1. What is Balanced Scorecard software?
Balanced Scorecard software is a strategic planning and management tool that helps organizations align their activities with their vision and strategy, improving performance through clear metrics.
2. What is the purpose of performance tracking in Balanced Scorecard software?
The purpose of performance tracking is to monitor progress against strategic goals, identify areas for improvement, and facilitate informed decision-making.
3. What does FCIL stand for in performance tracking?
FCIL stands for "Focus on Continuous Improvement and Learning," emphasizing the importance of ongoing development in achieving organizational goals.
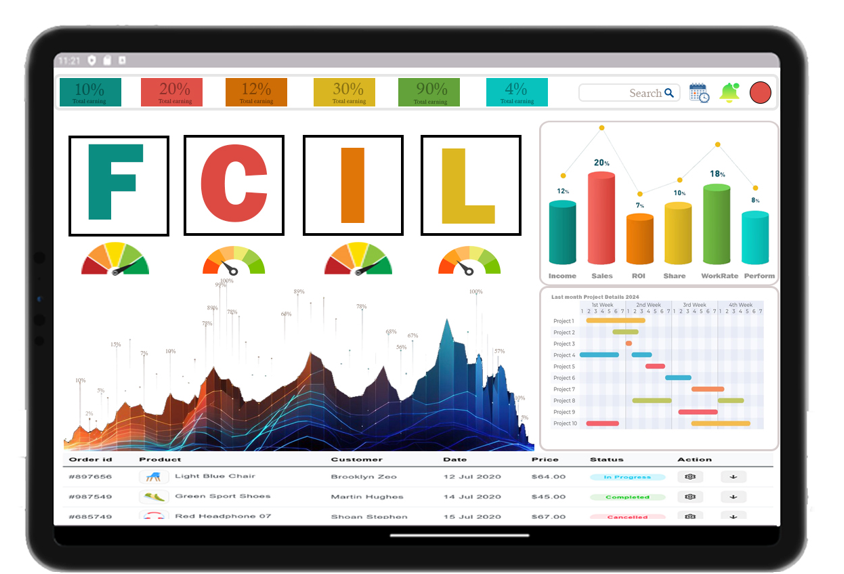
4. How does the FCIL framework help organizations?
The FCIL framework helps organizations by promoting a culture of continuous improvement, aligning processes with strategic goals, and enhancing overall performance.
5. What does SQDC stand for?
SQDC stands for Safety, Quality, Delivery, and Cost, representing key performance indicators essential for operational excellence.
6. How can SQDC metrics be integrated into Balanced Scorecard software?
SQDC metrics can be integrated by aligning them with strategic objectives in the software, allowing organizations to track performance across these critical areas effectively.
