Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) is a key performance indicator in manufacturing that helps assess the efficiency and effectiveness of production processes. By improving OEE, companies can reduce waste, enhance productivity, and maximize profitability. OEE is calculated based on three factors: Availability, Performance, and Quality. Addressing inefficiencies in each of these areas leads to significant improvements in overall production efficiency.
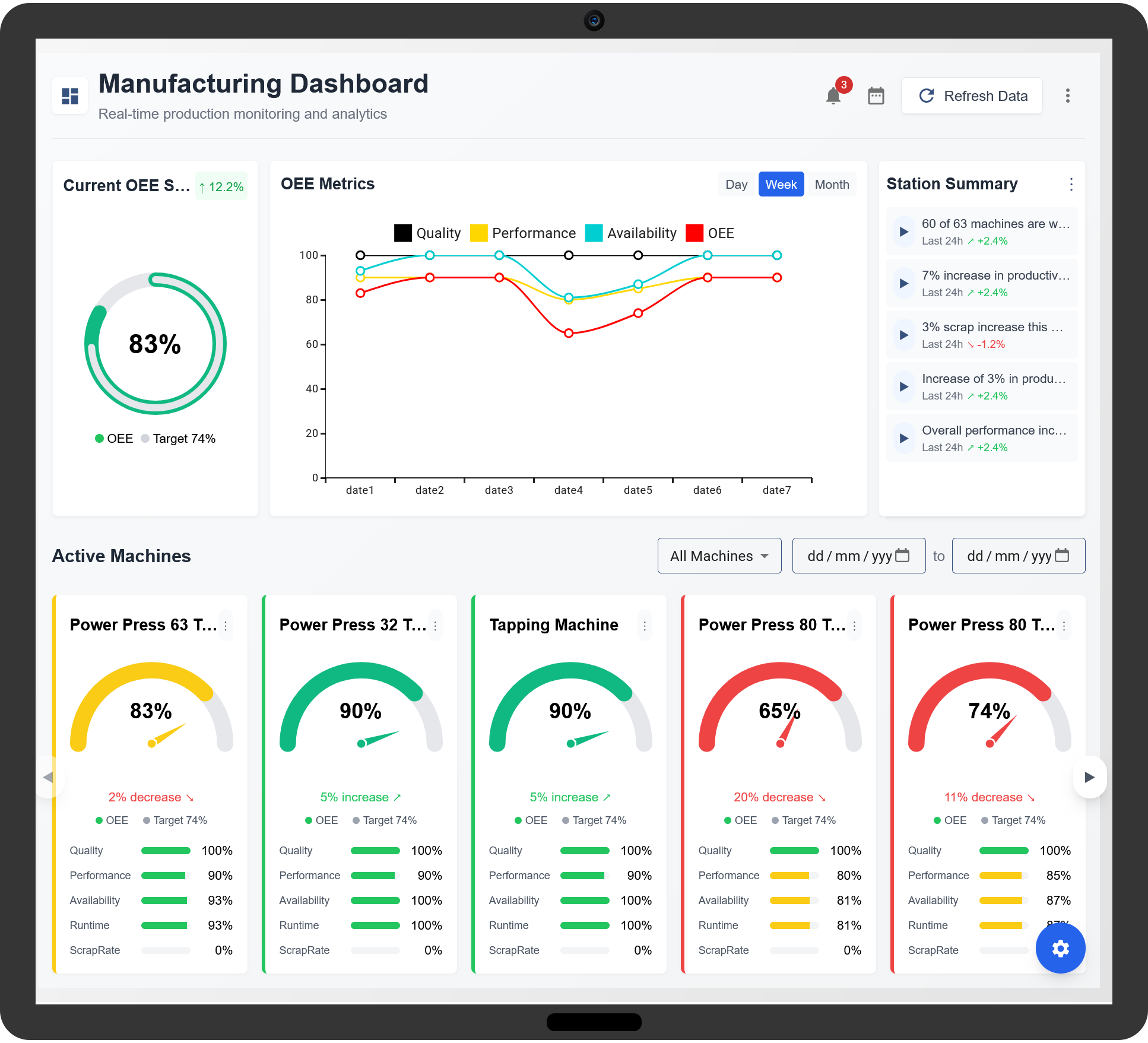
1. Understanding OEE Components
- Availability: Measures the percentage of planned production time during which equipment is available for use.
- Performance: Evaluates how fast machines operate compared to their designed speed.
- Quality: Assesses the proportion of defect-free products produced in a given period.
