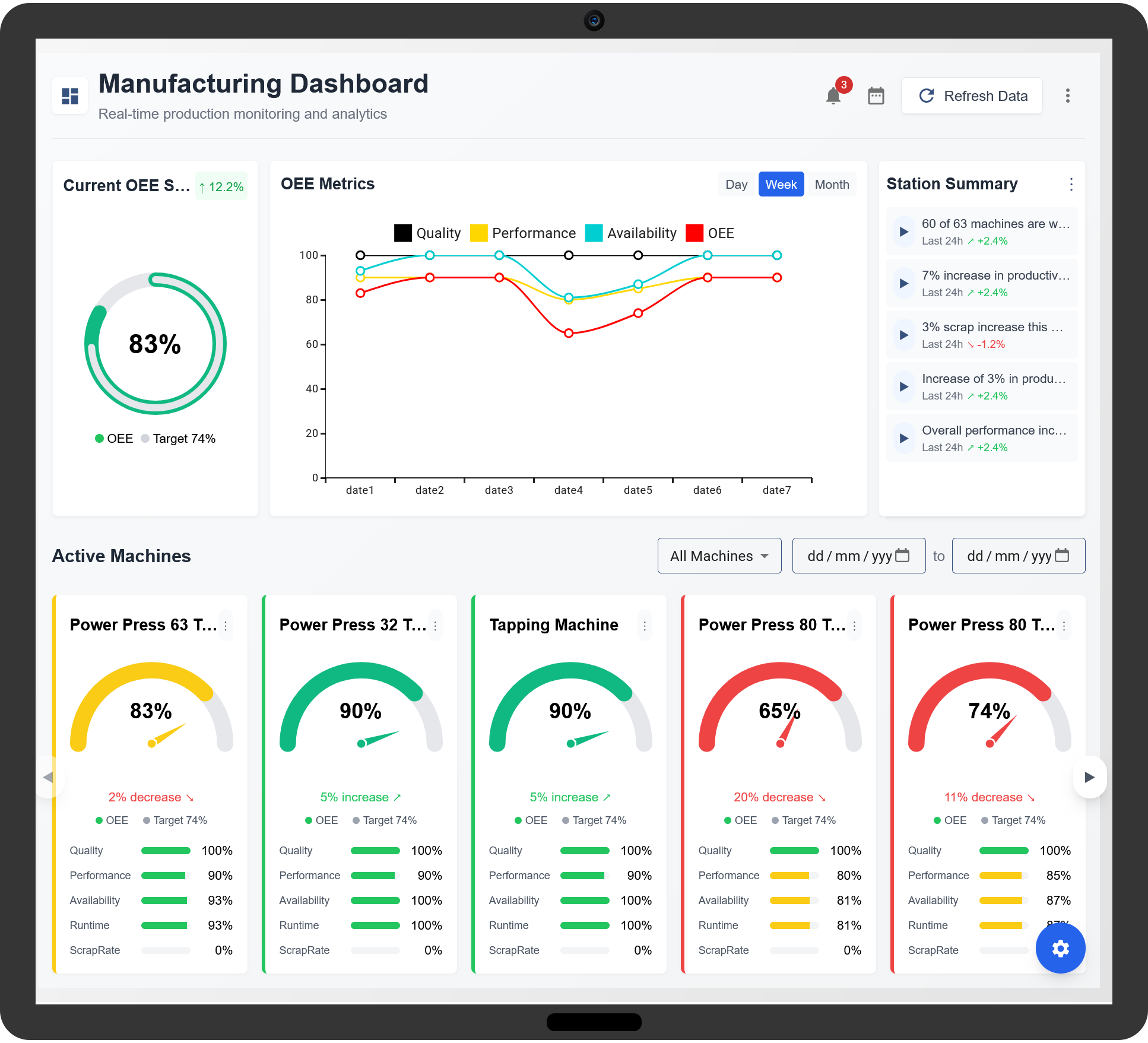
Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) is a key metric used in manufacturing to measure the efficiency and productivity of equipment. Understanding how to calculate OEE helps businesses identify areas for improvement and optimize operations.
1. Understanding OEE Components
OEE consists of three core factors:
- Availability: Measures the actual operating time compared to the planned production time.
- Performance: Assesses whether machines are running at optimal speed.
- Quality: Evaluates the proportion of good products produced without defects.
2. OEE Calculation Formula
The formula for calculating OEE is:
OEE = Availability × Performance × Quality
Step 1: Calculate Availability
Availability is determined using the following formula:
Availability (%) = (Operating Time / Planned Production Time) × 100
Example: If a machine was scheduled to run for 8 hours (480 minutes) but experienced 60 minutes of downtime, the availability calculation would be:
(420 / 480) × 100 = 87.5%
Step 2: Calculate Performance
Performance is measured as:
Performance (%) = (Actual Production Output / Ideal Production Output) × 100
Example: If the ideal cycle time allows 1000 units to be produced in 420 minutes but only 900 units were made, the performance calculation would be:
(900 / 1000) × 100 = 90%
Step 3: Calculate Quality
Quality is determined as:
Quality (%) = (Good Units / Total Units Produced) × 100
Example: If 900 units were produced and 30 were defective, the quality calculation would be:
(870 / 900) × 100 = 96.67%
Step 4: Calculate OEE
Now, using the values obtained:
OEE = 87.5% × 90% × 96.67%
OEE = 76.1%
3. Interpreting OEE Results
- 85% or higher: World-class efficiency.
- 60% – 84%: Good but has room for improvement.
- Below 60%: Requires significant improvements.
4. Improving OEE
To enhance OEE, focus on reducing downtime, improving speed, and minimizing defects. Strategies include predictive maintenance, employee training, and process optimization.
By accurately calculating and monitoring OEE, manufacturers can identify inefficiencies and implement data-driven solutions to improve productivity.
How to Calculate OEE: Formulas and Examples
What is OEE?
OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness) is a metric used in manufacturing to measure the efficiency and effectiveness of production equipment.
How is OEE calculated?
OEE is calculated using the formula:
OEE = Availability × Performance × Quality
What are the three main factors of OEE?
OEE consists of three components:
Availability (measures uptime), Performance (measures speed), and Quality (measures defect rate).
What is the formula for Availability in OEE?
Availability = (Operating Time / Planned Production Time) × 100%
What is the formula for Performance in OEE?
Performance = (Ideal Cycle Time × Total Count) / Operating Time × 100%
What is the formula for Quality in OEE?
Quality = (Good Count / Total Count) × 100%
What is the final OEE formula?
OEE = (Operating Time / Planned Production Time) × (Ideal Cycle Time × Total Count) / Operating Time × (Good Count / Total Count) × 100%
Can you provide an example OEE calculation?
Example: If Availability = 90%, Performance = 95%, and Quality = 98%, then OEE = 0.90 × 0.95 × 0.98 = 83.79%.
What is a good OEE score?
A world-class OEE score is 85% or higher. Most manufacturers aim for 60-80%.
How does downtime affect OEE?
Unplanned downtime reduces Availability, lowering overall OEE.
How do slow cycles impact OEE?
Slow production cycles decrease Performance, which lowers OEE.
How do defects influence OEE?
Defective products lower Quality, negatively affecting OEE.
How can OEE be improved?
OEE can be improved by reducing downtime, increasing speed, and minimizing defects.
What is the difference between OEE and TEEP?
OEE measures actual production efficiency, while TEEP (Total Effective Equipment Performance) considers all available time.
Why is OEE important in manufacturing?
OEE helps manufacturers identify inefficiencies and optimize productivity.