The Balanced scorecard (BSC) is a strategic planning and management framework that helps organizations translate their vision and strategy into a set of actionable objectives and measures. Developed by Robert Kaplan and David Norton in the early 1990s, the Balanced Scorecard is widely used across industries to improve performance and drive strategic change.
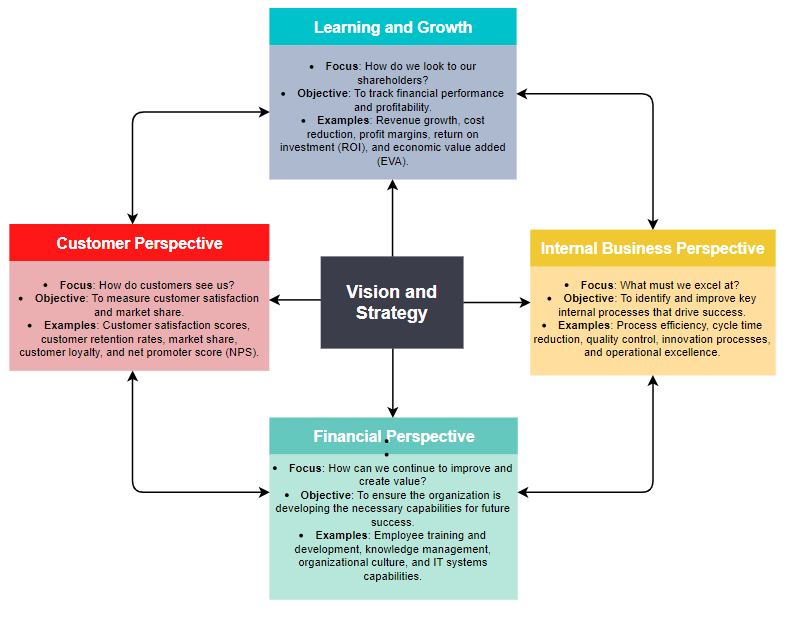
The Balanced scorecard (BSC) is based on four key perspectives, each representing a different aspect of the organization's operations. These perspectives work together to provide a balanced view of the organization's performance and help managers make informed decisions.
The four perspectives of the Balanced Scorecard are:
1.Financial Perspective:
The financial perspective focuses on financial objectives and measures that are critical for the organization's success. This perspective includes metrics such as revenue growth, profitability, and return on investment. By monitoring financial performance, organizations can ensure that their strategies are delivering value to shareholders and stakeholders.
2.Customer Perspective:
The customer perspective looks at how the organization is perceived by its customers and how well it is meeting customer needs. This perspective includes metrics such as customer satisfaction, customer retention, and market share. By focusing on the customer perspective, organizations can ensure that they are delivering products and services that meet customer expectations and drive customer loyalty.
3.Internal Business Processes Perspective:
The internal business processes perspective examines the internal processes and activities that are critical for delivering value to customers and achieving financial objectives. This perspective includes metrics such as process efficiency, quality, and innovation. By monitoring internal processes, organizations can identify areas for improvement and streamline operations to deliver better results.
4.Learning and Growth Perspective:
The learning and growth perspective focuses on the organization's ability to learn, innovate, and grow. This perspective includes metrics such as employee training and development, organizational culture, and the use of information systems. By investing in learning and growth, organizations can build the capabilities and resources needed to adapt to changing market conditions and drive long-term success.
Balanced Scorecard is a powerful framework that helps organizations align their activities with their strategic objectives and monitor their performance across key areas. By considering the financial, customer, internal business processes, and learning and growth perspectives, organizations can create a balanced view of their performance and make informed decisions to drive success.
Balanced scorecard template
A Balanced Scorecard template typically includes four key perspectives: Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, and Learning & Growth. Under each perspective, specific objectives, key performance indicators (KPIs), targets, and initiatives are defined.
Financial Perspective: Objectives focus on financial performance indicators like revenue growth, profitability, and cost management. KPIs might include revenue growth rate, gross margin, and return on investment (ROI).
Customer Perspective: Objectives center on customer satisfaction, retention, and market share. KPIs could include Net Promoter Score (NPS), customer retention rate, and market share percentage.
Internal Processes Perspective: Objectives relate to improving internal processes and operations. KPIs may include process cycle time, defect rate, and process efficiency.
Learning & Growth Perspective: Objectives aim to enhance employee skills, organizational culture, and information systems. KPIs might include employee training hours, employee satisfaction, and technology adoption rate.
KPI metrics
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are measurable values that demonstrate how effectively a company is achieving key business objectives.
Here are some common KPI metrics for each perspective of the Balanced Scorecard:
Financial Perspective:
Revenue Growth Rate: Measures the percentage increase in revenue over a specific period.
Profit Margin: Indicates the percentage of revenue that represents profit.
Return on Investment (ROI): Measures the profitability of an investment relative to its cost.
