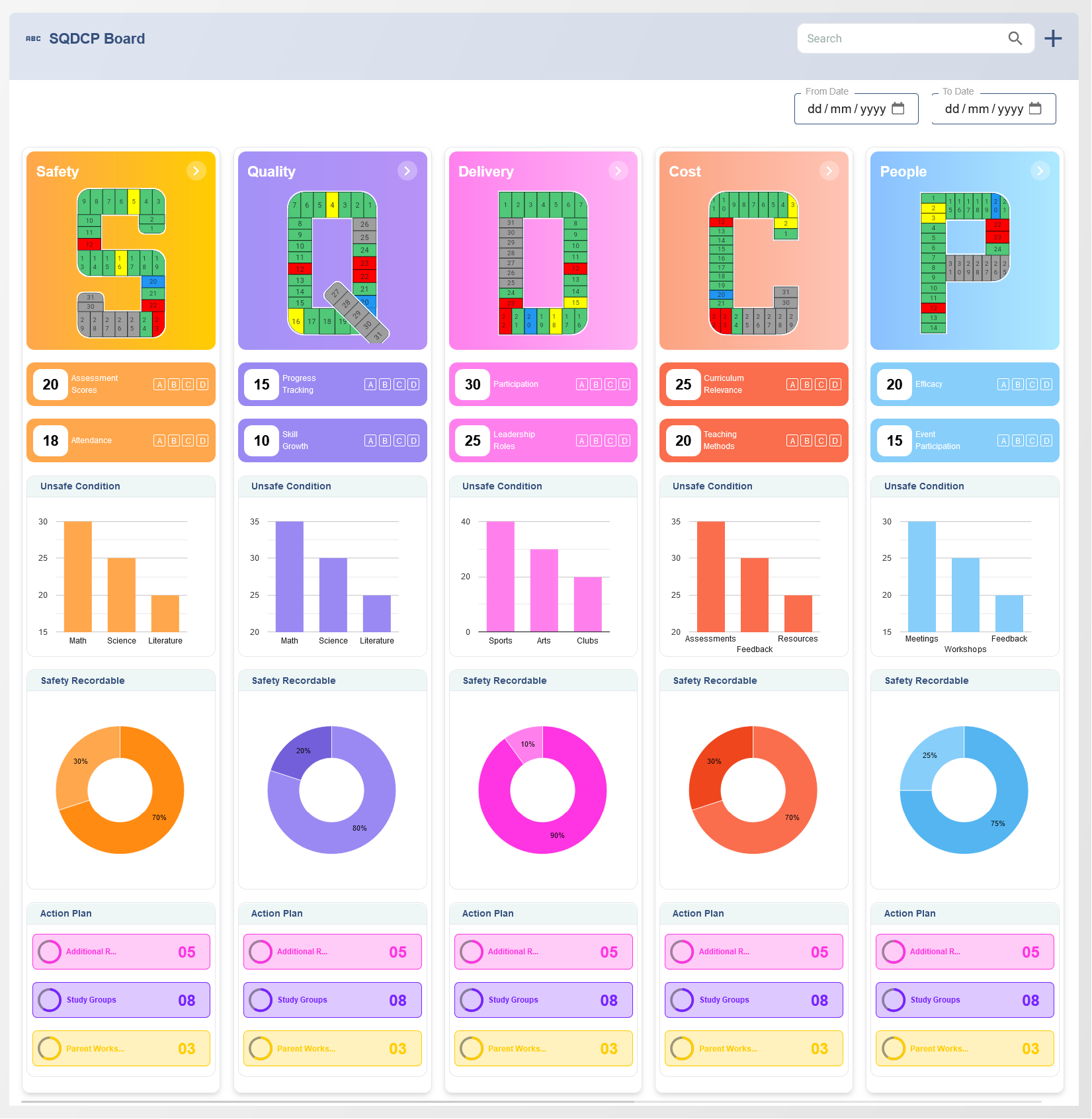
The Balanced Scorecard (BSC) is a strategic management tool that helps organizations track their performance in a comprehensive and balanced way. It integrates both financial and non-financial metrics, offering a multi-dimensional approach to business success. One of the key components of the BSC is its use of objectives, measures, targets, and initiatives. These elements help organizations translate their vision and strategy into actionable steps.