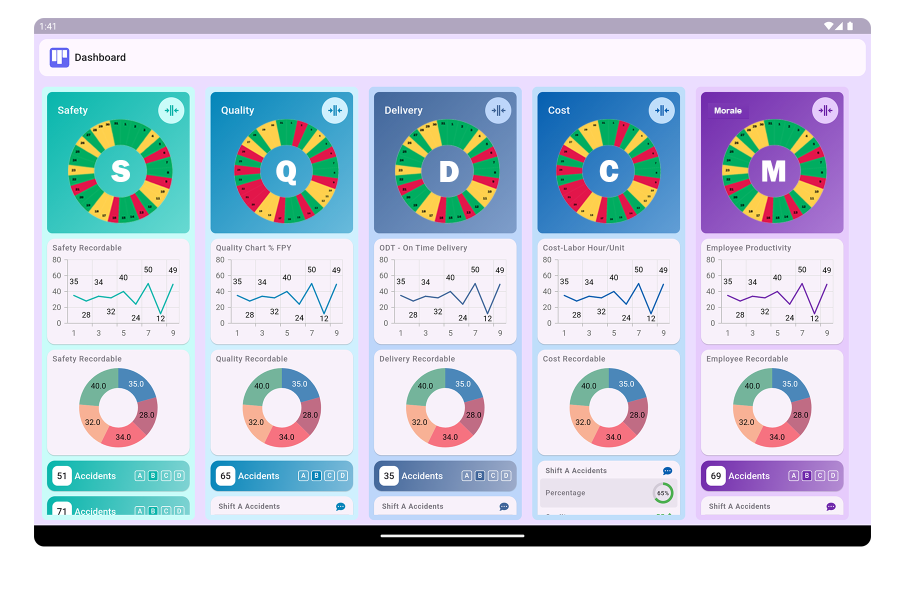
7. What is the SQDCP model?
The SQDCP model stands for Safety, Quality, Delivery, Cost, and People, expanding the SQDC framework by emphasizing the importance of human resources in performance tracking.
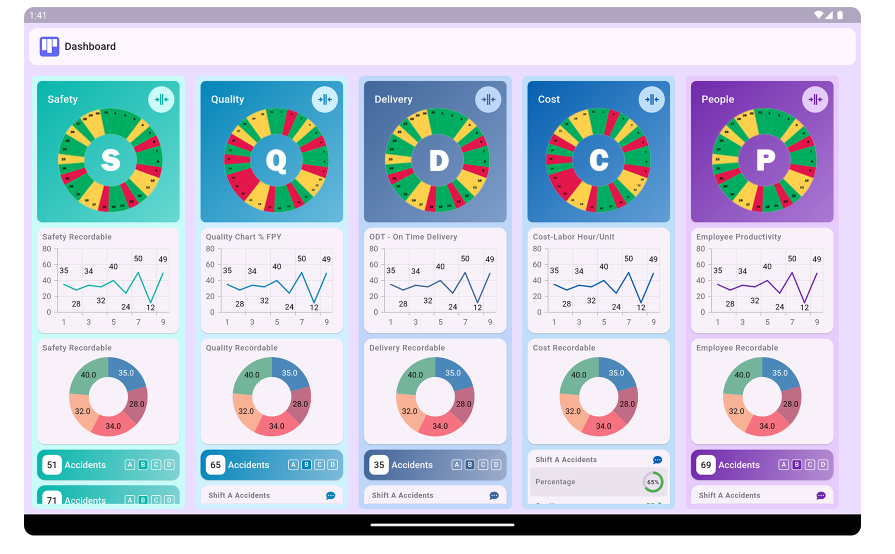
8. Why is the People aspect important in performance tracking?
The People aspect is crucial because employee engagement, skills, and satisfaction directly impact organizational performance and success.
9. What does SQCDL represent?
SQCDL represents Safety, Quality, Cost, Delivery, and Leadership, highlighting the importance of leadership in achieving operational excellence.
