Lean manufacturing is a methodology focused on minimizing waste while maximizing productivity. It aims to create more value with fewer resources by continuously improving processes.

1. 5S System
The 5S System consists of Sort, Set in Order, Shine, Standardize, and Sustain. It helps to organize the workplace for better efficiency and safety. Implementing 5S ensures that work areas are clean, items are in their proper place, and there is a standard for organization that everyone follows.
2. Value Stream Mapping (VSM)
Value Stream Mapping (VSM) is a visual tool used to analyze and design the flow of materials and information needed to bring a product or service to the customer. It helps identify areas of waste and streamline production processes by showing the current state and future state of operations.
3. Kaizen
Kaizen refers to continuous improvement. It encourages employees at all levels to work together proactively to achieve regular, incremental improvements in processes. Kaizen emphasizes a culture where small changes over time lead to significant overall improvements.
4. Kanban
Kanban is a scheduling system used to manage work efficiently. It visualizes the flow of tasks or materials through various stages of production. By limiting work in progress, it helps balance demand with capacity and avoid bottlenecks.
5. Just-in-Time (JIT)
JIT is a production strategy where materials and products are produced only when needed. This reduces excess inventory, minimizes waste, and ensures that resources are allocated effectively. JIT focuses on producing the right quantity at the right time.
6. Total Productive Maintenance (TPM)
Total Productive Maintenance (TPM aims to maximize the productivity of equipment by reducing downtime, increasing reliability, and extending equipment lifespan. It encourages operators to take part in maintaining their equipment and involves preventive and predictive maintenance strategies.
7. Poka-Yoke
Poka-Yoke refers to "mistake-proofing" in the production process. It involves designing processes or devices to prevent errors before they happen. Poka-Yoke tools ensure that mistakes are caught early and can be corrected without major disruptions.
8. Standard Work
Standard Work establishes the most efficient way to perform tasks consistently across the workforce. It involves documenting the best practices and ensuring that all workers follow the same process, which reduces variability and improves quality.
9. Takt Time
Takt time is the rate at which products must be produced to meet customer demand. It is calculated by dividing the available production time by customer demand. Takt time ensures that production is aligned with customer needs without overproduction.
10. Heijunka (Leveling Production)
Heijunka is the practice of leveling out production to avoid uneven workflows and fluctuations in output. By producing at a steady rate, manufacturers can reduce waste, increase efficiency, and better meet customer demand.
11. Gemba
Gemba refers to the practice of going to the place where value is created (the shop floor) to observe and understand the work process. It emphasizes firsthand observation rather than relying solely on reports or data to identify problems and opportunities for improvement.
12. Hoshin Kanri (Policy Deployment)
Hoshin Kanri is a strategic planning method that aligns the goals of the organization with the activities of the workforce. It ensures that everyone is working towards the same objectives, and there is a clear plan for how to achieve these goals.
13. Andon
Andon is a visual feedback system used in manufacturing to notify workers and supervisors of a problem in the production line. By signaling issues in real time, Andon helps ensure that problems are addressed immediately, minimizing downtime.
14. Continuous Flow
Continuous Flow involves producing items without interruptions or delays, ensuring that products move smoothly through each stage of production. This method eliminates waiting times, reduces inventory, and increases throughput.
