The Digital Balanced Scorecard (BSC) is a modernized version of the traditional Balanced Scorecard that integrates digital tools to track and enhance performance metrics across various business functions. By digitizing the BSC, organizations can achieve more real-time insights and make data-driven decisions to enhance operational efficiency. A key area where the Digital Balanced Scorecard proves particularly beneficial is in improving the SQDCP metrics—Safety, Quality, Delivery, Cost, and People.
1. Understanding SQDCP Metrics
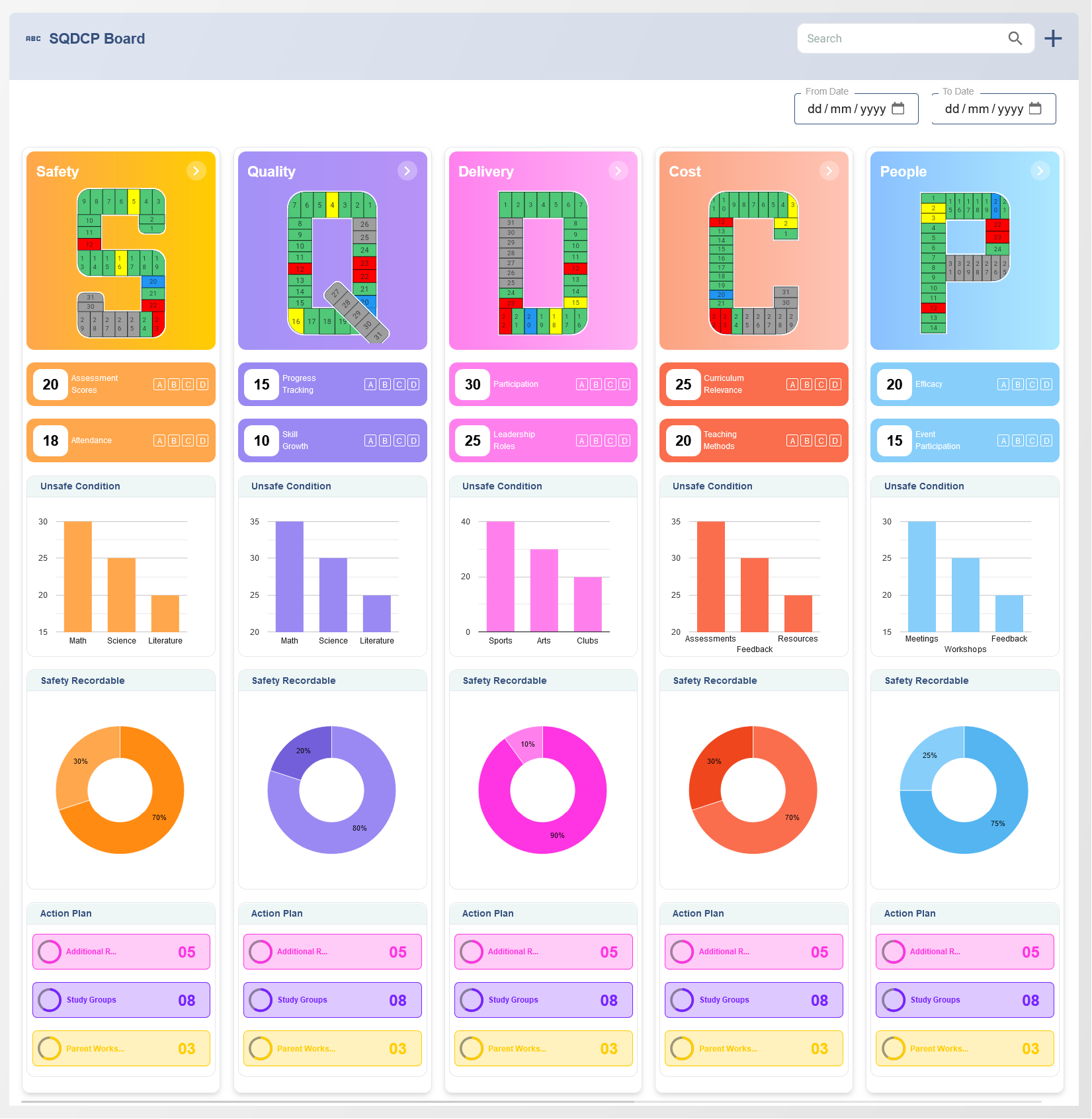
SQDCP metrics represent the critical areas that organizations monitor to achieve operational excellence:
- Safety: Ensures that safety protocols are followed to minimize workplace accidents and injuries.
