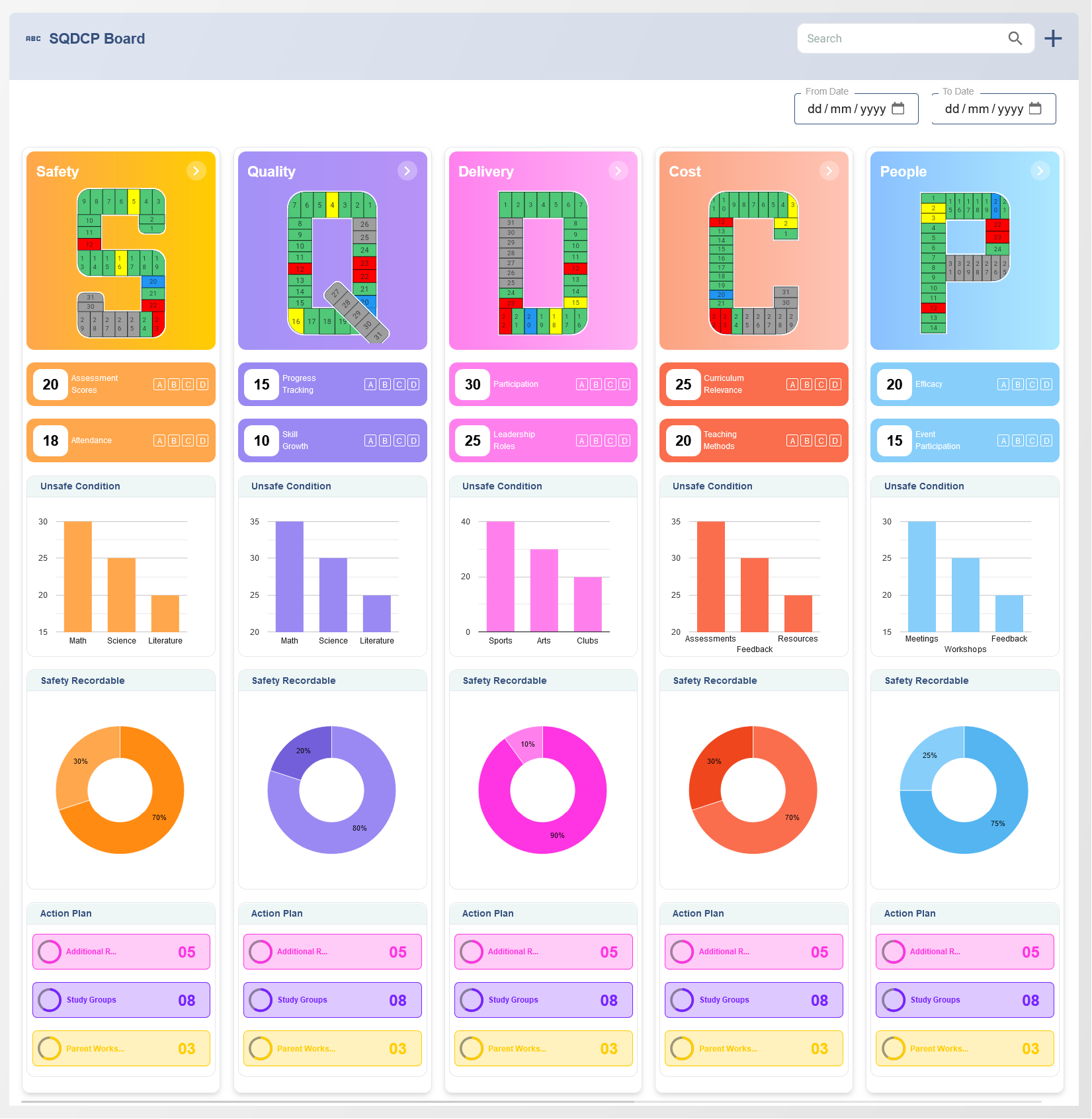
The Balanced Scorecard (BSC) is a strategic tool that aligns organizational goals with actionable metrics across multiple perspectives. When applied to quality inspections, the BSC provides a structured framework to ensure processes and outcomes meet predefined standards. By integrating the financial, customer, internal processes, and learning and growth perspectives, the BSC facilitates a holistic approach to quality control.
1. Financial Perspective
Quality inspections have direct and indirect financial implications. The financial perspective of the BSC focuses on measuring the cost-effectiveness and return on investment (ROI) of quality initiatives. Metrics for this perspective may include:
- Cost of Quality: The total cost associated with quality inspections, including prevention, appraisal, and failure costs.
- Defect Reduction Savings: The financial benefits realized by reducing defects through enhanced inspection processes.
- Resource Utilization: Metrics reflecting the efficient use of inspection tools, materials, and manpower.
Tracking these metrics enables organizations to assess whether their quality inspection strategies contribute positively to overall profitability.
2. Customer Perspective
The customer perspective emphasizes how quality inspections impact customer satisfaction and trust. Maintaining high product or service quality directly correlates with enhanced customer experiences and loyalty. Key metrics include:
- Customer Complaint Rate: The frequency of complaints related to quality issues.