1. Objectives
Objectives are the key goals or outcomes that an organization seeks to achieve. They define what the organization aims to accomplish in alignment with its overall strategy. These objectives are usually categorized into four perspectives of the Balanced Scorecard: Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, and Learning & Growth.
- Financial Perspective: Objectives under this category focus on maximizing profitability, revenue growth, and reducing costs. Examples include increasing return on investment (ROI), improving cash flow, and maximizing shareholder value.
- Customer Perspective: Objectives here are related to customer satisfaction, loyalty, and market positioning. Examples might include improving customer retention, enhancing product quality, or expanding market share in specific regions.
- Internal Processes Perspective: These objectives focus on improving operational efficiency, streamlining business processes, and reducing waste. They could include objectives like reducing cycle time, improving quality control, or implementing new technologies.
- Learning & Growth Perspective: This category centers on the development of human capital and organizational capability. Objectives in this area might include increasing employee satisfaction, enhancing skills through training, or fostering a culture of innovation.
2. Measures
Measures, also known as Key Performance Indicators (KPIs), are metrics used to assess the progress towards achieving the set objectives. They provide a quantitative or qualitative way to track performance and determine whether an organization is moving toward its strategic goals. Each objective typically has one or more associated measures.
- Financial Measures: Metrics like profitability (e.g., net profit margin), revenue growth, and cost reductions fall into this category. These measures give an insight into the financial health of the organization.
- Customer Measures: Metrics might include customer satisfaction scores, Net Promoter Scores (NPS), customer retention rates, or market share. These measures help evaluate how well the organization is meeting customer expectations.
- Internal Process Measures: Efficiency and quality-related metrics, such as defect rates, cycle times, or process throughput, are included here. They help determine how well the internal processes are functioning.
- Learning & Growth Measures: Employee engagement surveys, training completion rates, and turnover rates are examples of measures related to human capital. These indicate how well the organization is fostering its workforce and innovation capacity.
3. Targets
Targets represent the specific goals or desired outcomes for each measure. They define the expected level of performance that an organization strives to achieve within a given time frame. Targets help ensure that measures are not just tracked, but actively managed toward meaningful achievements. They are often set in a way that is challenging yet achievable, motivating teams to perform at their best.
- Financial Targets: Examples of financial targets include increasing annual revenue by 10%, reducing operational costs by 5%, or improving profit margins by 2% within a year.
- Customer Targets: Targets in this category might include increasing customer satisfaction by 15%, retaining 80% of customers over the next year, or achieving a certain market share percentage in a key region.
- Internal Process Targets: Internal targets could include reducing cycle time by 20%, cutting defect rates by 10%, or implementing a new technology solution in six months.
- Learning & Growth Targets: These might involve increasing employee training participation rates to 90%, reducing turnover by 5%, or ensuring that every employee achieves a specified level of performance or certification.
4. Initiatives
Initiatives are the strategic actions or projects that an organization undertakes to achieve its objectives and targets. They outline how the organization will accomplish its goals, often detailing the specific steps, resources, and timelines required. Initiatives are key to ensuring that strategy is executed effectively.
- Financial Initiatives: These could involve launching a new product line, expanding into new markets, or optimizing pricing strategies. For example, an initiative could be to streamline the supply chain to reduce costs and improve profitability.
- Customer Initiatives: Customer-related initiatives might include implementing a new CRM system, launching a loyalty program, or conducting customer satisfaction surveys to gather actionable insights.
- Internal Process Initiatives: These initiatives might involve process automation, adopting lean manufacturing practices, or implementing an enterprise resource planning (ERP) system to streamline operations.
- Learning & Growth Initiatives: Initiatives in this area could include employee development programs, leadership training, or the introduction of a knowledge-sharing platform to foster innovation.
