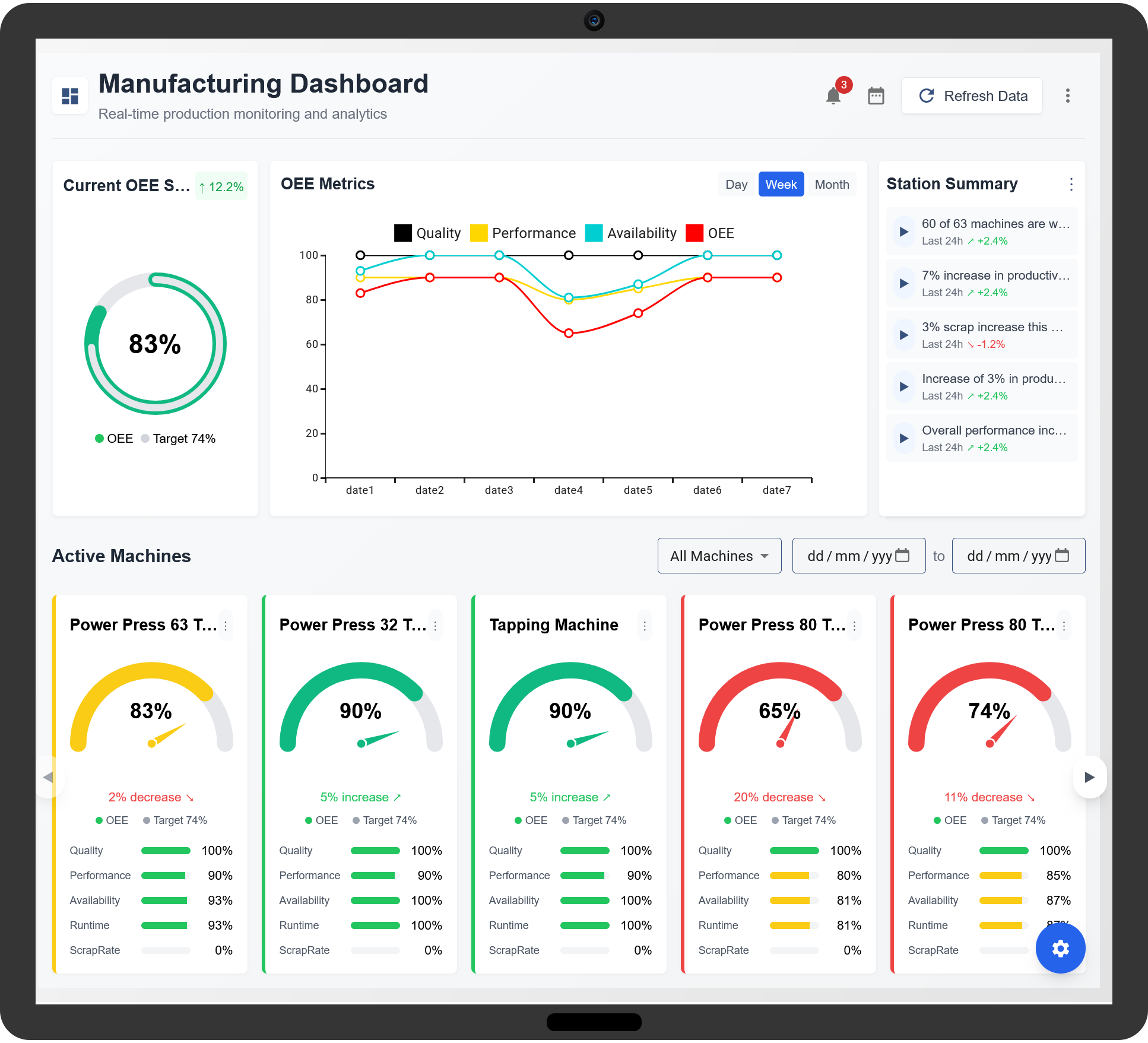
Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) is a crucial metric in manufacturing that helps assess the efficiency and effectiveness of production processes. By measuring OEE, manufacturers can identify inefficiencies, reduce downtime, and optimize productivity.
1. Understanding the Components of OEE
OEE consists of three primary factors that contribute to overall efficiency:
- Availability: Measures the actual production time compared to planned production time.