Customer Perspective:
Net Promoter Score (NPS): Measures customer loyalty based on the likelihood of customers to recommend the company to others.
Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT): Measures the level of customer satisfaction with a product or service.
Customer Retention Rate: Measures the percentage of customers retained over a specific period.
Internal Processes Perspective:
Process Cycle Time: Measures the average time it takes to complete a process or task.
First Pass Yield (FPY): Measures the percentage of products or services that pass through a process successfully without rework.
On-time Delivery: Measures the percentage of products or services delivered to customers on or before the agreed-upon delivery date.
Learning & Growth Perspective:
Employee Training Hours: Measures the number of hours employees spend in training and development activities.
Employee Satisfaction: Measures the level of satisfaction and engagement among employees.
Technology Adoption Rate: Measures the rate at which employees adopt and effectively use new technologies and tools.
How can you implement KPIs for Organizational Success?
Implementing Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) effectively can significantly contribute to organizational success. Here are some steps to implement KPIs successfully:
Define Clear Objectives: Start by clearly defining your organizational objectives. KPIs should directly align with these objectives to ensure they are meaningful and relevant.
Identify Relevant KPIs: Select KPIs that are relevant to your objectives and provide actionable insights. Ensure they are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
Engage Stakeholders: Involve key stakeholders in the KPI selection process to ensure buy-in and alignment with organizational goals.
Establish Baselines: Establish baseline measurements for each KPI to provide a starting point for tracking progress.
Set Targets: Set realistic and challenging targets for each KPI. Targets should be based on historical data, industry benchmarks, and organizational goals.
Implement KPI Tracking: Implement a system for tracking and monitoring KPIs. This could be a software tool, dashboard, or regular reporting process.
Communicate KPIs: Communicate KPIs to all employees to ensure they understand their role in achieving organizational objectives.
Monitor and Analyze: Regularly monitor KPIs and analyze the data to identify trends, opportunities for improvement, and areas of concern.
Take Action: Use KPI data to make informed decisions and take corrective actions as needed to drive improvement.
Review and Adjust: Regularly review KPIs to ensure they remain relevant and effective. Adjust KPIs and targets as necessary based on changing business needs.
Strategic planning
Strategic planning is the process through which an organization defines its strategy, direction, and allocation of resources to achieve its goals. It involves setting objectives, assessing the competitive environment, analyzing internal strengths and weaknesses, and developing strategies to achieve long-term success.
Key components of strategic planning include:
Vision and Mission: Defining the organization's purpose, values, and long-term goals.
Environmental Analysis: Assessing the external environment, including competitors, customers, and market trends.
SWOT Analysis: Identifying the organization's strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
Goal Setting: Establishing specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) objectives.
Strategy Development: Formulating strategies to achieve objectives, such as market expansion, product development, or cost leadership.
Implementation: Executing the strategies through action plans, resource allocation, and monitoring progress.
Monitoring and Evaluation: Continuously reviewing performance, adjusting strategies as needed, and learning from successes and failures.
Strategic planning helps organizations adapt to changing environments, align resources with priorities, and achieve sustainable competitive advantage.
Business strategy
Business strategy refers to a set of decisions and actions taken by a company to achieve specific goals and objectives. It involves analyzing the internal and external environment, determining the direction of the organization, and allocating resources to achieve a competitive advantage.
Key elements of business strategy include:
Mission and Vision: Defining the organization's purpose and desired future state.
Market Analysis: Assessing the industry, market trends, and competitors to identify opportunities and threats.
Competitive Advantage: Determining how the organization will differentiate itself from competitors to gain a competitive edge.
Strategic Objectives: Setting specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals to guide decision-making.
Resource Allocation: Allocating resources such as capital, human resources, and technology to support strategic objectives.
Implementation Plan: Developing action plans and timelines to execute the strategy effectively.
Monitoring and Evaluation: Tracking progress against strategic objectives and making adjustments as needed.
Business strategy can be formulated at different levels, including corporate strategy (for the whole organization), business unit strategy (for individual business units), and functional strategy (for specific functions such as marketing or operations). A well-defined business strategy helps organizations align their efforts, make informed decisions, and achieve sustainable growth.
Strategic management process
The strategic management process is a systematic approach that helps organizations define their strategy, make decisions, allocate resources, and execute plans to achieve their goals. It typically consists of several interconnected stages:
Environmental Analysis: This involves assessing the external environment to identify opportunities and threats. This includes analyzing the industry, market trends, competitor actions, and regulatory factors.
Internal Analysis: This involves evaluating the organization's internal strengths and weaknesses. This includes assessing resources, capabilities, and core competencies.
Strategy Formulation: Based on the environmental and internal analysis, the organization formulates its strategy. This involves setting objectives, determining the scope of operations, and defining how the organization will achieve its goals.