Balanced Scorecard objectives, measures, targets and initiatives
What are the objectives of a Balanced Scorecard?
The objectives of a Balanced Scorecard are the strategic goals that an organization aims to achieve. These objectives are typically aligned with the organization’s vision and mission and are categorized into four perspectives: financial, customer, internal processes, and learning and growth.
How do you define measures in a Balanced Scorecard?
Measures in a Balanced Scorecard are the key performance indicators (KPIs) that help assess how well an organization is achieving its objectives. These measures quantify performance in various areas and are used to track progress towards goals.
What are the targets in a Balanced Scorecard?
Targets in a Balanced Scorecard are specific, measurable goals that an organization aims to achieve within a certain timeframe. These targets are set for each measure and provide a benchmark against which actual performance can be compared.
How do initiatives support the Balanced Scorecard?
Initiatives in a Balanced Scorecard are the action plans or projects that are designed to achieve the objectives and targets. These initiatives are the concrete steps taken to improve performance in the key areas identified in the scorecard.
Why are objectives important in the Balanced Scorecard framework?
Objectives are critical in the Balanced Scorecard framework because they provide clear direction and focus for the organization. They translate strategic goals into specific, actionable areas of improvement across various aspects of the business, ensuring that the organization is aligned with its overall strategy.
How do you align objectives with the overall strategy in a Balanced Scorecard?
Objectives are aligned with the overall strategy by ensuring that each objective directly supports the broader organizational goals. This is done by mapping objectives from the four perspectives to the organization’s long-term vision, creating a direct connection between strategy and performance tracking.
What are the different types of measures used in a Balanced Scorecard?
The different types of measures in a Balanced Scorecard include financial measures (e.g., revenue growth), customer measures (e.g., customer satisfaction), internal process measures (e.g., cycle time), and learning and growth measures (e.g., employee training and development). Each measure assesses performance in its respective area.
How do you set effective targets in the Balanced Scorecard?
Effective targets are set in the Balanced Scorecard by considering both historical performance and future expectations. Targets should be realistic, achievable, and aligned with the organization’s strategic objectives. They should also be specific, measurable, and time-bound to track progress effectively.
Can you provide examples of initiatives in the Balanced Scorecard?
Examples of initiatives in the Balanced Scorecard could include launching a new customer feedback system (customer perspective), improving employee training programs (learning and growth perspective), or automating internal processes to reduce costs (internal processes perspective).
How do you track progress on Balanced Scorecard objectives?
Progress on Balanced Scorecard objectives is tracked by regularly measuring the relevant KPIs, comparing actual performance against the set targets, and analyzing trends over time. This helps identify areas that require attention or improvement.
How do the measures in the Balanced Scorecard relate to business performance?
Measures in the Balanced Scorecard directly relate to business performance by quantifying the key factors that drive success in the organization. These measures help evaluate how well the organization is performing in various areas, including profitability, customer satisfaction, and operational efficiency.
How do initiatives help achieve the targets set in the Balanced Scorecard?
Initiatives help achieve the targets set in the Balanced Scorecard by providing actionable steps and projects designed to address areas where performance is lacking or where there is an opportunity for improvement. These initiatives are key drivers for reaching the desired performance levels.
Why is it important to review Balanced Scorecard objectives periodically?
Periodic review of Balanced Scorecard objectives is important to ensure that they remain relevant and aligned with the organization’s changing strategy, market conditions, and goals. It helps to adjust objectives and targets as needed to stay on course toward achieving the long-term vision.
How do targets in the Balanced Scorecard impact decision-making?
Targets in the Balanced Scorecard impact decision-making by providing clear, measurable benchmarks for success. They guide managers and leaders in prioritizing resources, setting policies, and making decisions that align with organizational objectives and performance expectations.
What role do initiatives play in continuous improvement within the Balanced Scorecard framework?
Initiatives play a critical role in continuous improvement within the Balanced Scorecard framework by driving change and improvement efforts. They provide the specific actions and projects needed to close performance gaps, optimize processes, and help achieve the organization's strategic objectives.