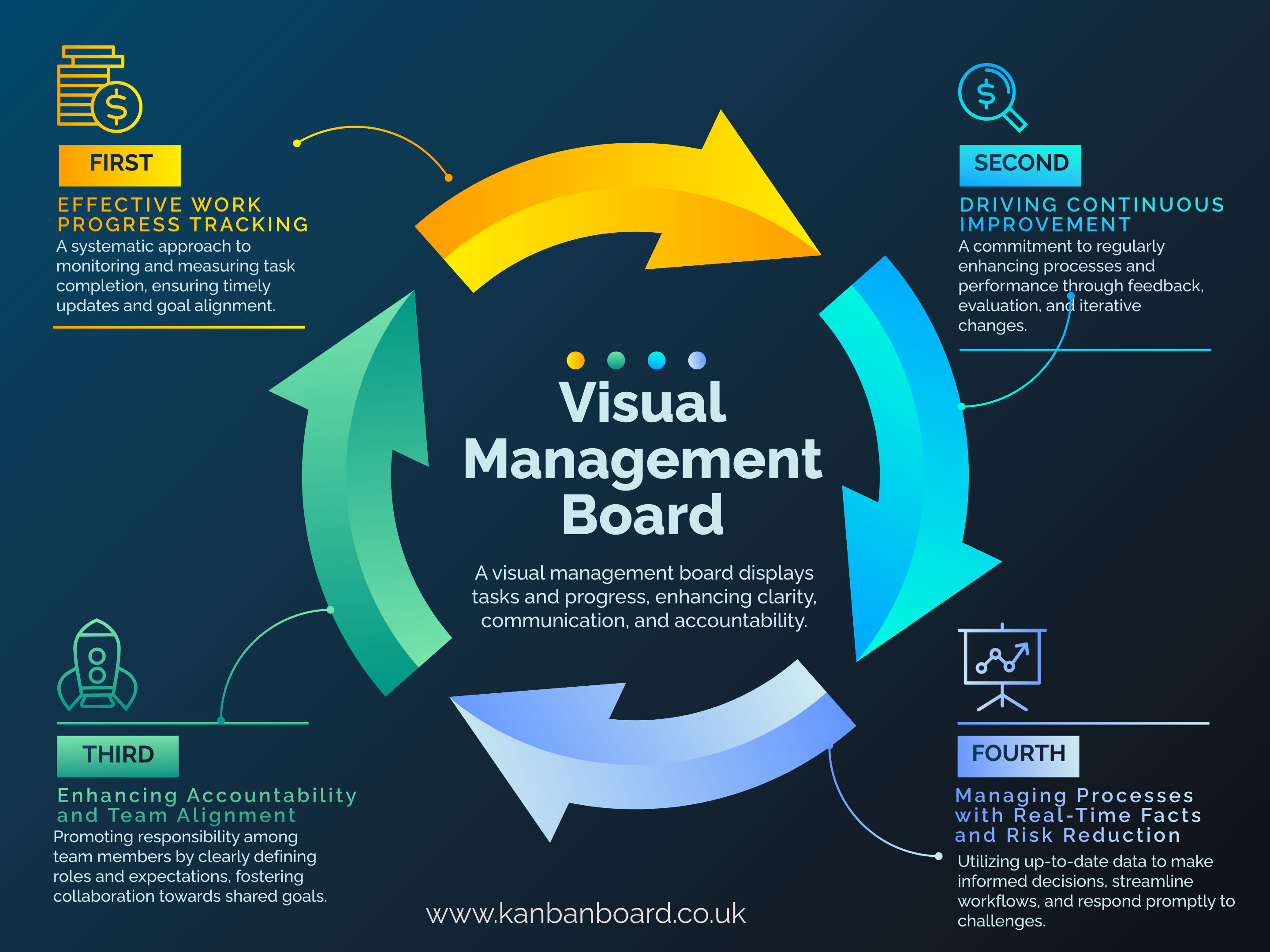
15. Visual Management
Visual Management uses signs, symbols, and charts to communicate important information quickly and effectively. By making key data visible at all times, it ensures that workers can stay informed and react quickly to issues.
16. Root Cause Analysis
Root Cause Analysis is a method for identifying the underlying causes of a problem. Instead of addressing the symptoms, it focuses on determining and fixing the root cause to prevent the problem from recurring.
17. Single Minute Exchange of Die (SMED)
SMED is a method for reducing the time it takes to change equipment or tools. By minimizing setup time, manufacturers can switch between production runs more quickly, increasing flexibility and reducing downtime.
18. Cellular Manufacturing
Cellular Manufacturing organizes workstations into cells, each of which is responsible for producing a specific part or product. This arrangement minimizes movement, reduces waste, and improves communication between workers, leading to faster production times.