The OEE formula is:
OEE = Availability × Performance × Quality
Improving OEE requires identifying inefficiencies and implementing corrective measures to enhance these three factors.
2. Strategies to Improve OEE
- Minimize Downtime: Implement preventive and predictive maintenance to reduce unexpected breakdowns.
- Optimize Production Scheduling: Plan production runs efficiently to minimize idle time and ensure smooth transitions.
- Enhance Equipment Performance: Monitor machine speeds and make necessary adjustments to maintain optimal performance.
- Improve Product Quality: Implement quality control measures to reduce defects and rework.
- Train Employees: Provide comprehensive training for operators to ensure best practices are followed.
3. How to Implement an OEE Improvement Plan
Step 1: Analyze Current OEE Metrics
Start by collecting OEE data from production lines to understand where inefficiencies occur. Identify recurring issues affecting availability, performance, and quality.
Step 2: Identify Root Causes of Losses
Use root cause analysis techniques to determine the main factors contributing to low OEE scores, such as frequent machine failures, slow cycle times, or high defect rates.
Step 3: Develop Targeted Improvement Strategies
Create action plans to address specific inefficiencies. This may include improving maintenance schedules, upgrading equipment, or refining production workflows.
Step 4: Implement and Monitor Changes
Introduce process changes gradually and track their impact on OEE metrics. Use real-time monitoring tools to assess improvements and make necessary adjustments.
Step 5: Continuously Optimize and Sustain Improvements
Regularly review OEE data and update strategies as needed. Encourage a culture of continuous improvement by involving employees in process enhancements.
4. Benefits of Improving OEE
- Higher Productivity: Optimized machine utilization leads to increased output.
- Reduced Costs: Minimizing downtime and defects lowers operational expenses.
- Better Resource Utilization: Efficient scheduling and machine use reduce material and energy waste.
- Enhanced Quality: Improved processes result in fewer defects and higher customer satisfaction.
- Stronger Competitive Advantage: A highly efficient manufacturing process enhances market competitiveness.
5. The Future of OEE Optimization
With advancements in automation, data analytics, and AI-driven predictive maintenance, manufacturers will have more tools to enhance OEE. Digital transformation and real-time monitoring will further refine processes, ensuring continuous efficiency gains. Companies that proactively improve their OEE will remain agile and competitive in an evolving manufacturing landscape.
By adopting structured OEE improvement strategies, manufacturers can significantly enhance productivity, reduce costs, and maintain high-quality production standards.
How to Improve OEE
What is OEE, and why is it important?
OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness) is a key metric in manufacturing that measures how efficiently equipment is utilized by evaluating availability, performance, and quality.
How is OEE calculated?
OEE is calculated using the formula: OEE = Availability × Performance × Quality, where each factor represents a percentage of efficiency.
What are the key components of OEE?
The three main components of OEE are Availability (uptime), Performance (speed), and Quality (defect-free production).
What are the main factors that reduce OEE?
OEE is negatively impacted by equipment downtime, slow production cycles, and defective products.
How can preventive maintenance improve OEE?
Preventive maintenance reduces unexpected breakdowns, ensuring higher availability and improved OEE.
What role does equipment availability play in OEE improvement?
High equipment availability minimizes unplanned downtime and ensures continuous production, boosting OEE.
How can optimizing machine performance boost OEE?
Maintaining optimal machine speeds, reducing cycle times, and eliminating bottlenecks improve performance and OEE.
What strategies can reduce quality defects and improve OEE?
Implementing quality control measures, standardizing processes, and training employees can reduce defects and enhance OEE.
How does downtime affect OEE, and how can it be minimized?
Downtime decreases availability and lowers OEE. It can be minimized through predictive maintenance, quick changeovers, and efficient scheduling.
What role does automation play in OEE improvement?
Automation reduces manual errors, increases production speed, and ensures consistency, leading to higher OEE.
How can employee training contribute to better OEE?
Well-trained employees can quickly identify and resolve issues, operate machines efficiently, and follow best practices to improve OEE.
What are the benefits of real-time OEE monitoring?
Real-time OEE monitoring helps track performance, detect inefficiencies, and make data-driven decisions for continuous improvement.
How does data analysis help in OEE improvement?
Analyzing OEE data identifies patterns, reveals improvement opportunities, and supports better decision-making in manufacturing.
What is the impact of Lean Manufacturing on OEE?
Lean Manufacturing eliminates waste, enhances efficiency, and ensures smoother workflows, contributing to higher OEE.
What are the best practices for sustaining high OEE levels?
Continuous monitoring, process optimization, regular maintenance, and employee engagement help maintain high OEE levels.