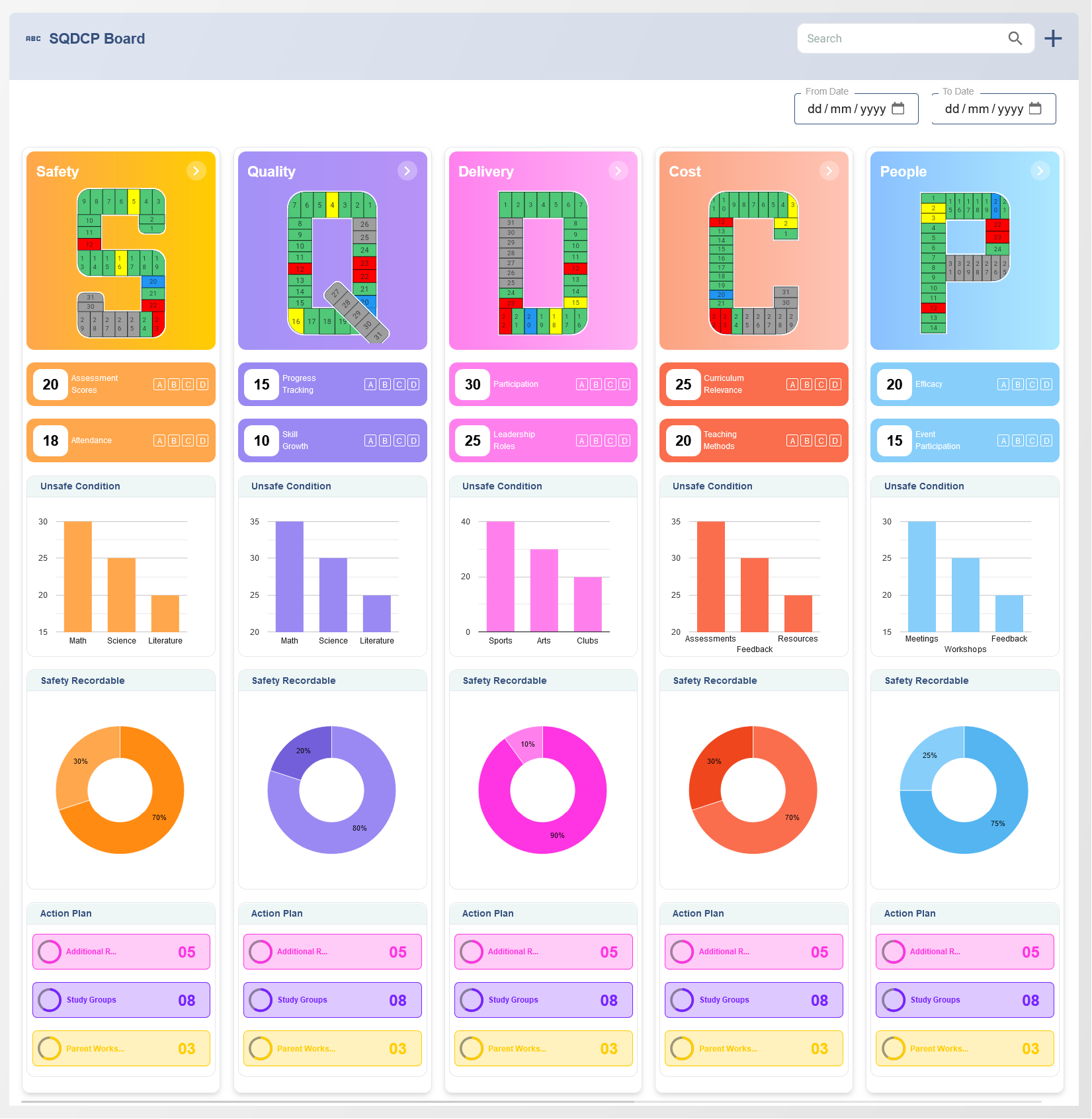
A Balanced Scorecard Dashboard is a digital tool used by organizations to track, measure, and manage key performance indicators (KPIs) across four important perspectives: financial, customer, internal processes, and learning and growth. The dashboard visually presents data and metrics, offering executives, managers, and team members an easy-to-understand overview of the organization’s performance against its strategic objectives. By consolidating data from various business areas, a Balanced Scorecard Dashboard allows decision-makers to evaluate performance, identify areas for improvement, and align actions with long-term goals.