- Quality: Measures the quality of products or services, focusing on reducing defects and improving overall standards.
- Delivery: Tracks delivery performance, including lead times, on-time delivery, and logistics efficiency.
- Cost: Focuses on controlling operational costs, optimizing resource allocation, and improving financial outcomes.
- People: Assesses employee satisfaction, skills development, and workforce productivity.
These metrics are crucial for improving operational performance, but effectively tracking and improving them requires a systematic and data-driven approach. The Digital Balanced Scorecard leverages modern technology to monitor these metrics more efficiently.
2. Digital Tools and Real-Time Insights
The integration of digital technologies with the Balanced Scorecard enables organizations to track SQDCP metrics in real time, leading to better decision-making. Some key digital tools include:
- Dashboards: Digital dashboards provide an interactive and visual representation of SQDCP metrics, making it easy to track performance across departments.
- Data Analytics: Advanced data analytics tools allow organizations to analyze trends and gain insights into the root causes of issues in the SQDCP areas.
- Automation: Automated reporting systems ensure that performance data is collected and updated continuously, reducing the time spent on manual data entry and ensuring accuracy.
- Mobile Access: Mobile applications allow managers and employees to access SQDCP metrics from anywhere, enabling more agile and responsive decision-making.
By incorporating these tools, the Digital Balanced Scorecard ensures that organizations can make informed decisions and take immediate corrective actions when needed.
3. Enhancing SQDCP Metrics with a Digital Balanced Scorecard
The Digital Balanced Scorecard enhances each of the SQDCP metrics in the following ways:
3.1. Improving Safety
Safety is one of the most critical metrics in any industry. In a digital BSC, safety performance can be tracked in real time through incident reporting systems, sensor data, and safety audits. For example:
- Real-time tracking of safety incidents, near misses, and hazard reports.
- Automated alerts to managers when safety standards are not met.
- Data analysis that highlights safety trends, helping organizations focus on areas with frequent incidents.
This enables a proactive approach to improving safety standards, reducing accidents, and ensuring compliance with safety regulations.
3.2. Enhancing Quality
Quality improvement is an ongoing process, and the Digital Balanced Scorecard provides a systematic way to monitor and improve quality metrics. Key features include:
- Tracking quality defects and deviations in real time.
- Linking quality issues with root causes through data analysis.
- Setting automated alerts for quality thresholds to ensure standards are maintained.
By having immediate visibility into quality performance, teams can quickly address issues, reduce defects, and improve product/service quality, ultimately leading to higher customer satisfaction.
3.3. Optimizing Delivery
Delivery performance is critical to customer satisfaction and operational efficiency. A Digital Balanced Scorecard helps improve delivery metrics by:
- Tracking lead times and delivery schedules against targets.
- Using predictive analytics to anticipate delays or bottlenecks in the delivery process.
- Automating status updates to stakeholders regarding delivery progress.
By automating and improving delivery tracking, organizations can meet delivery deadlines more consistently, reduce shipping costs, and improve customer experience.
3.4. Controlling Costs
Controlling costs is essential for maintaining profitability. The Digital Balanced Scorecard facilitates cost management by:
- Tracking expenses in real time and comparing them against budgeted costs.
- Analyzing cost variances to identify inefficiencies and optimize resource usage.
- Integrating data from various departments to provide a comprehensive view of cost drivers.
With automated cost tracking and analytics, organizations can make more accurate financial decisions, reduce waste, and improve profitability.
3.5. Empowering People
The final SQDCP metric focuses on people—the organization's most valuable asset. The Digital Balanced Scorecard enhances people-related metrics by:
- Tracking employee performance, satisfaction, and training progress.
- Providing real-time feedback on individual and team performance.
- Identifying skill gaps and training needs through performance analytics.
Empowering employees with the right tools and resources helps improve engagement, productivity, and overall job satisfaction, which contributes to higher performance across all areas.
4. Benefits of the Digital Balanced Scorecard for SQDCP Metrics
The integration of a Digital Balanced Scorecard with SQDCP metrics offers several advantages:
- Real-Time Monitoring: Digital tools allow organizations to track SQDCP metrics in real time, ensuring that performance issues are identified and addressed immediately.