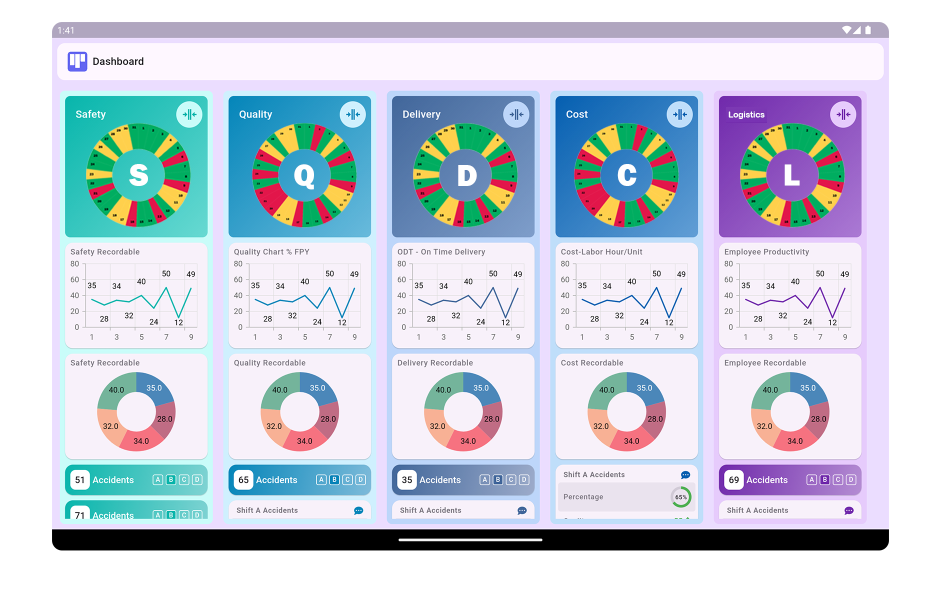
10. How does SQCDL impact customer satisfaction?
SQCDL impacts customer satisfaction by ensuring that safety, quality, and timely delivery are prioritized, leading to improved customer experiences and loyalty.
11. What is SQDIP?
SQDIP stands for Safety, Quality, Delivery, Improvement, and People, focusing on continuous improvement and the involvement of employees in enhancing performance.
12. How can continuous improvement be tracked using SQDIP?
Continuous improvement can be tracked using SQDIP by setting measurable goals, monitoring progress, and using feedback loops to adjust strategies as needed.
13. What does QCDMS stand for?
QCDMS stands for Quality, Cost, Delivery, and Management Systems, emphasizing the need for effective management systems in achieving operational goals.

14. How does QCDMS improve organizational performance?
QCDMS improves organizational performance by streamlining processes, enhancing quality control, and reducing costs through effective management practices.
15. What is the SQDCME framework?
SQDCME stands for Safety, Quality, Delivery, Cost, Motivation, and Engagement, integrating employee motivation as a key factor in achieving operational success.
16. Why is employee motivation important in performance tracking?
Employee motivation is important because engaged employees are more productive, contribute to a positive workplace culture, and drive better organizational outcomes.
17. How does Balanced Scorecard software facilitate strategic alignment?
Balanced Scorecard software facilitates strategic alignment by linking performance metrics to organizational goals, ensuring that all efforts are focused on achieving strategic objectives.
18. What are leading indicators in performance tracking?
Leading indicators are proactive measures that predict future performance and outcomes, allowing organizations to adjust strategies before issues arise.
19. What are lagging indicators?
Lagging indicators are retrospective measures that reflect past performance and outcomes, providing insights into whether strategic goals have been met.
20. How can organizations customize their Balanced Scorecard software?
Organizations can customize Balanced Scorecard software by defining specific metrics, setting performance targets, and aligning dashboards with their unique strategic goals.
21. What role does data visualization play in Balanced Scorecard software?
Data visualization plays a crucial role by presenting complex data in an easily digestible format, enabling stakeholders to quickly understand performance metrics and trends.
22. How often should performance metrics be reviewed?
Performance metrics should be reviewed regularly, typically on a monthly or quarterly basis, to ensure timely adjustments and ongoing alignment with strategic goals.
23. Can Balanced Scorecard software integrate with other business systems?
Yes, Balanced Scorecard software can often integrate with other business systems, such as ERP and CRM systems, allowing for a comprehensive view of organizational performance.
24. How does Balanced Scorecard software support decision-making?
Balanced Scorecard software supports decision-making by providing data-driven insights, enabling leaders to make informed choices aligned with strategic objectives.
25. What is the role of stakeholder engagement in Balanced Scorecard implementation?
Stakeholder engagement is crucial for Balanced Scorecard implementation as it ensures alignment, buy-in, and active participation from all levels of the organization.
26. How can organizations measure employee engagement using performance tracking?
Organizations can measure employee engagement through surveys, feedback mechanisms, and performance metrics that reflect employee contributions and satisfaction levels.
27. What are the challenges of implementing Balanced Scorecard software?
Challenges may include resistance to change, data integration issues, and the need for ongoing training and support to ensure effective usage of the software.