The Four Perspectives of a Balanced Scorecard Dashboard
The core idea behind the Balanced Scorecard is to measure organizational performance across multiple dimensions, rather than focusing solely on financial outcomes. The dashboard provides a visual representation of each of these perspectives, offering a more balanced approach to performance tracking:
1. Financial Perspective
The financial perspective measures the financial health of an organization. This includes key metrics such as revenue growth, profitability, return on investment (ROI), and cost management. By tracking these metrics, the organization can assess whether its financial goals are being achieved and whether the company is generating enough value to sustain and grow operations. Financial KPIs are often displayed as bar charts, graphs, or trends on the dashboard, making it easy to spot fluctuations and identify areas needing attention.
2. Customer Perspective
The customer perspective focuses on how well the organization is meeting customer needs, improving customer satisfaction, and maintaining loyalty. This area includes KPIs like customer satisfaction scores, retention rates, market share, and Net Promoter Score (NPS). A Balanced Scorecard Dashboard displays customer metrics to ensure that the company remains customer-centric, understanding customer behavior, and building long-term relationships. The dashboard enables quick identification of customer-related issues that may impact overall business success.
3. Internal Processes Perspective
Internal processes are at the core of an organization’s ability to deliver value to customers and stakeholders. This perspective evaluates the efficiency and effectiveness of internal operations, such as manufacturing processes, service delivery, product development, and supply chain management. KPIs in this category might include cycle time, defect rates, or productivity measures. The Balanced Scorecard Dashboard visualizes these KPIs, helping organizations spot inefficiencies, reduce waste, and improve operational workflows.
4. Learning and Growth Perspective
The learning and growth perspective assesses the organization's capacity to innovate, improve, and develop its workforce. It focuses on employee satisfaction, skill development, and the organization's ability to adapt to changing market conditions. Key metrics include employee turnover, training hours, and innovation rates. Displaying these metrics on a Balanced Scorecard Dashboard allows organizations to monitor the effectiveness of their learning and development initiatives, ensuring that the workforce is well-equipped to drive future success.
Key Features of a Balanced Scorecard Dashboard
A Balanced Scorecard Dashboard provides a comprehensive view of organizational performance, offering a variety of features that make it an essential tool for management. These features include:
1. Visual Representation of KPIs
The dashboard displays KPIs in visually appealing formats, such as graphs, charts, and tables, making it easier for managers and executives to interpret complex data. These visualizations help ensure that performance is easy to understand, track, and compare over time.
2. Real-Time Data Updates
A key advantage of a Balanced Scorecard Dashboard is its ability to present real-time data. By pulling information from various business systems and databases, the dashboard offers up-to-date insights into performance, ensuring that decision-makers have access to the latest information for timely decisions.
3. Customization
Different organizations may have different needs and priorities. A Balanced Scorecard Dashboard can often be customized to focus on specific metrics and KPIs that are most relevant to the organization’s objectives. This ensures that the dashboard is tailored to meet the unique needs of each user, whether it's senior management or department heads.
4. Drill-Down Capability
To gain a deeper understanding of the underlying factors driving performance, many Balanced Scorecard Dashboards offer drill-down capabilities. This allows users to click on a metric or KPI to access more detailed data and analysis. For example, if customer satisfaction is low, a user might drill down to see customer feedback, identify specific issues, and implement corrective actions.
5. Goal Tracking and Alerts
The Balanced Scorecard Dashboard helps organizations track progress toward their strategic goals. It can send automatic alerts or notifications if performance is off-track, allowing managers to take immediate action to address any issues. This proactive approach helps prevent small problems from escalating into bigger ones and ensures that the organization stays aligned with its long-term objectives.
Benefits of Using a Balanced Scorecard Dashboard
The Balanced Scorecard Dashboard offers several advantages for organizations seeking to improve their performance management processes:
1. Enhanced Decision-Making
The dashboard consolidates important data across multiple areas of the business, providing a comprehensive view of organizational performance. This helps leaders make informed decisions based on a wide range of metrics, not just financial data. With clear and actionable insights, executives and managers can act strategically to drive performance improvements.
2. Improved Strategic Alignment
By tracking performance across financial, customer, internal, and learning perspectives, the Balanced Scorecard Dashboard ensures that the organization’s strategy is aligned with its goals. This alignment helps ensure that efforts in different areas of the business contribute to the overall vision, avoiding siloed thinking and enhancing organizational coherence.
3. Greater Accountability
Using a Balanced Scorecard Dashboard makes it easier to assign responsibility for performance outcomes to specific teams or individuals. By visualizing KPIs and progress toward goals, the dashboard promotes accountability and encourages individuals to take ownership of their performance areas.