Strategy Implementation: Once the strategy is formulated, it needs to be implemented. This involves developing action plans, allocating resources, and aligning the organization's structure, processes, and culture to support the strategy.
Strategy Evaluation: After implementation, the organization evaluates the effectiveness of the strategy. This involves monitoring performance, comparing actual results to planned objectives, and making adjustments as needed.
Control and Feedback: The final stage involves controlling the implementation process and providing feedback to ensure that the strategy is on track. This may involve adjusting plans, reallocating resources, or changing the strategy if necessary.
The strategic management process is iterative, meaning that organizations continuously review and adjust their strategies in response to changes in the external environment and internal capabilities. It is a dynamic process that requires ongoing monitoring and adaptation to ensure long-term success.
FCIL in the Balanced Scorecard Framework - Faq
What is FCIL in the context of the Balanced Scorecard?
FCIL stands for **Finance, Customer, Internal processes, and Learning and Growth**. It is a strategic framework within the Balanced Scorecard methodology that ensures a comprehensive approach to performance management by balancing financial goals with customer needs, internal processes, and employee development.
How does FCIL enhance strategic management?
FCIL enhances strategic management by providing a balanced view of organizational performance. It aligns financial outcomes with customer satisfaction, internal process efficiency, and workforce development, ensuring that all critical areas are addressed to achieve strategic objectives effectively.
What are the key components of the FCIL framework?
The key components of the FCIL framework include:
- Finance: Focuses on financial performance metrics and objectives.
- Customer: Addresses customer satisfaction and relationship management.
- Internal Processes: Emphasizes the efficiency and effectiveness of internal operations.
- Learning and Growth: Focuses on employee development, innovation, and organizational learning.
How can FCIL be implemented in an organization?
To implement FCIL, organizations should start by defining strategic objectives for each component. Next, they need to develop key performance indicators (KPIs) that align with these objectives, set targets, and establish measurement systems. Regular reviews and adjustments ensure that the framework remains aligned with the organization’s goals.
What are the benefits of using FCIL in strategic planning?
FCIL provides several benefits, including a holistic view of organizational performance, improved alignment between strategic goals and operational activities, better decision-making through comprehensive data, and enhanced ability to track progress and achieve long-term objectives.
How does FCIL differ from other Balanced Scorecard frameworks?
FCIL is a specific configuration of the Balanced Scorecard that emphasizes the four perspectives: Finance, Customer, Internal Processes, and Learning and Growth. Other frameworks may include additional or different perspectives based on organizational needs and industry requirements.
Can FCIL be adapted for different industries?
Yes, FCIL can be adapted for various industries. The framework is flexible and can be customized to address the specific strategic goals and performance metrics relevant to different sectors, ensuring it meets industry-specific needs and challenges.
What challenges might organizations face when using FCIL?
Challenges include aligning the FCIL framework with existing processes, ensuring accurate data collection, maintaining consistency across different components, and integrating FCIL with other management tools. Overcoming these challenges requires careful planning and ongoing support.
How does FCIL support continuous improvement?
FCIL supports continuous improvement by providing a structured approach to monitoring and evaluating performance across key areas. The framework encourages regular reviews and updates, helping organizations identify areas for enhancement and adjust strategies accordingly.
What role do KPIs play in the FCIL framework?
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are essential in the FCIL framework as they measure progress towards achieving objectives in each component. KPIs provide actionable insights and help organizations track performance, make informed decisions, and drive improvements.
How often should organizations review their FCIL performance metrics?
Organizations should review their FCIL performance metrics regularly, typically on a quarterly or semi-annual basis. Frequent reviews allow for timely adjustments and ensure that the framework remains aligned with evolving strategic goals and market conditions.
What tools can assist with implementing FCIL?
Tools that assist with implementing FCIL include Balanced Scorecard software, performance management systems, data analytics platforms, and reporting tools. These tools help organizations track KPIs, generate reports, and analyze performance data effectively.
How can leadership use FCIL to drive organizational success?
Leadership can use FCIL to drive success by setting clear strategic objectives, aligning operations with these objectives, and utilizing performance data to make informed decisions. Effective communication and regular updates on FCIL metrics also help maintain focus and drive organizational success.
What is the importance of the Learning and Growth component in FCIL?
The Learning and Growth component is crucial for fostering employee development, innovation, and organizational learning. It ensures that the workforce is equipped with the skills and knowledge needed to support strategic goals and adapt to changing business environments.
How does FCIL contribute to achieving financial goals?
FCIL contributes to achieving financial goals by aligning financial performance metrics with customer satisfaction, efficient internal processes, and effective employee development. This alignment helps ensure that financial objectives are met through balanced and strategic management of all critical areas.
What should organizations consider when setting up FCIL metrics?
Organizations should consider factors such as relevance to strategic goals, measurability, accuracy, and alignment with other performance metrics. It is important to ensure that the chosen metrics provide a comprehensive view of performance and support informed decision-making.