- Inspection Accuracy: The percentage of inspections that identify and address defects effectively before reaching customers.
- Product Recall Rate: The occurrence of recalls due to missed quality issues during inspections.
Organizations should ensure that their inspection processes align with customer expectations and industry standards to maintain competitive advantage.
3. Internal Process Perspective
This perspective focuses on optimizing the processes involved in quality inspections to enhance efficiency and effectiveness. Identifying and improving internal workflows ensures that inspections are thorough and timely. Relevant metrics may include:
- Cycle Time: The average time taken to complete a quality inspection.
- Inspection Coverage: The proportion of products or services inspected in a given period.
- Defect Detection Rate: The percentage of defects identified during inspections.
By analyzing these metrics, organizations can identify bottlenecks, reduce redundant steps, and standardize inspection procedures.
4. Learning and Growth Perspective
Continuous improvement is at the heart of effective quality inspections. The learning and growth perspective focuses on building the capabilities of the workforce and leveraging technology to enhance inspection processes. Metrics for this perspective might include:
- Training Hours: The time invested in training employees on quality inspection methods and standards.
- Employee Certification Rate: The proportion of inspection staff certified in relevant quality control standards.
- Innovation Rate: The frequency of implementing new technologies or methodologies to improve inspections.
Investing in learning and growth ensures that the organization stays ahead of evolving quality standards and customer expectations.
Implementing the Balanced scorecard for Quality Inspections
To effectively use the BSC for quality inspections, organizations should follow these steps:
- Define Objectives: Establish clear goals for each BSC perspective, tailored to the organization’s quality control needs.
- Select Metrics: Choose relevant metrics that provide actionable insights into the quality inspection process.
- Integrate Systems: Use centralized platforms to collect and analyze data from various inspection stages.
- Monitor Progress: Regularly review performance against targets to identify trends and areas for improvement.
- Adapt Strategies: Update goals and processes based on insights gained from BSC analysis.
Benefits of Using the Balanced scorecard for Quality Inspections
Integrating the BSC into quality inspections offers several advantages:
- Enhanced Alignment: Aligns inspection activities with broader organizational goals.
- Improved Accountability: Clearly defined metrics ensure that all stakeholders understand their roles in maintaining quality.
- Comprehensive Insights: Provides a multidimensional view of performance, enabling data-driven decision-making.
- Continuous Improvement: Facilitates the identification and resolution of recurring issues, leading to long-term gains in quality.
Balanced scorecard for Quality Inspections
What is the Balanced Scorecard for quality inspections?
The Balanced Scorecard for quality inspections is a strategic tool that measures and monitors the effectiveness of quality control processes across multiple perspectives, ensuring alignment with organizational goals.
How does the Balanced Scorecard enhance quality control?
It enhances quality control by providing a structured approach to track performance metrics, identify gaps, and align quality processes with strategic objectives.
What perspectives are used in the Balanced Scorecard for quality inspections?
The perspectives include customer satisfaction, internal process efficiency, financial impact, and learning and growth related to quality practices.
How is performance measured in quality inspections using the Balanced Scorecard?
Performance is measured using key performance indicators (KPIs) such as defect rates, inspection turnaround times, compliance levels, and customer feedback scores.
Can the Balanced Scorecard improve compliance with quality standards?
Yes, it tracks compliance metrics and helps ensure that quality inspections adhere to regulatory and organizational standards.
How does the Balanced Scorecard align quality goals with organizational objectives?
It links quality metrics with broader organizational goals, ensuring that quality efforts contribute directly to overall success.
What metrics can be included in the Balanced Scorecard for quality control?
Metrics include inspection accuracy, defect rates, rework percentages, adherence to quality standards, and customer satisfaction related to product quality.
How does the Balanced Scorecard support continuous improvement in quality inspections?
It identifies trends and areas for improvement, enabling teams to implement targeted actions for better quality outcomes over time.
What role does data visualization play in the Balanced Scorecard for quality control?
Data visualization tools provide clear insights into performance metrics, helping stakeholders understand progress and identify issues quickly.
Can the Balanced Scorecard be customized for specific industries?
Yes, the Balanced Scorecard can be tailored to include industry-specific quality metrics and objectives for better relevance and impact.
How does the Balanced Scorecard reduce errors in quality inspections?
By monitoring inspection accuracy and identifying root causes of errors, the Balanced Scorecard helps implement measures to reduce mistakes.
Can the Balanced Scorecard be integrated with digital tools for quality control?
Yes, it can be integrated with digital tools and systems to automate data collection, reporting, and analysis for quality inspections.
What challenges exist when implementing the Balanced Scorecard for quality inspections?
Challenges include identifying appropriate metrics, aligning stakeholders, and ensuring consistent data collection and analysis.
How can the Balanced Scorecard drive innovation in quality control processes?
By tracking innovation-related metrics and fostering a culture of continuous improvement, it encourages new approaches to quality control.
What are the benefits of using the Balanced Scorecard for quality inspections?
Benefits include improved quality outcomes, better compliance, enhanced customer satisfaction, and alignment of quality efforts with organizational goals.