19. Six Big Losses
This tool focuses on reducing the six major sources of productivity loss in manufacturing: equipment failure, setup and adjustments, idling, reduced speed, process defects, and reduced yield. Addressing these areas helps improve overall equipment effectiveness.
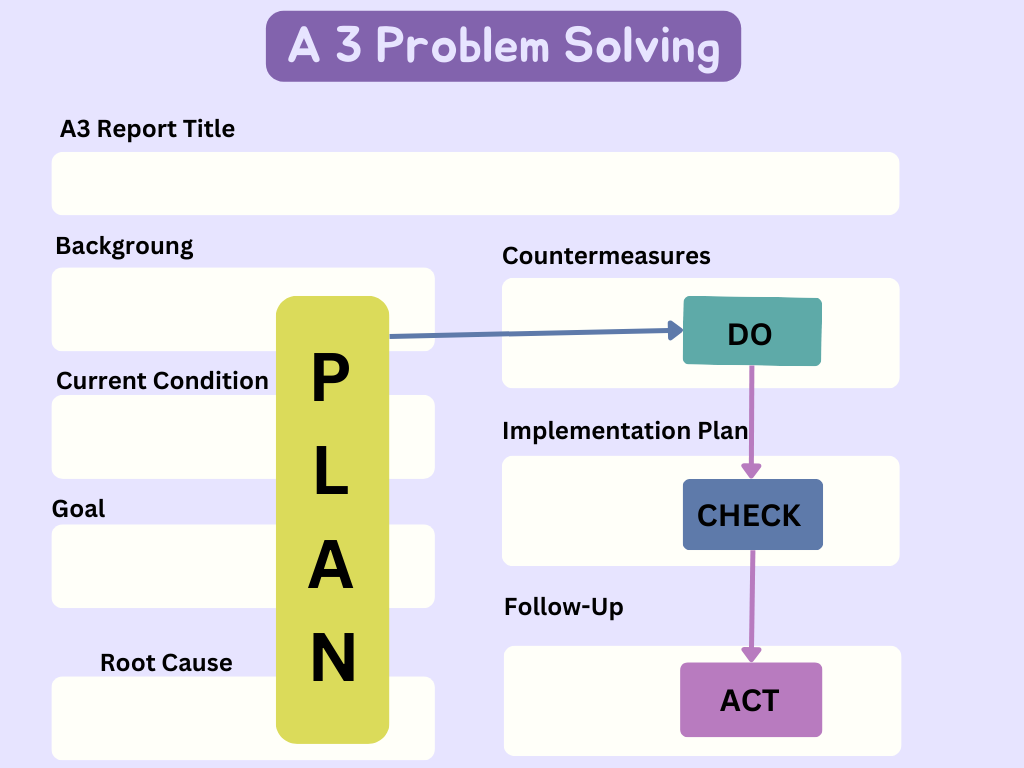
20. A3 Problem Solving
A3 is a structured problem-solving approach that uses a single-page document to outline a problem, analyze its root cause, and propose solutions. It encourages clear communication and accountability in addressing process issues.
21. Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) Cycle
PDCA is an iterative approach to problem-solving and continuous improvement. It involves four stages: Plan (identify a goal or problem), Do (implement a solution), Check (evaluate the results), and Act (make adjustments based on the evaluation).
22. FMEA (Failure Modes and Effects Analysis)
FMEA is a tool for identifying potential failure points in a product or process and analyzing their impact. By addressing these potential failures before they occur, manufacturers can prevent defects and reduce the cost of quality issues.
23. Jidoka (Automation with Human Touch)
Jidoka refers to automating processes while ensuring that machines stop automatically if an abnormality is detected. This ensures that quality is maintained without the need for constant human supervision, reducing defects and downtime.
24. Lean Metrics
Lean Metrics are key performance indicators (KPIs) used to measure the success of Lean initiatives. Common Lean metrics include cycle time, lead time, throughput, and overall equipment effectiveness (OEE). These metrics help track progress and identify areas for improvement.
25. Right First Time (RFT)
RFT focuses on producing goods correctly the first time to reduce rework, waste, and defects. By emphasizing quality