4. Continuous Improvement
Since the Balanced Scorecard Dashboard provides real-time data and allows for the tracking of progress toward strategic objectives, it encourages continuous improvement. Organizations can easily spot areas of weakness and take corrective actions to improve performance, ensuring ongoing success and growth.
Implementing a Balanced Scorecard Dashboard
To implement a Balanced Scorecard Dashboard, organizations should follow these steps:
1. Define Strategic Objectives
The first step is to define the organization’s strategic objectives across the four perspectives. These objectives should be aligned with the overall vision and mission of the company. Clear and measurable objectives set the foundation for selecting appropriate KPIs.
2. Identify KPIs
After setting the strategic objectives, organizations need to identify KPIs for each of the four perspectives. These KPIs should be quantifiable, actionable, and relevant to the organization's goals.
3. Choose the Right Tools
Select a tool or platform that supports the creation and monitoring of Balanced Scorecard Dashboards. Many software options provide templates and customization features to help organizations build their dashboards.
4. Regular Monitoring and Review
Once the dashboard is set up, regular monitoring and review are essential to ensure that the KPIs are on track. Managers should schedule periodic reviews to evaluate progress, identify areas of improvement, and adjust strategies if necessary.
Balanced Scorecard Dashboard
What is a Balanced Scorecard Dashboard?
A Balanced Scorecard Dashboard is a visual tool that displays key performance indicators (KPIs) from various perspectives (Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, and Learning & Growth) to track and manage organizational performance.
Why is a Balanced Scorecard Dashboard important?
It helps organizations to track performance across multiple dimensions in real-time, ensuring strategic goals are met while providing actionable insights to improve decision-making.
What are the key components of a Balanced Scorecard Dashboard?
The key components include performance metrics, KPIs, goals, trends, and visual elements like charts, graphs, and tables to represent performance in different perspectives.
How does a Balanced Scorecard Dashboard work?
The dashboard consolidates data from various sources, categorizes them according to the four Balanced Scorecard perspectives, and presents them visually to help monitor and analyze organizational performance.
What are the benefits of using a Balanced Scorecard Dashboard?
The benefits include better strategic alignment, real-time monitoring of performance, improved decision-making, clearer communication of goals, and the ability to quickly identify areas needing improvement.
Can a Balanced Scorecard Dashboard be customized?
Yes, most Balanced Scorecard Dashboards can be customized to display specific KPIs, metrics, and targets that align with the organization’s unique goals and strategies.
What is the role of KPIs in a Balanced Scorecard Dashboard?
KPIs are used to measure the progress toward strategic goals, and they are the foundation of the Balanced Scorecard Dashboard. They track performance across financial, customer, process, and learning perspectives.
How often should a Balanced Scorecard Dashboard be updated?
The dashboard should be updated regularly—typically on a daily, weekly, or monthly basis—depending on the organization’s needs, the nature of the metrics, and the data availability.
Can a Balanced Scorecard Dashboard be used for forecasting?
Yes, a Balanced Scorecard Dashboard can be used for forecasting by analyzing past data and trends to predict future performance, helping to make proactive decisions.
What type of organizations can benefit from a Balanced Scorecard Dashboard?
All types of organizations, from small businesses to large corporations, can benefit from using a Balanced Scorecard Dashboard to monitor and align their strategic goals with performance metrics.
What is the difference between a Balanced Scorecard Dashboard and a regular dashboard?
A Balanced Scorecard Dashboard is specifically designed to track performance across multiple strategic perspectives, while a regular dashboard might focus solely on operational data or specific metrics.
Is it easy to implement a Balanced Scorecard Dashboard?
Implementation can vary depending on the complexity of the organization’s goals and the dashboard software, but many modern tools provide user-friendly templates and integration features to simplify the process.
What types of data can be displayed on a Balanced Scorecard Dashboard?
Data can include financial metrics, customer satisfaction scores, operational efficiency statistics, employee development data, and other KPIs that align with the company’s strategic objectives.
How does a Balanced Scorecard Dashboard align with strategic goals?
The dashboard visually tracks KPIs related to the organization’s strategic objectives, ensuring that day-to-day operations are aligned with long-term goals and priorities.
What are the key challenges in using a Balanced Scorecard Dashboard?
Key challenges include ensuring data accuracy, managing the complexity of multiple KPIs, integrating the dashboard with existing systems, and maintaining consistent updates to reflect organizational changes.