The Balanced Scorecard (BSC) is a strategic planning and management framework that helps organizations align their activities with their vision and strategy. It provides a structured approach to track performance metrics across multiple perspectives, enabling informed decision-making and effective execution of strategies. The BSC is widely regarded as a powerful tool for ensuring that strategic goals translate into actionable outcomes, improving organizational efficiency and effectiveness.
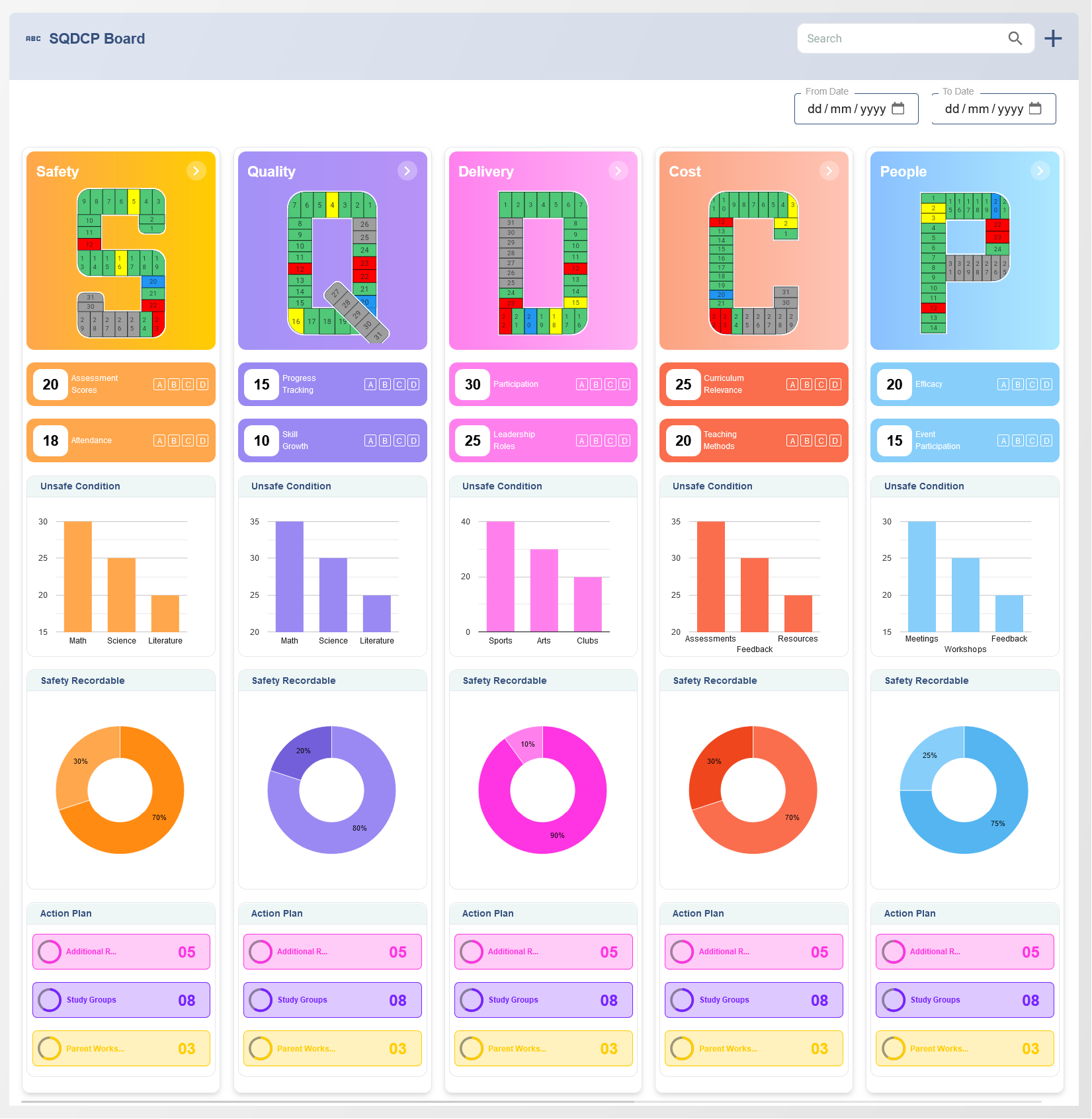
Understanding the Balanced Scorecard Framework
The BSC operates on the principle of balancing performance metrics across four key perspectives:
- Financial Perspective: Focuses on financial performance indicators such as revenue growth, cost management, and profitability. These metrics provide insights into whether the organization is achieving its financial objectives.
- Customer Perspective: Examines customer satisfaction, retention, and acquisition metrics. This perspective ensures the organization is delivering value to its customers.
- Internal Process Perspective: Analyzes the efficiency and effectiveness of internal processes. Metrics here help identify areas for operational improvements.
- Learning and Growth Perspective: Focuses on employee skills, organizational culture, and technology development. This perspective ensures the organization is well-equipped to adapt to future challenges.
Steps in Developing a Balanced Scorecard
Implementing a BSC involves several key steps:
- Define Vision and Strategy: Clearly articulate the organization's long-term goals and strategic objectives. Ensure alignment among stakeholders to establish a unified direction.
- Identify Strategic Objectives: Break down the vision into specific, actionable objectives for each of the four perspectives. These objectives should align with the overall strategy.
- Develop Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Create measurable KPIs for each objective to track progress. Choose metrics that provide meaningful insights into performance.
