance indicators from the Balanced Scorecard align with MES and ERP data by tracking metrics such as production efficiency, inventory management, and customer satisfaction, all of which are critical for performance optimization.
What are the long-term advantages of maintaining an integrated Digital Balanced Scorecard system?
Long-term advantages include improved decision-making, enhanced alignment between strategic and operational goals, ongoing performance optimization, and a stronger ability to adapt to market changes and customer needs.