28. How can organizations ensure data accuracy in performance tracking?
Organizations can ensure data accuracy by implementing data validation processes, regular audits, and providing training to employees on accurate data entry.
29. What are some best practices for using Balanced Scorecard software?
Best practices include setting clear objectives, regularly reviewing performance metrics, ensuring cross-functional collaboration, and utilizing data visualization tools.
30. How can Balanced Scorecard software help in resource allocation?
Balanced Scorecard software aids in resource allocation by providing insights into performance metrics, allowing organizations to prioritize resources effectively based on strategic needs.
31. What is the significance of setting SMART goals in performance tracking?
Setting SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound) goals is significant as it provides clarity, focus, and accountability in performance tracking efforts.
32. How does Balanced Scorecard software aid in identifying performance gaps?
Balanced Scorecard software aids in identifying performance gaps by comparing actual performance against set targets, highlighting areas needing improvement.
33. Can Balanced Scorecard software be used for project management?
Yes, Balanced Scorecard software can be adapted for project management by tracking project performance against strategic objectives and measuring success criteria.
34. How does performance tracking support risk management?
Performance tracking supports risk management by identifying potential risks through performance metrics, allowing organizations to proactively address issues before they escalate.
35. What is the importance of benchmarking in performance tracking?
Benchmarking is important as it allows organizations to compare their performance against industry standards or competitors, identifying areas for improvement.
36. How can organizations use performance tracking to enhance customer satisfaction?
Organizations can enhance customer satisfaction by tracking metrics related to service quality, response times, and customer feedback, enabling continuous improvement.
37. What role does training play in effective performance tracking?
Training plays a critical role by equipping employees with the necessary skills and knowledge to accurately track performance metrics and utilize the software effectively.
38. How can Balanced Scorecard software help in strategic communication?
Balanced Scorecard software helps in strategic communication by providing a common framework for discussing performance metrics and aligning team efforts towards strategic goals.
39. What is the relationship between performance tracking and organizational culture?
The relationship is significant as a culture that values performance tracking encourages transparency, accountability, and continuous improvement within the organization.
40. How can organizations track supplier performance using Balanced Scorecard software?
Organizations can track supplier performance by integrating relevant metrics into the Balanced Scorecard, monitoring quality, delivery, and cost-effectiveness.
41. What is the role of feedback in the Balanced Scorecard process?
Feedback is essential in the Balanced Scorecard process as it helps organizations assess performance, refine strategies, and enhance overall effectiveness.
42. How does Balanced Scorecard software assist in compliance and regulatory requirements?
Balanced Scorecard software assists in compliance by providing tools to track adherence to regulations and standards, ensuring that organizations meet necessary requirements.
43. Can Balanced Scorecard software facilitate cross-functional collaboration?
Yes, Balanced Scorecard software facilitates cross-functional collaboration by aligning goals across departments, promoting teamwork, and enhancing communication.
44. What are some common pitfalls to avoid in performance tracking?
Common pitfalls include setting vague objectives, neglecting data accuracy, failing to engage stakeholders, and overlooking the need for regular reviews.
45. How does technology impact performance tracking?
Technology impacts performance tracking by providing advanced tools for data collection, analysis, and visualization, enhancing the overall effectiveness of performance management.
46. What is the future of performance tracking in business?
The future of performance tracking in business is likely to involve increased automation, advanced analytics, and a greater focus on real-time data to drive strategic decisions.
47. How can performance tracking enhance sustainability efforts?
Performance tracking can enhance sustainability efforts by measuring and monitoring key metrics related to environmental impact, resource usage, and social responsibility.
48. What is the role of leadership in performance tracking?
Leadership plays a critical role by setting the vision, promoting a culture of accountability, and driving the effective implementation of performance tracking practices.
49. How can organizations use performance tracking to adapt to changing market conditions?
Organizations can adapt to changing market conditions by using performance tracking to identify trends, assess competitive positioning, and make data-driven strategic adjustments.