- Performance: Evaluates whether machines are operating at their maximum speed without slow cycles.
- Quality: Assesses the proportion of defect-free products manufactured.
2. How to Calculate OEE in Manufacturing
Step 1: Calculate Availability
Availability is calculated using the formula:
Availability (%) = (Actual Operating Time / Planned Production Time) × 100
This metric considers machine downtime and unplanned stoppages.
Step 2: Calculate Performance
Performance is determined as:
Performance (%) = (Total Pieces Produced × Ideal Cycle Time) / Actual Operating Time × 100
It highlights inefficiencies due to slow cycles or minor stoppages.
Step 3: Calculate Quality
Quality is measured by the ratio of good products to total products:
Quality (%) = (Good Pieces Produced / Total Pieces Produced) × 100
It indicates the effectiveness of production in minimizing defects.
Step 4: Compute OEE
OEE is the product of the three metrics:
OEE (%) = Availability × Performance × Quality / 10000
This final percentage provides a comprehensive measure of production efficiency.
3. Benefits of Measuring OEE
- Improved Equipment Utilization: Identifies production bottlenecks and minimizes downtime.
- Enhanced Productivity: Ensures machines operate at peak performance.
- Higher Quality Standards: Reduces defects and improves product consistency.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Enables informed decisions for process improvement.
- Cost Reduction: Minimizes waste and optimizes resource utilization.
4. Best Practices for OEE Measurement
- Regularly monitor and update OEE metrics to track progress.
- Automate data collection to improve accuracy and efficiency.
- Train employees on OEE principles for better implementation.
- Use historical data analysis to identify trends and improvement opportunities.
- Implement continuous improvement strategies to enhance OEE over time.
5. Future of OEE in Manufacturing
With advancements in automation, IoT, and AI, manufacturers can further refine OEE measurement and optimization. Smart factories leveraging real-time data and predictive analytics will continue to enhance production efficiency.
By accurately measuring OEE, manufacturers can improve performance, maintain high-quality standards, and achieve greater competitiveness in the industry.
How to measure OEE in manufacturing?
What is OEE in manufacturing?
OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness) is a key performance metric that measures the efficiency and effectiveness of manufacturing operations by evaluating availability, performance, and quality.
Why is OEE important for manufacturers?
OEE helps manufacturers identify production losses, improve efficiency, and maximize equipment utilization for better productivity.
How is OEE calculated in manufacturing?
OEE is calculated using the formula: Availability × Performance × Quality, where each factor represents a key aspect of equipment effectiveness.
What are the three main factors of OEE?
The three factors of OEE are availability (uptime vs. downtime), performance (operating speed vs. ideal speed), and quality (good units vs. total units produced).
How does availability impact OEE?
Availability measures the percentage of planned production time where the equipment is running, factoring in unplanned stops and maintenance downtime.
How does performance affect OEE measurement?
Performance evaluates whether equipment is running at its optimal speed, considering slow cycles, minor stoppages, and speed losses.
What role does quality play in OEE calculation?
Quality measures the percentage of defect-free products by comparing the number of good units produced to the total output.
What is a good OEE score in manufacturing?
An OEE score of 85% is considered world-class, while 60-70% is average, and below 50% indicates significant improvement opportunities.
How can manufacturers improve their OEE score?
Manufacturers can improve OEE by reducing downtime, optimizing machine speed, minimizing defects, and implementing preventive maintenance.
What are the common losses that reduce OEE?
Common OEE losses include equipment failures, unplanned downtime, slow cycles, minor stops, scrap production, and rework.
How often should OEE be measured?
OEE should be measured continuously in real-time or analyzed at regular intervals, such as daily, weekly, or monthly, to track improvements.
Can OEE be used for real-time monitoring?
Yes, real-time OEE monitoring helps detect inefficiencies immediately, allowing for quick corrective actions to prevent production losses.
How does downtime impact OEE measurement?
Downtime reduces availability, which lowers OEE by decreasing the total productive manufacturing time.
What tools can help track OEE in manufacturing?
Manufacturers use digital dashboards, automated data collection systems, and analytics tools to track and improve OEE performance.
Is OEE applicable to all types of manufacturing industries?
Yes, OEE can be applied across various manufacturing industries, including automotive, food processing, electronics, and pharmaceuticals.