- Data-Driven Decisions: With advanced analytics, organizations can make better-informed decisions based on real-time data, leading to more accurate and effective improvements.
- Proactive Problem Solving: Automated alerts and analytics enable organizations to identify trends and issues before they escalate, leading to proactive rather than reactive management.
- Improved Collaboration: With digital tools, teams across different functions can collaborate more effectively by sharing performance data, insights, and best practices.
- Continuous Improvement: By constantly tracking and analyzing SQDCP metrics, organizations can continuously improve their operations, reduce inefficiencies, and stay ahead of the competition.
How Digital Balanced Scorecard Enhance SQDCP Metrics?
What is the SQDCP model?
The SQDCP model stands for Safety, Quality, Delivery, Cost, and People. It is used to track and improve key performance metrics in operations, ensuring that organizations focus on both efficiency and employee well-being.
How does a digital Balanced Scorecard enhance SQDCP metrics?
A digital Balanced Scorecard enhances SQDCP metrics by providing real-time data tracking, visualizations, and performance insights, allowing organizations to monitor and adjust their operations more effectively across all five key areas.
How do SQDCP metrics impact operational excellence?
SQDCP metrics drive operational excellence by ensuring that safety, quality, delivery, cost efficiency, and employee engagement are continually monitored and optimized, leading to better overall performance and customer satisfaction.
What are the key components of the SQDCP model?
The key components of the SQDCP model are: Safety (ensuring a safe work environment), Quality (producing defect-free products), Delivery (on-time fulfillment), Cost (cost-effective processes), and People (employee engagement and development).
How does the SQDCP model align with strategic goals?
The SQDCP model aligns with strategic goals by focusing on the critical operational areas that contribute to the overall success of the organization. By tracking these metrics, companies can ensure that their strategies are being executed efficiently and effectively.
What role does data visualization play in enhancing SQDCP metrics?
Data visualization plays a crucial role by transforming raw data into clear, understandable charts and graphs that make it easier for decision-makers to analyze trends, identify issues, and take corrective actions in real-time.
How does digital tracking of SQDCP metrics improve decision-making?
Digital tracking provides up-to-date, accurate information on SQDCP metrics, enabling managers to make informed decisions based on real-time data. This helps improve responsiveness and ensures that issues are addressed promptly.
How can a digital Balanced Scorecard improve data accuracy in SQDCP?
A digital Balanced Scorecard ensures data accuracy by automating data collection, reducing human error, and allowing for consistent tracking of SQDCP metrics across departments, resulting in reliable and timely information.
What are the benefits of using a digital Balanced Scorecard for SQDCP metrics?
Benefits include streamlined tracking, real-time insights, enhanced data accuracy, improved communication across teams, and the ability to quickly identify and address performance gaps in SQDCP metrics.
How do SQDCP metrics contribute to continuous improvement?
SQDCP metrics contribute to continuous improvement by providing a framework to monitor and assess performance in key areas. Regular reviews of these metrics help organizations identify areas for enhancement and implement corrective actions to drive long-term improvement.
What is the role of the Balanced Scorecard in tracking SQDCP performance?
The Balanced Scorecard tracks SQDCP performance by providing a structured approach to measure the effectiveness of safety, quality, delivery, cost, and people. It enables organizations to align operational activities with strategic goals and continuously monitor progress.
How does digital automation of SQDCP metrics save time and resources?
Digital automation of SQDCP metrics saves time by eliminating manual data entry and enabling faster updates. This allows employees and managers to focus on analysis and decision-making, rather than spending time on administrative tasks.
Can the digital Balanced Scorecard be customized for SQDCP metrics?
Yes, the digital Balanced Scorecard can be customized to include specific SQDCP metrics relevant to an organization’s goals, enabling it to track performance in ways that directly support operational objectives and strategic initiatives.
How do organizations use SQDCP metrics to measure operational efficiency?
Organizations use SQDCP metrics to measure operational efficiency by evaluating performance across the five critical areas. For example, measuring quality helps identify production inefficiencies, while cost tracking shows opportunities to improve cost-effectiveness.
What are the challenges in tracking SQDCP metrics digitally, and how can they be overcome?
Challenges in tracking SQDCP metrics digitally may include data integration issues, resistance to change, and system complexity. These can be overcome by choosing an adaptable and user-friendly system, providing adequate training, and ensuring proper data synchronization across systems.