- Establish Targets: Set specific, time-bound targets for each KPI to provide a benchmark for success.
- Create Initiatives: Identify initiatives and projects that will help achieve the objectives. Assign responsibilities and resources to ensure successful execution.
- Implement and Monitor: Deploy the BSC across the organization and monitor performance regularly. Use dashboards and reports to track progress against targets.
- Review and Refine: Periodically review the BSC to ensure it remains relevant and effective. Update metrics and objectives as needed to align with changing priorities.
Benefits of Using a Balanced Scorecard
The BSC offers several advantages for strategy planning, management, and execution:
- Alignment: Ensures that all organizational activities are aligned with strategic goals, fostering unity and focus.
- Holistic View: Provides a comprehensive perspective on organizational performance by integrating financial and non-financial metrics.
- Improved Decision-Making: Delivers actionable insights that enable data-driven decisions and proactive problem-solving.
- Enhanced Communication: Facilitates clear communication of strategy across all levels of the organization, ensuring everyone understands their role in achieving objectives.
- Continuous Improvement: Encourages a culture of continuous improvement by regularly reviewing and refining performance metrics and objectives.
Examples of Balanced Scorecard Applications
The BSC can be tailored to meet the needs of various industries and organizations:
- Healthcare: Focuses on patient satisfaction, operational efficiency, and clinical outcomes.
- Manufacturing: Tracks production efficiency, quality metrics, and employee training programs.
- Education: Measures student outcomes, faculty development, and resource utilization.
- Retail: Analyzes customer loyalty, sales growth, and supply chain efficiency.
Challenges in Implementing a Balanced Scorecard
While the BSC is a powerful tool, its implementation can pose challenges:
- Resistance to Change: Employees may resist adopting new processes or systems. Effective change management is crucial to overcome this.
- Complexity: Developing and maintaining a BSC requires significant effort and expertise. Simplifying the framework can help address this issue.
- Data Collection: Gathering accurate and timely data for KPIs can be challenging. Leveraging technology can streamline data collection and analysis.
- Alignment: Ensuring alignment across diverse teams and departments requires clear communication and collaboration.
Best Practices for Balanced Scorecard Success
To maximize the effectiveness of a BSC, consider the following best practices:
- Start Small: Begin with a pilot implementation to refine the approach before scaling across the organization.
- Engage Stakeholders: Involve stakeholders at all levels in the development and implementation process to build buy-in and support.
- Focus on Key Metrics: Avoid overwhelming the BSC with too many KPIs. Focus on metrics that align closely with strategic priorities.
- Leverage Technology: Use software tools to automate data collection, visualization, and reporting for greater efficiency.
- Continuous Review: Regularly review and update the BSC to ensure it remains relevant and effective.
Balanced Scorecard for Strategy Planning, Management and Execution
What is a Balanced Scorecard?
The Balanced Scorecard is a strategic management tool that provides a framework to translate an organization’s vision and strategy into a set of measurable objectives across multiple perspectives.
How does a Balanced Scorecard aid in strategy planning?
It helps organizations break down their strategy into actionable goals, align resources with strategic priorities, and monitor progress toward achieving long-term objectives.
What are the four perspectives of the Balanced Scorecard?
The four perspectives are Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, and Learning & Growth, which together provide a holistic view of organizational performance.
How can a Balanced Scorecard be used for performance management?
It sets clear performance metrics linked to strategic goals, enabling organizations to measure progress, identify gaps, and ensure accountability at all levels.
What are the benefits of implementing a Balanced Scorecard?
Benefits include improved strategic alignment, enhanced decision-making, better communication of goals, and a comprehensive approach to performance monitoring.
How does the Balanced Scorecard link strategy to execution?
It translates strategic objectives into actionable initiatives and performance metrics, ensuring that all activities directly contribute to the organization’s vision.
What is the role of KPIs in a Balanced Scorecard?
KPIs (Key Performance Indicators) are used to measure progress toward achieving the objectives outlined in each perspective of the Balanced Scorecard.
How does a Balanced Scorecard align organizational goals?
It aligns goals by linking individual and departmental objectives to the organization’s overarching strategy, ensuring cohesive efforts across the organization.
What industries commonly use Balanced Scorecards?
Industries such as healthcare, manufacturing, finance, and education use Balanced Scorecards to track performance and align operations with strategic goals.
What are the challenges in implementing a Balanced Scorecard?
Challenges include resistance to change, lack of clear objectives, insufficient training, and difficulty in defining measurable KPIs.
How do you measure success with a Balanced Scorecard?
Success is measured by tracking progress against KPIs, evaluating whether strategic objectives are being met, and analyzing outcomes for continuous improvement.
What is the difference between a Balanced Scorecard and a KPI dashboard?
A Balanced Scorecard focuses on aligning strategy with measurable goals across perspectives, while a KPI dashboard primarily tracks operational metrics without a strategic framework.
Can a Balanced Scorecard be customized for small businesses?
Yes, it can be tailored to focus on the specific goals, resources, and challenges of small businesses, ensuring relevance and practicality.
How often should a Balanced Scorecard be reviewed?
It should be reviewed monthly or quarterly to ensure goals remain aligned with changing priorities and external conditions.
What tools can support Balanced Scorecard implementation?
Tools such as performance tracking software, data visualization platforms, and project management tools can enhance the implementation and monitoring of Balanced Scorecards.